ROS(1和2)機器人作業系統相關書籍、資料和學習路徑
ROS機器人相關書籍與資料(更新日期2017年11月)
之前寫過一篇博文總結過相關書籍(流行版本和相關書籍彙總),但是並沒有具體介紹。
學習ROS基礎知識以官網和書籍為主,如果需要了解ROS最新成果和進展,以論文和會議資料為主。使用ROS進行機器人設計與開發,那就需要在掌握機器人相關基本理論和知識的基礎上,大量閱讀原始碼,學習引數優化、演算法改進等。
ROS learning curve is a little steep and to become proficient is pretty hard for a complete beginner. 掌握ROS並非易事。
需要掌握一定的Linux基礎、C++和Python之後,具備機器人結構、電子、運動學等知識之後再學習ROS工具進行功能包開發。
查閱了幾乎全部已有的ROS資料,發現最主流的ROS課程還是以基礎內容+專題形式展開介紹:
同時也會輔助一些有趣的競賽:
下面介紹一下學習ROS的英中文書籍和資料。
1 ROS in 5 days
這個系列由四本書構成,分別為基礎、感知、導航、操作。
基礎篇:介紹ROS特點,模組化和複用性以及基本的工具、概念等。主要內容包括控制機器人,讀取感測器資料,並行任務處理,複雜資料和視覺資訊的視覺化等,課程分為兩個部分,第一部分,學習ROS並練習,執行程式碼並使用不同的機器人完成模擬;第二部分,開發一個專案,應用之前學過知識,完成一個控制機器人的專案。
具體目錄:0,簡介;1,基本概念;2,主題-釋出;3,主題-訂閱;4,服務-呼叫;5,服務-提供;6,行為-呼叫;7,行為-提供;8,除錯工具;9,課程專案。當然也可以在ROS官網找到對應章節內容進行學習:topic
感知篇:機器人要實現自動控制,感知是必不可少的重要內容。書中介紹在ROS中實現機器人的感知。
導航篇:書中介紹了關於導航的基礎知識,地圖建立、定位、路徑規劃、視覺化導航過程資料、使用RViz除錯、配置不同的導航點等。
操作篇:ROS操作主要是在環境中通過機器人對物體進行操作的術語,通過基本工具瞭解ROS如何操作物體並實現。
比較全面,移動機器人蔘考導航,工業機械手參考操作,功能全面服務機器人需要融合導航和操作。
2 A Systematic Approach to Learning Robot Programming with ROS
使用ROS學習機器人程式設計的系統方法通過對簡單程式碼示例以及相應操作理論的詳細解釋,全面介紹了ROS的基本元件。本書探討了ROS的組織,如何理解ROS軟體包,如何使用ROS工具,如何將現有的ROS軟體包納入新的應用程式,以及如何開發新的機器人和自動化軟體包。它還通過準備讀者更好地瞭解現有的線上文件來促進繼續教育。
這本書分為六部分。
1. 首先介紹ROS基礎,包括編寫ROS節點和ROS工具。訊息,類和伺服器也被覆蓋。
2. 本書的第二部分是ROS的模擬和視覺化,包括座標變換。
3. 本書的這一部分討論了ROS中的感知處理。它包括在ROS中使用攝像頭,深度成像和點雲以及點雲處理。
4. 本書第四部分介紹了ROS中的移動機器人控制和導航。
5. 本書的第五部分包含機器人手臂在ROS中的使用。本節探討機器人手臂運動學,手臂運動規劃,使用Baxter Simulator進行手臂控制以及物體抓取包。
6. 本書的最後一部分重點介紹系統整合和更高級別的控制,包括基於感知和移動操作。
3 更多書籍
http://wiki.ros.org/Books





















4 論文集 Robot Operating System (ROS)

5 重要會議 ROSCon 2012-2017
6 官方網站和原始碼 ROS和Github
7 視訊資料
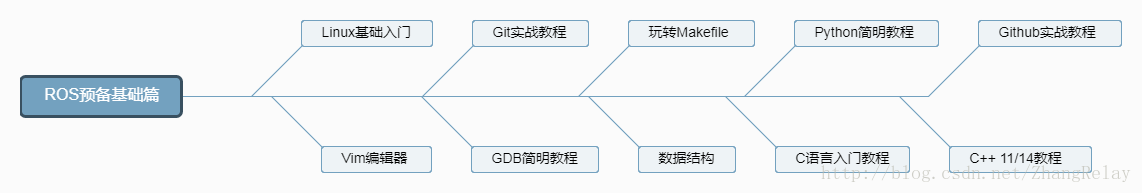
學習路徑:ROS官網初級教程+中級教程+座標變換(TF)+機器人模型(URDF)+視覺化(RViz)+行為庫(actionlib)+外掛庫(pluginlib)+nodelets+導航(navigation)+工業機器人(ROS-I)+ROS(1、2)等;
然後,結合所需要使用的場景,選擇1-3本書籍進行系統練習與複習。
參考資料目錄:
01 張建偉, 張立偉, 胡穎等 開源機器人作業系統----ROS[M]. 科學出版社, 2012.
