操作符(++,+,+=,小於號,(),--等)過載
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-10
1. 操作符(++,+,+=,小於號等)過載
新建QT專案,編寫標頭檔案
#ifndef DIALOG_H #define DIALOG_H #include <QDialog> #include<QLabel> namespace Ui { class Dialog; } //編寫自己的Label class myLabel { public: //一定要是共有的,才可以被呼叫 QLabel *ql; int cx; int cy; myLabel() { ql=new QLabel("12345") ; cx=cy=300; ql->move(cx,cy);//移動位置 } ~myLabel() { delete ql; } void show() { ql->show(); } }; class Dialog : public QDialog { Q_OBJECT public: int x;//長,寬 int y; int cx;//移動到的位置x座標 int cy; public: explicit Dialog(QWidget *parent = 0); //通過友元函式進行過載 friend void operator +=(Dialog &d,myLabel &my); ~Dialog(); //過載右加號 void operator ++(); void setxy(); void settoxy(int a,int b); //二元運算子,過載+號 Dialog * operator +(Dialog const &adddata); //過載等號 Dialog *operator =(Dialog const &setdata); //過載+= Dialog *operator +=(int length); //過載< bool operator < (Dialog const &data); private: Ui::Dialog *ui; }; #endif // DIALOG_H
編寫標頭檔案的實現類
#include "dialog.h" #include "ui_dialog.h" Dialog::Dialog(QWidget *parent) : QDialog(parent), ui(new Ui::Dialog) { ui->setupUi(this); x = y = 300; //將視窗大小固定 this->resize(x,y); cx = cy = 0; this->move(cx,cy); } Dialog::~Dialog() { delete ui; } //過載左加號,語法:括號裡面有int,預設後++,沒有int,預設前-- void Dialog::operator ++() { this->cx++; this->cy++; this->move(cx,cy); } void Dialog::setxy() { this->resize(x,y); } void Dialog::settoxy(int a,int b) { this->x = a; this->y = b; } //二元運算子,過載+號 Dialog * Dialog::operator +(Dialog const &adddata) { Dialog *p=new Dialog; p->x=this->x+adddata.x; p->y=this->y+adddata.y; return p; } //過載等號 Dialog * Dialog::operator =(Dialog const &setdata) { this->x = setdata.x; this->y = setdata.y; this->setxy(); return this; } //過載+=,如果+號前的變數和定義的變數型別一致,只需要一個引數 Dialog * Dialog::operator +=(int length) { this->x+= length; this->y+= length; this->setxy(); return this; } //過載< bool Dialog::operator < (Dialog const &data) { return (this->x * this->y) < (data.x * data.y); }
編寫主函式
#include "dialog.h" #include <QApplication> #include <windows.h> #include <QDebug> //在棧上定義一個臨時的Dialog,顯示,然後休眠2秒鐘後消失 void add(Dialog &add1,Dialog &add2) { Dialog temp; //棧上,用完了馬上回收 temp.x = add1.x + add2.x; temp.y = add1.y + add2.y; temp.show(); temp.setxy(); //發現這裡在停留2秒鐘後,視窗消失了。 Sleep(2000); } //在堆上,只有自己回收才消失 Dialog * addX(Dialog &add1,Dialog &add2) { //在堆上建立一個Dialog,只有當自己回收了的時候才會被銷燬 Dialog *p = new Dialog; p->x = add1.x + add2.x; p->y = add1.y + add2.y; p->show(); p->setxy(); return p; } //測試方法的方式實現+操作 //1.(分為兩種情況:1.棧上,2,堆上) //2.通過過載+操作符的方式實現 int main1(int argc, char *argv[]) { QApplication a(argc, argv); Dialog w1; //不管最終怎樣,因為這裡使用了w1.show()所以永遠有下面視窗 w1.show(); Dialog w2; //不管最終怎樣,因為這裡使用了w1.show()所以永遠有下面視窗 w2.show(); add(w1,w2); //下面開始使用在堆上建立視窗的方式演示效果,最後 Dialog *p = addX(w1,w2); //顯示視窗 p->show(); //下面通過過載+號的方式顯示視窗 Dialog *p2 = w1 + w2; p2->setxy(); p2->show(); return a.exec(); } //過載右++,因為右邊沒有引數,所以就不需要帶引數 int main2(int argc,char *argv[]) { QApplication a(argc,argv); Dialog w; w.show(); //將視窗先移動到(0,0)位置 w.move(0,0); for(int i=0;i<400;i++) { //過載左加號,語法:括號裡面有int,預設後++,沒有int,預設前-- ++w; Sleep(5); } return a.exec(); } //> //= //+= //友元過載+=,=不同類的物件的位置,因為這裡的泛型是類,所以下面使用class template<class T> void showall(T* myt) { myt->show(); } //測試上面的友元函式,測試過載函式,+=過載 //友元函式的好處:訪問私有變數 //如果過載的時候,用到私有變數的時候,不需要友元 int main3(int argc,char *argv[]) { QApplication a(argc,argv); //呼叫預設的Label,如果只寫下面這兩句,也會顯示一個帶有Label的小視窗 QLabel *ql = new QLabel("1234567"); ql->show(); myLabel label1; showall(&label1);//通過模板的方式實現顯示label //再定義一個Label,驗證上面的過載函式 Dialog w1; //下面傳遞一個指標 showall(&w1); return a.exec(); } //測試=,+=,<操作符 int main(int argc,char *argv[]) { QApplication a(argc,argv); Dialog w1; w1.setWindowTitle("w1視窗"); w1.show(); w1.settoxy(400,700); w1.setxy(); Dialog w2; w2.setWindowTitle("w2視窗"); w2.show(); w2.settoxy(700,400); w2.setxy(); //使用過載的=號操作符,執行效果是視窗2的大小和視窗1的大小一樣了 //如果下面的這行註釋掉,那麼就發現兩個視窗大小變成一樣了。 w1=w2; w2.show(); Dialog w3; w3.setWindowTitle("w3視窗"); w3.show(); w3.settoxy(300,1050); w3.setxy(); w3+=230; w3.show(); //<過載的是面積比大小 qDebug() << (w1 < w2); qDebug() << (w2 < w3); return a.exec(); }
