分治法-線性時間選擇
線性時間選擇問題:
給定線性序集中n個元素和一個整數k,1≤k≤n,要求找出這n個元素中第k小的元素。
1、隨機劃分線性選擇
基本思想:
- 只對劃分出的子陣列之一進行遞迴處理。
- 子陣列的選擇與劃分元和k相關。
#include <iostream> #include <ctime> using namespace std; int a[] = {5, 7, 3, 4, 8, 6, 9, 1, 2}; template<class Type> void Swap(Type &x, Type &y); inline int Random(int x, int y); template<class Type> int Partition(Type a[], int p, int r); template<class Type> int RandomizedPartition(Type a[], int p, int r); template<class Type> Type RandomizedSelect(Type a[], int p, int r, int k); int main() { for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { cout << a[i] << " "; } cout << endl; cout << RandomizedSelect(a, 0, 8, 3) << endl; } template<class Type> void Swap(Type &x, Type &y) { Type temp = x; x = y; y = temp; } inline int Random(int x, int y) { srand((unsigned) time(0)); int ran_num = rand() % (y - x) + x; return ran_num; } template<class Type> int Partition(Type a[], int p, int r) { int i = p, j = r + 1; Type x = a[p]; while (true) { while (a[++i] < x && i < r); while (a[--j] > x); if (i >= j) { break; } Swap(a[i], a[j]); } a[p] = a[j]; a[j] = x; return j; } template<class Type> int RandomizedPartition(Type a[], int p, int r) { int i = Random(p, r); Swap(a[i], a[p]);//隨機獲得的一個位置元素,與所要劃分的子陣列起始位置元素交換 return Partition(a, p, r); } template<class Type> Type RandomizedSelect(Type a[], int p, int r, int k) { if (p == r) { return a[p]; } int i = RandomizedPartition(a, p, r);//劃分元位置i int j = i - p + 1;//左子陣列a[p:i]的元素個數 if (k <= j) { return RandomizedSelect(a, p, i, k); } else { //由於已知道子陣列a[p:i]中的元素均小於要找的第k小元素 //因此,要找的a[p:r]中第k小元素是a[i+1:r]中第k-j小元素。 return RandomizedSelect(a, i + 1, r, k - j); } }
註釋:
1、利用隨機函式產生劃分基準,將陣列a[p:r]劃分成兩個子陣列a[p:i]和a[i+1:r],使a[p:i]中的每個元素都,不大於,a[i+1:r]中的每個元素。
2、計算a[p:i]中元素個數j=i-p+1。
3、如果k<=j,則a[p:r]中第k小元素在子陣列a[p:i]中。
4、如果k>j,則第k小元素在子陣列a[i+1:r]中,要找的a[p:r]中第k小元素是a[i+1:r]中第k-j小元素。
5、在最壞的情況下,找到最小元素時,總是在最大元素處劃分,這是時間複雜度為O(n^2)。但平均時間複雜度與n呈線性關係,為O(n)。
2、利用中位數線性時間選擇
問題分析:
- 如果能線上性時間內找到一個劃分基準,使得劃分得到的兩個子陣列的長度都至少為原陣列長度的ε倍(0<ε<1)。
- 那麼就可以在最壞情況下用O(n)時間完成選擇任務。
- 若ε=0.9,則T(n)≤T(0.9n)+O(n),由此得,T(n)=O(n)?
例子:
按遞增順序,找出下面29個元素的第18個元素:8,31,60,33,17,4,51,57,49,35,11,43,37,3,13,52,6,19,25,32,54,16,5,41,7,23,22,46,29.
(1) 把前面25個元素分為6(=ceil(29/5
(8,31,60,33,17),(4,51,57,49,35),(11,43,37,3,13),(52,6,19,25,32),(54,16,5,41,7),(23,22,46,29)
(2) 提取每一組的中值元素,構成集合{31,49,13,25,16,29}。
(3) 遞迴地使用演算法求取該集合的中值,得到m=29。
(4) 根據m=29, 把29個元素劃分為3個子陣列:
- P={8,17,4,11, 3,13,6,19, 25,16,5,7,23,22}
- Q={29}
- R={31,60,33,51,57,49,35,43,37,52,32,54,41,46}
(5) 由於|P|=14,|Q|=1,k=18,所以放棄P,Q,使k=18-14-1=3,對R遞迴地執行本演算法。
(6) 將R劃分成3(ceil(14/5))組:
{31,60,33,51,57},{49,35,43,37,52},{32,54,41,46}
(7) 求取這3組元素的中值元素分別為:{51,43,46},這個集合的中值元素是43。
(8) 根據43將R劃分成3組:
{31, 33, 35,37,32, 41},{43},{60, 51,57, 49, 52,54, 46}
(9) 因為k=3,第一個子陣列的元素個數大於k,所以放棄後面兩個子陣列,以k=3對第一個子陣列遞迴呼叫本演算法。
(10) 將這個子陣列分成5個元素的一組:
{31,33,35,37,32}、{41},取其中值元素為33。
(11) 根據33,把第一個子陣列劃分成
{31,32},{33},{35,37}
(12) 因為k=3,而第一、第二個子陣列的元素個數之和為3,所以33即為所求取的第18個小元素。
template<class Type>
void BubbleSort(Type a[], int p, int r);
template<class Type>
Type Select(Type a[], int p, int r, int k);
template<class Type>
void BubbleSort(Type a[], int p, int r) {
//記錄一次遍歷中是否有元素的交換
bool exchange;
for (int i = p; i <= r - 1; i++) {
exchange = false;
for (int j = i + 1; j <= r; j++) {
if (a[j] < a[j - 1]) {
Swap(a[j], a[j - 1]);
exchange = true;
}
}
//如果這次遍歷沒有元素的交換,那麼排序結束
if (false == exchange) {
break;
}
}
}
template<class Type>
Type Select(Type a[], int p, int r, int k) {
if (r - p < 75) {
BubbleSort(a, p, r);
return a[p + k - 1];
}
//(r-p-4)/5相當於n-5
for (int i = 0; i <= (r - p - 4) / 5; i++) {
//將元素每5個分成一組,分別排序,並將該組中位數與a[p+i]交換位置
//使所有中位數都排列在陣列最左側,以便進一步查詢中位數的中位數
BubbleSort(a, p + 5 * i, p + 5 * i + 4);
Swap(a[p + 5 * i + 2], a[p + i]);
}
//找中位數的中位數
Type x = Select(a, p, p + (r - p - 4) / 5, (r - p - 4) / 10);
int i = Partition(a, p, r, x);
int j = i - p + 1;
if (k <= j) {
return Select(a, p, i, k);
} else {
return Select(a, i + 1, r, k - j);
}
}
int main() {
int a[100];
srand((unsigned) time(0));
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
a[i] = Random(0, 500);
cout << "a[" << i << "]:" << a[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "第83小元素是" << Select(a, 0, 99, 83) << endl;
//重新排序,對比結果
BubbleSort(a, 0, 99);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
cout << "a[" << i << "]:" << a[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}劃分原理分析:
1、將全部的數劃分為兩個部分,小於基準的在左邊,大於等於基準的在右邊。
2、在上述情況下,找出的基準x至少比3 ⌊(n-5)/10⌋ 個元素大
推導:3 ⌊(n-5)/10⌋
(1)因為在剩餘一半的組中⌊n/5-1⌋*(1/2),每一組中有2個元素小於本組的中位數,有⌊n/5-1⌋*(1/2)*2= ⌊n/5-1⌋個小於基 準。
(2)在⌈ n/5 ⌉箇中位數中,1/2*⌊n/5-1⌋=⌊(n-5)/10⌋個小於基準x
(3)因此,總共有,3 ⌊(n-5)/10⌋個元素小於基準x,同理,基準x也至少比3 ⌊(n-5)/10⌋個元素小。
3、當n≥75時,3 ⌊(n-5)/10⌋≥n/4,所以按此基準劃分所得的2個子陣列長度都至少縮短1/4。
演算法複雜度分析:
- 當n<70時,演算法所用的計算時間不超過一個常數C1
- 分組求中位數的for迴圈執行時間為O(n)
- 以中位數x為基準對陣列進行劃分,需要O(n)時間
- 設:對n個元素的數組調用select需要T(n)時間
- 則找出中位數的中位數x,至多需要T(n/5)時間
- 已證明劃分得到的子陣列長度不超過3n/4
- 無論對哪個子陣列調用select至多需T(3n/4)時間
- 因此,T(n)≤2*O(n)+T(n/5)+T(3n/4)
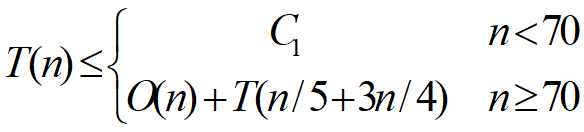
演算法分析:
- 分組大小固定為5,以70作為是否遞歸呼叫的分界點
- 這兩點保證了T(n)的遞迴式中2個自變數之和n/5+3n/4=19n/20=εn,0<ε<1
- 這是使T(n)=O(n)的關鍵之處