02 馬丁內斯, 費爾南德斯 劉品傑 ROS機器人程式設計:Learning ROS for robotics programming[M]. 機械工業出版社, 2014.
03 Quigley M, Conley K, Gerkey B P, et al. ROS: an open-source Robot Operating System[C]// ICRA Workshop on Open SourceSoftware. 2009.
04 王之元, 周雲,易曉東等. 機器人作業系統研究型課程建設[J].計算機教育,2016, No.253(1):77-80.
05 肖軍浩, 盧惠民,薛小波等. 將機器人作業系統(ROS)引入本科實踐教學[J].科技創新導報,2016(22):157-158.
06 R.帕特里克・戈貝爾,戈貝爾,羅哈斯.ROS入門例項[M].中山大學出版社,2016.
07 R.帕特里克・戈貝爾,戈貝爾,羅哈斯.ROS進階例項[M].中山大學出版社,2017.
08 李振偉. ROS入門與實戰[M].中國礦業大學出版社,2016.
09 恩裡克·費爾南德斯等著,劉錦濤、張瑞雷譯 ROS機器人程式設計(原書第2版)[M]機械工業出版社2016
10 傑森 M. 奧凱恩著; 肖軍浩譯 機器人作業系統淺析[M]國防工業出版社2016
11 周興社 機器人作業系統ROS原理與應用[M]機械工業出版社2017
12 郎坦·約瑟夫(LentinJoseph)機器人系統設計與製作:Python語言實現[M]機械工業出版社2017
13 何炳蔚,張立偉,張建偉 基於ROS的機器人理論與應用[M]科學出版社2017
14 陳金寶 ROS開源機器人控制基礎[M]上海交通大學出版社2016
15 盧惠民,肖軍浩,鄭志強 ROS與中型組足球機器人[M]國防工業出版社2016
16 Wyatt Newman A Systematic Approach toLearning Robot Programming with ROS[M]Chapman and Hall/CRC 2017
17 Lentin Joseph ROS Robotics Projects[M] Packt Publishing 2017
18 Anil Mahtani, Aaron Martinez, EnriqueFernandez Perdomo, Luis Sánchez Effective Robotics Programming with ROS - ThirdEdition[M] PacktPublishing 2016