2.過載--,()操作符的程式碼:
標頭檔案:
#ifndef DIALOG_H
#define DIALOG_H
#include <QDialog>
namespace Ui {
class Dialog;
}
class Dialog : public QDialog
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
int x;
int y;
//過載++操作符
void operator ++();
//過載--操作符
void operator --();
//過載()
void operator ()(int num);
//過載+操作符,建立視窗的時候在堆上
Dialog * operator +(Dialog & adddata2);
void setxy(int a,int b)
{
this->x = a;
this->y = b;
this->resize(this->x,this->y);
}
public:
explicit Dialog(QWidget *parent = 0);
~Dialog();
private:
Ui::Dialog *ui;
};
#endif // DIALOG_H
標頭檔案的實現類
#include "dialog.h"
#include "ui_dialog.h"
Dialog::Dialog(QWidget *parent) :
QDialog(parent),
ui(new Ui::Dialog)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
this->x = 300;
this->y = 400;
this->resize(x,y);
}
Dialog::~Dialog()
{
delete ui;
}
//過載++操作符
void Dialog::operator ++()
{
this->x++;
this->y++;
this->resize(x,y);
}
//過載--操作符
void Dialog::operator --()
{
this->x--;
this->y--;
this->resize(x,y);
}
//過載()
void Dialog::operator ()(int num)
{
this->x = num;
this->y = num / 2;
this->resize(x,y);
}
//過載+操作符,建立視窗的時候在堆上
Dialog * Dialog::operator +(Dialog & adddata2)
{
Dialog *p=new Dialog;
p->x=this->x+adddata2.x;
p->y=this->x+adddata2.y;
p->resize(p->x,p->y);
p->show();
return p;
}
主函式所在類
#include "dialog.h"
#include <QApplication>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QApplication a(argc, argv);
Dialog w;
w.show();
for(int i = 0;i<800;i++)
{
++w;
}
for(int i=800;i>0;i++)
{
--w;
}
for(int i = 1000;i>300;i--)
{
w(i);
}
return a.exec();
}
3.通過友元的方式過載操作<<和>>還有+操作符
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class mycomplex
{
public:
//友元,需要操作類的內部
//ostream,引用標準輸入輸出流
friend ostream & operator <<(ostream & out, mycomplex & Complex);
friend istream & operator >>(istream & in, mycomplex & Complex);
friend mycomplex operator +(mycomplex adddata1, mycomplex adddata2);
friend mycomplex operator +(mycomplex adddata1, int x);
//友元函式可以處理不同的型別交錯
//成員函式不能實現的,友元函式都可以實現
int x;
int y; //x,y座標
//沒有構造無法使用this初始化
mycomplex()
{
this->x = 0;
this->y = 0;
}
//建構函式過載
mycomplex(int x, int y) :x(x), y(y)
{
}
~mycomplex()
{
}
void show()
{
std::cout << x << "+" << y << "i" << std::endl;
}
//過載++操作符
void operator ++()
{
this->x++;
this->y++;
}
//過載--操作符
void operator --();
//過載函式呼叫運算子,變數名可以當作一個函式呼叫引數,返回結果
int operator()(int num)
{
cout << num << endl;
return num + num;
}
protected:
private:
};
void mycomplex::operator--()
{
this->x--;
this->y--;
}
//輸入輸出,cout,螢幕,fout檔案
ostream & operator <<(ostream & out, mycomplex & Complex)
{
out << Complex.x << "+" << Complex.y << "i" << std::endl;
return out;
}
istream & operator >>(istream & in, mycomplex & Complex)
{
cout << "請輸入X,Y" << endl;
in >> Complex.x >> Complex.y;
return in;
}
mycomplex operator +(mycomplex adddata1, mycomplex adddata2)
{
mycomplex temp;
temp.x = adddata1.x + adddata2.x;
temp.y = adddata1.y + adddata2.y;
return temp;
}
mycomplex operator + (mycomplex adddata1, int x)
{
mycomplex temp;
temp.x = adddata1.x + x;
temp.y = adddata1.y + x;
return temp;
}
void main()
{
mycomplex my1(7,8),my2(9,10);
//my1+my2這裡+實現了過載功能,返回的是一個mycomplex物件,其中<<又被過載了
std::cout << my1 + my2 << std::endl;
//my1+3這裡+實現了過載功能,返回的是一個mycomplex物件,其中<<又被過載了
std::cout << my1 + 3 << std::endl;
std::cin.get();
}
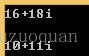
執行結果:
void main()
{
mycomplex my1;
//>>呼叫了過載
cin >> my1;
cout << my1;
//my1++;
//左加加,括號中不需要帶引數
++my1;
cout << my1;
my1--;
cout << my1;
//下面每行執行的時候分別輸出了2行資料。
std::cout << my1(1) << std::endl;
std::cout << my1(2) << std::endl;
std::cin.get();
std::cin.get();
}
執行結果如下: