遺傳演算法求解旅行商問題
1.遺傳演算法
遺傳演算法是受大自然的啟發,模擬生物在自然環境中的遺傳和進化過程而形成的一種自適應、具有全域性優化能力的隨機搜尋演算法。
自然界的進化包括3個原則:
(1)適者生存原則,這意味著適應能力強的物種,會在殘酷的競爭中生存下來,而適應能力差的物種會逐漸地消亡。
(2) 兩性繁殖。這意味著種群中性別不同的個體,生活在一起,產生新的個體。
(3) 變異。 由於環境的變化,新物種的出現,以及不同物種的互動都會引起種群的變異。
遺傳演算法的思路是通過從給定一個初始群體出發,利用選擇運算元、雜交運算元以及變異運算元來模擬自然進化的三種原則,逐步改進種群,一步步逼近最優解,以達到求解最優華問題的目的。
GA演算法的計算步驟:
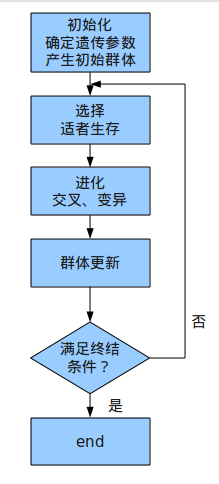
記住遺傳演算法的過程很重要,首先是初始化一群解,然後再在這些解中選擇較優的一部分,將選擇的這一部分解進行交叉,且以一定概率變異,(交叉一般能得到比當前解更好的解,而變異則很可能讓結果變差,所以變異的概率一般不是很大,但是這樣有助於我們跳出區域性最優)。交叉變異以後進行群體更新,對於TSP問題,群體更新時儲存這一次迭代產生的最好的解,然後繼續進行下一次迭代,直到滿足終結條件為止。
GA的演算法過程:

初始化t,t代表while迴圈已經迭代了多少次。其中f(pop(t))是指這個解的適應度,對於TSP問題,適應度就是它的代價,第8行是按一定的概率選擇較有的解。第9行以Pc概率進行交叉,第10行以Pm概率進行變異。
2. 問題建模
遺傳演算法其實很簡單,就是初始化一群解,然後選擇這一群裡面較優的解,在較優的解裡面,讓其中的個體交叉,使得交叉後得到更好的解,再按一定概率進行變異,希望變異能跳出區域性最優。對於遺傳演算法求解TSP問題,最難的地方在於問題建模,剛開始根本不知道如何用遺傳演算法來求解旅行商問題,如何交叉,如何變異。
首先初始化一群解,可以通過C++提供的庫函式來產生一個城市的隨機排列,每一個排列代表一個解random_shuffle(temp.path, temp.path + nCities)。然後以一定概率選擇較優的解,選擇的方法有很多,我們不一定非要按照上面虛擬碼的方式來選擇,比如我們希望每次儲存當前這群解中的前60%,則我們可以按解的適應度排序,然後取前60%的解,對於後40%的解,我們可以用前40%的解去覆蓋它,則前40%的解就有2個副本,只要我們交叉的時候不要讓相同的兩個副本交叉就行了,因為相同的兩個解交叉,不會讓結果變得更好。
變異也很簡單,只需要在一個解中隨機的選擇兩個城市,然後交換它們即可。注意,變異的概率不宜太大。
原始碼中採用類似於三交換啟發交叉(THGA),我把它改成了二交叉的。
三交換啟發交叉方法的基本思想如下:
選3個參加交配的染色體作為父代,以8個城市為例來說明這一過程,其中dij由前面的表1給出,父代染色體為
A = 3 2 1 4 8 7 6 5
B = 2 4 6 8 1 3 5 7
C = 8 7 5 6 4 3 2 1
SUM1=42,SUM2=40,SUM3=46(SUM1,SUM2,SUM3分別為這3種排法所走的距離總和數).
隨機選出初始城市j=1,Sj=3右轉動,使3成為3父代的第1位置.