19 Fairchild, Carol and Harman, Dr. Thomas ROS Robotics By Example[M]Packt Publishing 2016
20 Quigley, Morgan and Gerkey, Brian andSmart, William D. Programming Robots with ROS[M] O'Reilly Media 2015
21 Lentin Joseph Learning Robotics using Python[M] PacktPublishing 2015
22 Koubaa A. Robot Operating System (ROS)The Complete Reference (Volume 1) [M]. Springer International Publishing, 2016.
23 Koubaa A. Robot Operating System (ROS)The Complete Reference (Volume 2) [M]. Springer International Publishing, 2017.
-End-
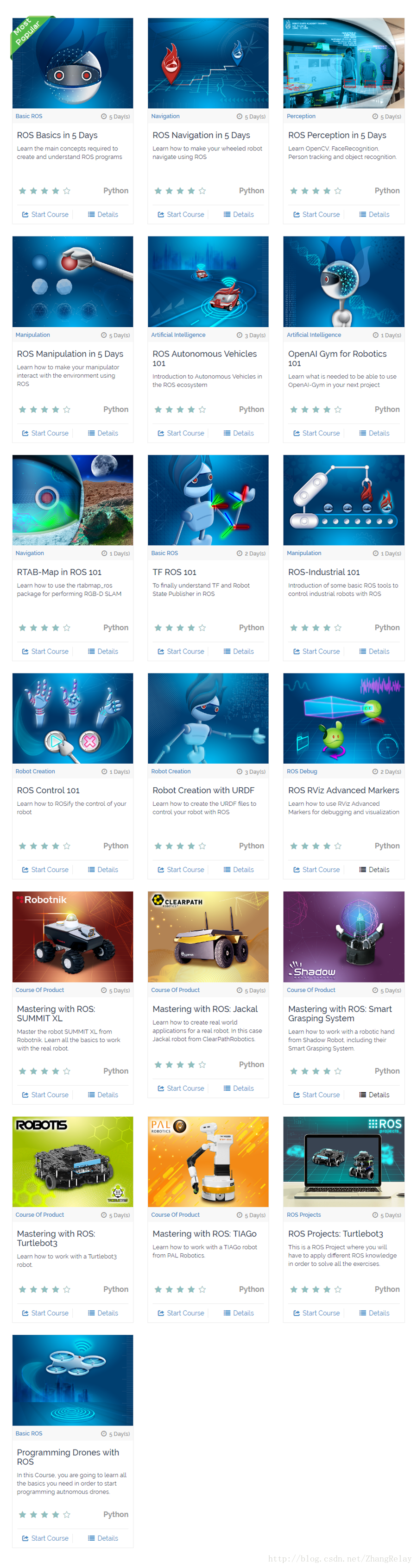
附錄課程大綱彙總:
ROS BASICS IN 5DAYS
Learnthe main concepts required to create and understand ROS programs
Abrief summary
ROSIn 5 Days is the ideal course if you are new to ROS. Here you will learn ROSfast!!!
Theobjective of this course is to give you the basic tools and knowledge to beable to understand and create any basic ROS related project. You will be ableto move robots, read their sensor data, make the robots perform intelligenttasks, see visual representations of complex data such as Point Clouds anddebug errors in the programs.
Whatyou will learn
Atthe end of this course, we will feel comfortable about the following subjects:
1. ROSBasic Structure
2. ROS Topics
3. ROSServices
4. ROSActions
5. ROSDebugging Tools
Unit 0: CoursePreview
1. Interactingwith a simulated robot
2. Whatyou will need to learn to program a robot with ROS
Unit 1: Guide forROS in a Single Week
1. It ispossible to learn ROS fast if you have the proper method
2. Robotswe are going to use along the course
3. MainObjective of this course
4. LearningROS: attack in two ways
5. Applywhat you learnt to a Robot Project
6. How toproceed with the whole course
Unit 2: ROS Basics
1. BasicConcepts
2. Move aRobot with ROS
3. What'sa ROS Package
4. What isa launch file
5. Createa ROS Package
6. Yourfirst ROS program
7. ROSNodes
8. Compilinga ROS Package
9. ParameterServer
10. ROSCore
11. EnvironmentVariables
Unit 3: ROS Topics- part 1
1. TopicPublisher
2. ROSMessages
3. Exercises
Unit 4: ROS Topics- part 2
1. TopicSubscriber
2. CustomTopic Message Compilation
3. ROSTopics Mini Project
Unit 5: ROSServices - part 1
1. Topics- Services - Actions
2. ServicesIntroduction
3. How tocall a ROS Service
4. Exercises
Unit 6: ROSServices - part 2
1. How togive a Service
2. How tocreate your own service message
3. CustomService Compilation
Unit 7: ROSActions - part 1
1. Playingwith the Quadrotor simulation
2. Whatare ROS Actions
3. Callingan Action Server
4. Performingother tasks while the Action is in progress
5. Theaxclient
Unit 8: ROSActions - part 2
1. Writingan Action Server
2. Creatingyour own Action Server Message
3. CustomAction Messages compilation
Unit 9: DebuggingTools
1. ROSWhat The F*ck
2. ROSDebugging Messages and RQT-Console
3. Plottopic data and RQT Plot
4. NodeConnections and RQT graph
5. Recordexperimental data and ROSBags
6. VisualizeComplex data and RViz
Unit 11: CourseProject
1. Win theSphero Race
2. WhatSphero provides to program It
3. Ideasto start working on
4. Stepsyou should cover
Unit 12: TurtlebotProject
1. Win theTurtleBot Race!
2. WhatTurtlebot provides to program It
3. Ideasto start working on
4. Stepsyou should cover
Unit 13: What todo after the Course?
1. KeepLearning
ROS NAVIGATION IN5 DAYS
Learnhow to make your wheeled robot navigate using ROS
Abrief summary
Theobjective of this course is to give you the basic tools and knowledge to beable to understand and create any basic ROS Navigation related project.
Youwill be able to create maps of environments, localize the robot in theenvironment, make the robots perform path planning, visualize data of thedifferent Navigation processes, debug errors using RViz and configure thedifferent Navigation nodes.
