Java集合詳解--什麼是List
簡述
上章簡單介紹了什麼是集合,集合有哪幾種種類。
在這章中我們主要介紹Collection的其中一種實現方式,List。
什麼是List
在上一章,我們已經瞭解了List主要分為3類,ArrayList, LinkedList和Vector。
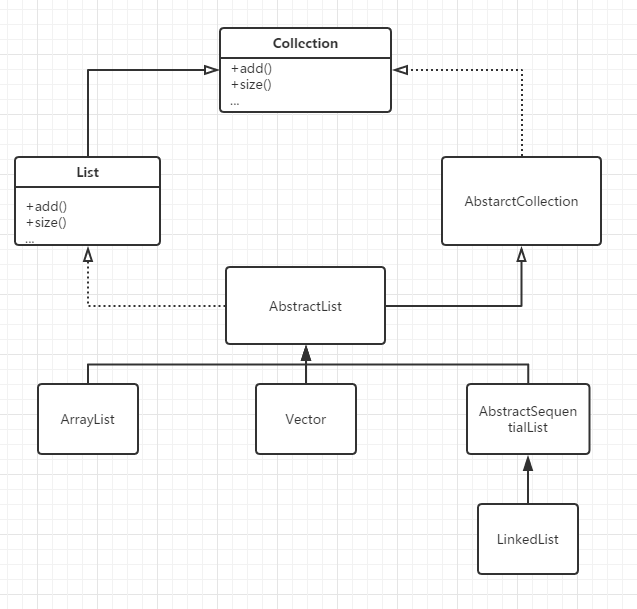
為了進一步清晰List的結構,我在這手工畫了一張圖,用於回顧下
AbstarctCollection在上一張Java集合詳解–什麼是集合已經有簡單的介紹,它是Collection介面的部分實現
1.List介面
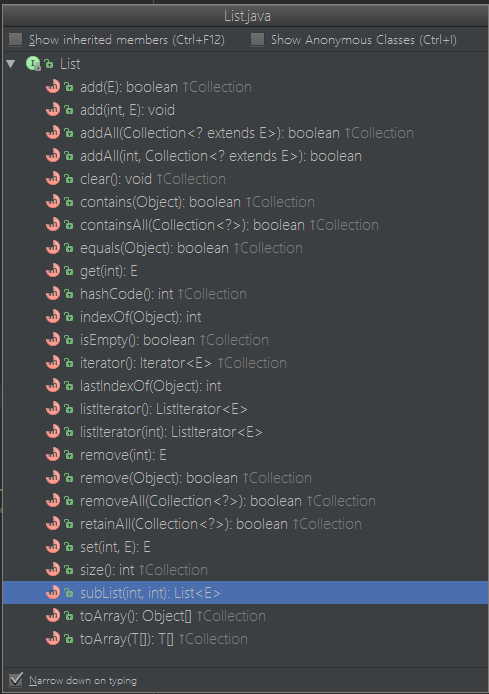
首先看下List的官方定義
這段描述解決了許多公司經常問的兩個問題List有什麼特點和Set有什麼區別。
上面清楚的說明了List是一個有序的集合,和set不同的是,List允許儲存項的值為空,也允許儲存相等值的儲存項,還舉了e1.equal(e2)的例子。
List是繼承於Collection介面,除了Collection通用的方法以外,擴充套件了部分只屬於List的方法。
從上圖可以發現,List比Collection主要多了幾個add(…)方法和remove(…)方法的過載,還有幾個index(…), get(…)方法。
而AbstractList也只是實現了List介面部分的方法,和AbstractCollection是一個思路,這裡就不具體介紹了,有興趣的同學可以自行研究下。
2.ArraryList
ArrayList是一個數組實現的列表,由於資料是存入陣列中的,所以它的特點也和陣列一樣,查詢很快,但是中間部分的插入和刪除很慢。我們來看幾段關鍵的程式碼。
首先是ArrayList的類關係和成員變數
//ArrayList繼承了Serializable並且申明瞭serialVersionUID,表示ArrayList是一個可序列化的物件,可以用Bundle傳遞
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189 然後是建構函式
//ArrayList有2個建構函式,一個是預設無參的,一個是傳入陣列大小的
//在JavaEffect書中明確提到,如果預先能知道或者估計所需資料項個數的,需要傳入initialCapacity
//因為如果使用無參的建構函式,會首先把EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA賦值給elementData
//然後根據插入個數於當前陣列size比較,不停呼叫Arrays.copyOf()方法,擴充套件陣列大小
//造成效能浪費
/**
* Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
}
/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
*/
public ArrayList() {
super();
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}然後是add()操作
//首先看到,不過是指定index執行add操作,還是在尾部執行add操作,都會先確認當前的陣列空間是否夠插入資料
//並且從
//int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
//int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
//if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
// newCapacity = minCapacity;
//看出,ArrayList預設每次都是自增50%的大小再和minCapacity比較,如果還是不夠,就把當的
//size擴充至minCapacity
//然後,如果是隊尾插入,也簡單,就把陣列向後移動一位,然後賦值
//如果是在中間插入,需要用到System.arraycopy,把index開始所有資料向後移動一位
//再進行插入
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this
* list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and
* any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}然後是remove操作
//個人感覺整個remove操作的程式碼寫了很冗餘,不像甲骨文這些大神的風格
//首先來看remove(int index)
//先進行邊界確認,傳入的index是否超過了當前陣列的大小,如果是丟擲異常
//如果在陣列範圍內,就把index之後的資料整體向前移動一位,最後一位值清空
//如果是remove(Object o),傳入的是一個物件,就會進行一次indexOf的操作,去當前陣列中尋找
//判斷是否存在,這裡的程式碼就十分冗餘了,就是把indexOf的程式碼拷貝了一次,完全可以呼叫indexOf方法
//根據返回值是否為-1來判斷該值是否存在,如果存在就呼叫fastRemove方法
//fastRemove(int index)和remove(int index)方法除了邊界檢查一模一樣
//完全可以在remove呼叫完rangeCheck(index)後呼叫fastRemove就可以了
//這裡不是很明白設計者的意圖
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their
* indices).
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element that was removed from the list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}
/**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list,
* if it is present. If the list does not contain the element, it is
* unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index
* <tt>i</tt> such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>
* (if such an element exists). Returns <tt>true</tt> if this list
* contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list
* changed as a result of the call).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list contained the specified element
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/*
* Private remove method that skips bounds checking and does not
* return the value removed.
*/
private void fastRemove(int index) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
}indexof
//這裡就和上面remove尋找是一模一樣的,就不進行探討了
public int indexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}3.Vector
Vector就是ArrayList的執行緒安全版,它的方法前都加了synchronized鎖,其他實現邏輯都相同。
如果對執行緒安全要求不高的話,可以選擇ArrayList,畢竟synchronized也很耗效能
4.LinkedList
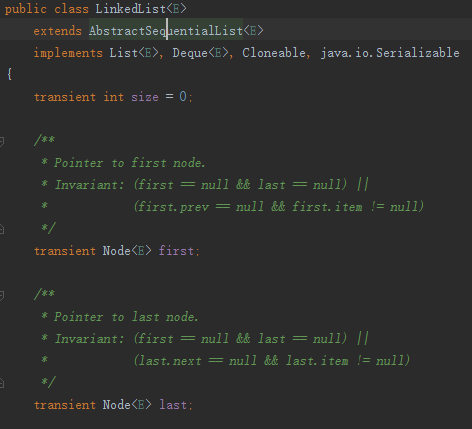
故名思意就是連結串列,和我們大學在資料結構裡學的連結串列是一會事,LinkedList還是一個雙向連結串列。
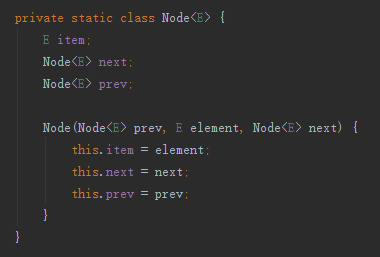
LinkedList繼承於AbstractSequentialList,和ArrayList一個套路。內部維護了3個成員變數,一個是當前連結串列的頭節點,一個是尾部節點,還有是連結串列長度。然後我們在來看下Node這個資料結構。
和C語言實現方式差不多,由於是雙向連結串列,所以記錄了next和prev,只不過把C語言裡的指標換成了物件。
然後我們簡單的在來看下連結串列額度查詢,插入和刪除操作
首先是add(E e)操作
//學過資料結構的同學看這部分程式碼特別輕鬆
//首先來看下void linkLast(E e),尾部插入
//就是把newNode的前面節點執行現在的尾部節點,newNode的後面節點執行null,因為是在尾部嘛
//然後把現在的尾部節點的後面節點指向newNode,因為現在的尾部節點不是最後一個了
//然後再來看下中間插入
//也是一個套路。假設現在在3號位插入一個newNode
//就是通過現在的3號Node的prev找到2號節點,然後修改2號節點的next,指向nowNode
//然後nowNode的prev指向2號節點,next指向3號節點
//最後3號節點的prev變成了nowNode,next不變
//這樣就完成了一次中間插入
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any
* subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
/**
* Links e as last element.
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