A = 3 2 1 4 8 7 6 5
B = 3 5 7 2 4 6 8 1
C = 3 2 1 8 7 5 6 4
由於d(3,2)>d(3,5),所以有:
A = × 5 2 1 4 8 7 6
B = × 5 7 2 4 6 8 1
C = × 5 6 4 2 1 8 7
由此規則計算可得:
O = 3 5 7 6 8 4 2 1
我們本來是3個不同的解,現在得到了一個比三個解都優的解,總不能讓原來的三個解都等於現在的這個區域性最優解吧,這樣不利於下次交叉,我們可以用如下的方法改變另外兩個解的路徑:Rotate(q.path, nCities, rand() % nCities);上行程式碼執行以後,它的代價還是和原來一樣的,路徑也是一樣,只是起點變了,這樣有什麼好處呢?有利於下次交叉的時候,原來的兩個相同代價,不同路徑的解能和其他解交叉出不同的結果,這樣有利於找到更好的解。
3. 程式碼實現
/*
* *
* *
* * Copyright(c) Computer Science Department of XiaMen University
* *
* *
* * Authored by lalor on: 2012年 06月 29日 星期五 23:49:57 CST
* *
* *
* * Email: mingxinglai(at)gmail.com
* *
* *
* * @desc:
* *
* *
* * @history
* *
* *
* * 說明:本程式使用的測試資料來自權威的benchmark,其最優解是1211.資料儲存在source.txt
* * 本例的測試資料來自http://www.iwr.uni-heidelberg.de/groups/comopt/software/TSPLIB95/tsp/
* * rat99.tsp.gz
* * 資料如下
* ﹡格式:(城市編號,橫座標,縱座標)
1 6 4
2 15 15
3 24 18
4 33 12
5 48 12
6 57 14
7 67 10
8 77 10
9 86 15
10 6 21
11 17 26
12 23 25
13 32 35
14 43 23
15 55 35
16 65 36
17 78 39
18 87 35
19 3 53
20 12 44
21 28 53
22 33 49
23 47 46
24 55 52
25 64 50
26 71 57
27 87 57
28 4 72
29 15 78
30 22 70
31 34 71
32 42 79
33 54 77
34 66 79
35 78 67
36 87 73
37 7 81
38 17 95
39 26 98
40 32 97
41 43 88
42 57 89
43 64 85
44 78 83
45 83 98
46 5 109
47 13 111
48 25 102
49 38 119
50 46 107
51 58 110
52 67 110
53 74 113
54 88 110
55 2 124
56 17 134
57 23 129
58 36 131
59 42 137
60 53 123
61 63 135
62 72 134
63 87 129
64 2 146
65 16 147
66 25 153
67 38 155
68 42 158
69 57 154
70 66 151
71 73 151
72 86 149
73 5 177
74 13 162
75 25 169
76 35 177
77 46 172
78 54 166
79 65 174
80 73 161
81 86 162
82 2 195
83 14 196
84 28 189
85 38 187
86 46 195
87 57 194
88 63 188
89 77 193
90 85 194
91 8 211
92 12 217
93 22 210
94 34 216
95 47 203
96 58 213
97 66 206
98 78 210
99 85 204
﹡*
* *
* */
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <iterator>
#include <algorithm>
#include <limits.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
const int nCities = 99; //No. of node
//const double PC = 0.9; //交叉概率
double PM = 0.1; //變異概率
double PS = 0.8;//保留概率
int GEN_MAX = 50; //最大代數
const int UNIT_NUM = 5000; //群體規模為50
double length_table[nCities][nCities];//distance
//城市
struct node
{
int num;//城市的編號
int x;//橫座標
int y;//縱座標
}nodes[nCities];
struct unit
{
double length;//代價,總長度
int path[nCities];//路徑
bool operator < ( const struct unit &other) const //用於群體的排序
{
return length < other.length;
}
};
//群體規模(群體規模是指有 UNIT_NUM 個不同的解,而bestone 用於儲存最好的一個解)
struct unit group[UNIT_NUM];
//儲存最好的一個解
unit bestone = {INT_MAX, {0} };
// create matrix to storage the Distance each city
void init_dis();
//計算 unit 中的length, 也就是群體的一個個體(一個解)的長度
void CalCulate_length(unit &p);
//查詢id (代表城市) 在當前解中的位置,用於兩個解的交叉
int search_son(unit &p, int id);
//列印一個解
void print( unit &p);
//初始化群體,由C++ 中的 random_shuff 產生一個隨機排列
void Initial_group( unit group[]);
//開始進化,在本函式中執行群體中個體的交叉和變異
void Evolution_group(unit group[]);
//變異,隨機的選擇一個群體,然後隨機選擇兩個點,交換它們的位置
void Varation_group(unit group[]);
//交叉
void Cross_group( unit &p, unit &q);
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
srand(time(NULL));
init_dis();
//初始化種群
Initial_group( group );
//種群進化:選擇,交叉,變異
Evolution_group( group );
cout << "變異概率PM = " << PM << endl;
cout << "保留概率PS = " << PS << endl;
cout << "最大代數 = " << GEN_MAX << endl;
cout << "群體規模 = " << UNIT_NUM << endl;
cout << "代價是: = " << bestone.length << endl;
print(bestone);
}
void init_dis() // create matrix to storage the Distance each city
{
int i, j;
ifstream in("source.txt");
for (i = 0; i < nCities; i++)
{
in >> nodes[i].num >> nodes[i].x >> nodes[i].y;
}
for (i = 0; i < nCities; i++)
{
length_table[i][i] = (double)INT_MAX;
for (j = i + 1; j < nCities; j++)
{
length_table [i][j] = length_table[j][i] =sqrt(