Whatyou will learn
Atthe end of the course you will be comfortable with the following subjects:
1. The ROSNavigation Stack
2. What isneeded to work with the Navigation Stack
3. What isthe move_base node and why it is so important
4. Whichparts take place in the move_base node
Unit 0: BasicConcepts
1. What isneeded to perform robot navigation with ROS
2. How toconfigure your Robot
3. TheNavigation Stack
4. HardwareRequirements
5. Themove_base node
Unit 1: Guide forROS Navigation in 5 Days
1. It ispossible to learn ROS fast if you have the proper method
2. Robotswe are going to use along the course
3. MainObjective of this course
4. LearningROS Navigation: attack in two ways
5. Applywhat you learnt to a Robot Project
6. How toproceed with the whole course
Unit 2: Mapping
1. VisualizeMapping in RViz
2. SimultaneousLocalization and Mapping (SLAM)
3. HardwareRequirements
4. Transforms
5. Creatinga launch file for the slam_gmapping node
6. Build aMap Using Logged Data
Unit 3:Localization
1. VisualizeLocalization in RViz
2. MonteCarlo Localization (MCL)
3. TheAMCL Package
4. HardwareRequirements
5. Creatinga launch file for the AMCL node
6. AMCLthrough Services
Unit 4: PathPlanning 1
1. VisualizingPath Planning in RViz
2. Themove_base package
3. TheGlobal Planner
4. GlobalCostmap
Unit 5: PathPlanning 2
1. TheLocal Planner
2. LocalCostmap
3. RecoveryBehaviors
4. ClearCostmap
5. OscillationSuppression
6. DynamicReconfigure
Unit 6: NavigationProject
1. Navigatethe Summit Robot
2. Whatthe Summit provide for programming it
3. Stepsyou should cover
ROS PERCEPTION IN5 DAYS
LearnOpenCV, FaceRecognition, Person tracking and object recognition.
Abrief summary
Perceptionis probably one of the most important things when we talk about autonomy.
Inthis course you will learn how perception is performed by robots using the ROSFramework.
Whatyou will learn
Atthe end of this course you will fell comfortable about making robots do thefollowing things:
1. Trackobjects by its color blobs
2. Navigatefollowing floor lines with only RGB camera
3. Detecthuman faces and track them
4. Recognizedifferent faces
5. Track aperson through a 3D environment
6. Recognizeflat surfaces like tables where object might be placed
7. Recognizeobjects and track them in 3D space with PointCloudSensors
Unit 1: Perceptionwith ROS Intro
1. WorkingExample: Mira Robot Follows the Ball
2. Overview
Unit 2: VisionBasics Blob Tracking
1. Roll ,Pitch and Yaw
2. Blobtracking with OpenCV and python part 1: color encoding
3. Blobtracking with OpenCV and python part 2: start blob tracking with cmvision
4. Exercises
Unit 3: VisionBasics Follow Line
1. GetImages from a ROS topic and show them with OpenCV
2. ApplyFilters To the Image
3. Movethe TurtleBot based on the position of the Centroid
4. AdditionalStep: Follow Multiple Centroids
5. PIDcontroller with perception
Unit 4: Surfaceand Object Recognition
1. TableTop Detector
2. 2D and3D Object Finder
3. Moveand spawn objects
4. 3DObject Detection
Unit 5: FaceDetection and tracking
1. FaceDetector in ROS
2. FaceDetector Client
3. Visualizethe Face Detections
Unit 6: FaceRecognition
1. Startingthe Face Recognition package
2. MultipleFace Detection at the same time
Unit 7: PeopleTracking
1. ROSpackage for tracking people
2. LegDetector
3. DetectUpperBody
4. Pedestriandetector
5. Combiningall together
Unit 8: AiboPerception Project
1. YourOwn Simplified Aibo ERS7
2. RGB,Depth and Point Cloud
3. TheCamera-Optic frame problem
4. Elementsof the Simulated World
5. Projectexercises
Unit 10: What todo next
1. KeepLearning
ROS MANIPULATION IN 5 DAYS
Learnhow to make your manipulator interact with the environment using ROS
Abrief summary
ROSManipulation is the term used to refer to any robot that manipulates somethingin its environment.
Themain goal of this Course is to teach you the basic tools you need to know inorder to be able to understand how ROS Manipulation works, and teach you how toimplement it for any manipulator robot.
