資料結構之哈夫曼樹
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-10
一.什麼是哈夫曼樹
基本概念 節點之間的路徑:一個結點到另一個結點,所經過節點的結點序列。 結點之間的路徑長度:結點之間路徑上的分支數(邊),如汽車到下一站的路徑長度為1。 樹的路徑長度:從根結點到每個葉子結點的路徑長度之和。 帶權路徑: 路徑上加上的實際意義 。如汽車到下一站的距離我們叫做權值 樹的帶權路經長度: 每個葉子結點到根的路徑長度*權值 之和,記作WPL。還是汽車的例子,汽車到達天津有2條路 可以走。第一條路經過3個站,每個站相距13km。第二條有2個站,每個站相距18km。那麼有距離的路我們叫做帶權路徑。根結點為天津的樹,那麼第一條路帶權路徑為 3*13 = 39,第二條為2*18。樹的帶權路徑WPL 3*13+2*18. 哈夫曼樹: 重點來了,什麼是哈夫曼樹呢。二叉樹是n個結點的結合,它的度(所有孩子個數的最大值)小於等於2。n個結點構成一個二叉樹有許多方法。使二叉樹的帶權路徑最小的樹 ,我們叫做哈夫曼樹。
二.哈夫曼樹有什麼用
介紹了這麼多概念,不知道它有什麼用,讓初學者感覺資料結構沒什麼勁。哈夫曼樹主要用在資料的壓縮如JPEG格式圖片,在通訊中我們可以先對傳送的資料進行哈夫曼編碼壓縮資料提高傳輸速度。查詢優化 在工作中我們我們身邊放許多工具,由於空間限制我們不能把所有工具放在我們最容易拿到的地方,所有我們把使用頻率最高的工具放在最容易的位置。同樣的道理在查詢的時候我們把查詢頻率最高的資料建立索引,這些都是使用了哈夫曼演算法的思想。
三.怎麼構造哈夫曼樹
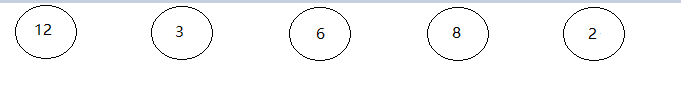
給定權值為12 3 6 8 2 如果構造其哈夫曼樹
1.給定n個權值{w1,w2,w3…..,wn}構成 n棵二叉樹的集合F={T1,T2,T3…..Tn}, 其中每棵樹只有權值為Wi的根節點。
構成的二叉樹為
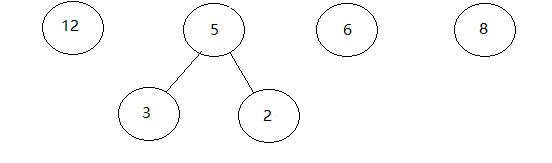
2.在F中選取權值最小的兩棵樹作為 左子樹和右子樹 構成新的二叉樹根的權值為兩棵樹之和
3.將前兩棵樹從F刪除 加入新樹
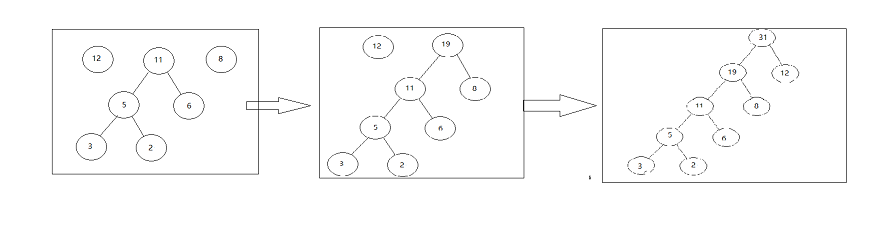
4.重複2和3直到只剩一棵樹
三.程式碼實現哈夫曼樹
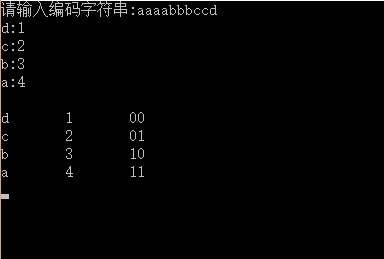
程式功能輸入一串字元,統計字元個數,並把字元個數作為權值構造一棵哈夫曼樹,求出字元的編碼
程式效果圖
1.程式碼
//標頭檔案
//為了學習 我使用連結串列來實現
//從樹種找出權值最小的兩個樹 我先對樹排序 取最小的兩棵
//新的樹先和最後一棵樹 比較 找到合適位置進行插入 也就是插入排序
#include <stdio.h>
#define STACKSIZE 20 //棧的大小