(nodes[i].x - nodes[j].x) * (nodes[i].x - nodes[j].x) +
(nodes[i].y - nodes[j].y) * (nodes[i].y - nodes[j].y) );
}
}
}
void CalCulate_length(unit &p)
{
int j = 0;
p.length = 0;
for (j = 1; j < nCities; j++)
{
p.length += length_table[ p.path[j-1] ][ p.path[j] ];
}
p.length += length_table[ p.path[nCities - 1] ][ p.path[0] ];
}
void print( unit &p)
{
int i;
cout << "代價是:" << p.length << endl << "路徑是:";
// for (i = 0; i < nCities; i++)
// {
// cout << p.path[i] << " ";
// }
copy(p.path, p.path + nCities, ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " -> "));
cout << p.path[0] << endl;
}
//函式物件,給generate 呼叫
class GenByOne
{
public:
GenByOne (int _seed = -1): seed(_seed)
{
}
int operator() ()
{
return seed += 1;
}
private:
int seed;
};
//隨機產生 UNIT_NUM 個解空間
void Initial_group( unit group[])
{
int i, j;
unit temp;
//1, 2, 3, 4 ...... nCities
generate(temp.path, temp.path + nCities, GenByOne(0));
// 產生 UNIT_NUM 個解,也就是群體
for (i = 0; i < UNIT_NUM; i++)
{
//產生一個隨機排列,也就是初始化一個解
random_shuffle(temp.path, temp.path + nCities);
memcpy(&group[i], &temp, sizeof(temp));
CalCulate_length(group[i]);
}
}
void Evolution_group(unit group[])
{
int i, j;
int n = GEN_MAX;
int num1, num2;
//以PS 的概率選擇前 num2 個解,拋棄其後的num1 個解。
num1 = UNIT_NUM * ( 1 - PS);
num2 = UNIT_NUM * PS;
//迭代幾次,即繁衍多少代
while (n-- ) //迴圈GEN-MAX次
{
//選擇部分優秀的種群
sort(group, group + UNIT_NUM);
if (group[0].length < bestone.length)
{
memcpy(&bestone, &group[0], sizeof(unit));
}
for (j = 0; j <= num1 - 1; j++)
{
memcpy(&group[ num2 + j], &group[j], sizeof(unit));
}
//交叉
for (j = 0; j < UNIT_NUM / 2; j+= 1)
{
Cross_group(group[j], group[ UNIT_NUM - j -1]);
}
//變異
Varation_group(group);
}
//儲存已找最好的解
sort(group, group + UNIT_NUM);
if (group[0].length < bestone.length)
{
memcpy(&bestone, &group[0], sizeof(unit));
}
}
void Varation_group(unit group[])
{
int i, j, k;
double temp;
//變異的數量,即,群體中的個體以PM的概率變異,變異概率不宜太大
int num = UNIT_NUM * PM;
while (num--)
{
//確定發生變異的個體
k = rand() % UNIT_NUM;
//確定發生變異的位
i = rand() % nCities;
j = rand() % nCities;
//exchange
temp = group[k].path[i];
group[k].path[i] = group[k].path[j];
group[k].path[j] = temp;
CalCulate_length(group[k]);
}
}
int Search_son( int path[], int len, int city)
{
if (city <= 0 || city > nCities)
{
cout << "city outfiled, city = " << city << endl;
return -1;
}
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if (path[i] == city)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//reverse a array
//it's a auxiliary function for Rotate()
void Reverse(int path[], int b, int e)
{
int temp;
while (b < e)
{
temp = path[b];
path[b] = path[e];
path[e] = temp;
b++;
e--;
}
}
//旋轉 m 位
void Rotate(int path[],int len, int m)
{
if( m < 0 )
{
return;
}
if (m > len)
{
m %= len;
}
Reverse(path, 0, m -1);
Reverse(path, m, len -1);
Reverse(path, 0, len -1);
}
void Cross_group( unit &p, unit &q)
{
int i = 0, j ,k;
int pos1, pos2;
int len = nCities;
int first;
double len1 = length_table[p.path[0] ][ p.path[1] ];
double len2 = length_table[q.path[0] ][ q.path[1] ];
if (len1 <= len2)
{
first = p.path[0];
}
else
{
first = q.path[0];
}
pos1 = Search_son( p.path + i, len, first);
pos2 = Search_son( q.path + i, len, first);
Rotate(p.path + i, len, pos1);
Rotate(q.path + i, len, pos2);
while ( --len > 1)
{
i++;
double span1 = length_table[ p.path[i - 1] ][ p.path[i] ];
double span2 = length_table[ q.path[i - 1] ][ q.path[i] ];
if ( span1 <= span2 )
{
pos2 = Search_son( q.path + i, len, p.path[i]);
Rotate(q.path + i, len, pos2);
}
else
{
pos1 = Search_son( p.path + i, len, q.path[i]);
Rotate(p.path + i, len, pos1);
}
}
Rotate(q.path, nCities, rand() % nCities);
CalCulate_length(p);
CalCulate_length(q);
}4.參考資料:
[2] 演算法設計與分析(高階教程),國防工業出版社