/**
* Inserts element e before non-null Node succ.
*/
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}然後是void linkLast(E e)操作
//indexOf操作非常簡單,就是從頭開始遍歷整個連結串列,如果沒有就反-1,有就返回當前下標
/**
* Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the lowest index {@code i} such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>,
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*
* @param o element to search for
* @return the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in
* this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element
*/
public int indexOf(Object o) {
int index = 0;
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null)
return index;
index++;
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
index++;
}
}
return -1;
}雖然indexOf非常簡單,但是我在這還是寫了個例子,幫助大家理解下
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("zero");
list.add(null);
list.add("two");
list.add(null);
list.add("three");
Log.i("test", "index : " + list.indexOf(null));在不看答案的情況下 大家能準確的說出答案嗎?
Answer:I/test: index : 1
從這個例子可以看出三點List的特徵
1.是按順序查詢
2.允許儲存項為空
3.允許多個儲存項的值相等
最後看下remove操作
//如果直接調無參的remove(),就會預設刪除頭節點
//刪除頭節點非常簡單,就是把頭節點的值清空,next清空
//然後把nextNode只為頭節點,然後清空next的prev
//最後size減1
//如果是刪除中間節點,呼叫remove(int index)
//首先判斷Index對應的節點是否為頭節點,即index是否為0
//如果不是中間節點,就是x的prev指向x的next
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}
public E removeFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) {
// assert l == last && l != null;
final E element = l.item;
final Node<E> prev = l.prev;
l.item = null;
l.prev = null; // help GC
last = prev;
if (prev == null)
first = null;
else
prev.next = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
/**
* Unlinks non-null node x.
*/
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
/**
* Unlinks non-null first node f.
*/
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
final E element = f.item;
final Node<E> next = f.next;
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
first = next;
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}總結
通過上面對ArrayList和LinkedList的分析,可以理解List的3個特性
1.是按順序查詢
2.允許儲存項為空
3.允許多個儲存項的值相等
可以知其然知其所以然
然後對比LinkedList和ArrayList的實現方式不同,可以在不同的場景下使用不同的List
ArrayList是由陣列實現的,方便查詢,返回陣列下標對應的值即可,適用於多查詢的場景
LinkedList由連結串列實現,插入和刪除方便,適用於多次資料替換的場景
再下一章中,我們可以瞭解set是如何實現的,還有set又有哪些特性