Whatyou will learn
Atthe end of this Course you will feel comfortable about the following subjects:
1. Basicsof ROS Manipulation
2. How tocreate and configure a MoveIt! package for a manipulator robot
3. How toperform Motion Planning.
4. How toperform Grasping.
Unit 1:Introduction to the Course
1. What isROS Manipulation
2. Do youwant to have a taste?
3. Whatyou will learn with this Course
4. How youwill learn it
5. Minimumrequirements for the course
6. SpecialThanks
Unit 2: BasicConcepts
1. Whatyou need to perform ROS Manipulation
2. Structureof a Manipulator Robot
3. BasicTerminology
Unit 3: Creating aMoveIt package
1. What isMoveIt!
2. GeneratingMoveIt! configuration package using Setup Assistant tool
3. Themove_group node
4. BasicMotion Planning
5. MoveIt!planning scene
6. MoveIt!kinematics handling
7. MoveIt!collision checking
8. Movingthe real robot
Unit 4: PerformMotion Planning programmatically
1. Exercise
2. Planninga trajectory
3. Planningto a joint space goal
4. Gettingsome useful data
5. Executinga trajectory
Unit 5: AddingPerception
1. Exercise
2. AddingPerception to MoveIt!
Unit 6: Grasping
1. What isGrasping
2. Graspingusing MoveIt!
3. Creatinga pick and place task
4. Graspingin the Real Robot
Unit 7: Project
1. Buildthe MoveIt! package
2. Connectthe MoveIt! package with the simulation
3. PythonScript
4. AddPerception to the MoveIt! package
5. Grasping
Unit 8: FinalRecommendations
1. KeepLearning
ROS AUTONOMOUSVEHICLES 101
Introductionto Autonomous Vehicles in the ROS ecosystem
Abrief summary
Thegoal of this course is to show you the basic knowledge you need to master inorder to program autonomous cars for a Level 3 of autonomy.
Thismeans, it is expected that all task should be performed autonomously, but atthe same time it is expected to intervene a human driver whenever required.This level is called conditional automation.
Whatyou will learn
Inthis course you are going to learn the essentials for doing autonomous carscontrol using ROS.
Youare going to learn:
1. Whatare the sensors required for an autonomous car and how to access them using ROS
2. How todo autonomous navigation using a GPS
3. How tocreate an obstacle avoider for an autonomous car
4. How tointerface ROS with a car that follows the DBW interface
Unit 1: Unit 0:Introduction
1. Introduction
2. Sensors
3. Autonomousnavigation
4. The DBWinterface for autonomous cars and CAN-Bus
5. Minimumrequirements for this course
6. Specialthanks
Unit 2: Unit 1:Sensors
1. BasicSensors List
Unit 3: Unit 2:GPS Navigation
1. Introduction
2. Creatinga GPS Subscriber
3. Move ToWayPoint GPS ACTION Server
4. Move ToWayPoint GPS ACTION Client
Unit 4: Unit 3:Obstacles and Security
1. Controlethe Car movement Data Flow
2. SystemFailure Mesures and DeadMansSwitch
3. ObstacleDetection
Unit 5: Unit 4:CAN-Bus
1. HowCan-Bus messages look like
2. How weuse CAN-Bus in the simulation
3. Exercises
Unit 6: Unit 5:Microproject
1. Instructionsand the Project itself
Unit 7: Finalrecommentations
1. KeepLearning
OPENAI GYM FORROBOTICS 101
Learnwhat is needed to be able to use OpenAI-Gym in your next project
Abrief summary
Theobjective of this course is to teach how to use OpenAI-Gym through environmentsdefined for Gazebo Simulator.
Thismeans that although the examples in this course will be exclusively in GazeboSimulator, the knowledge acquired will be applicable to any system. You will beable to define environments for Gazebo, but also for other simulators or evenother systems.
Whatyou will learn
Atthe end of the course , the following topics will have been addressed:
1. Basicsof openai-gym API
2. Definitionof environment files for openai-gym, centered in gazebo-ROS simulations.
3. Importingof environments and communication with Gazebo Simulations through ROS.
4. Registeringof learning results and data plot
5. Createyour own environment through a hands on example with a drone in Gazebo.
Unit 1:introduction openai-gym
1. What isOpenAI-Gym
2. What'sin this OpenAI Gazebo-Gym Course
3. How youwill learn all that
4. Minimumrequirements for this course
5. SpecialThanks
Unit 2: Running anenvironment
1. Makethe robot learn how to move
2. Selectthe environment
3. Startup the monitoring
Unit 3:Environment file configuration
1. Whereto find the environment files
2. Exercises
Unit 4: Plotresults
1. PlotResults from Monitor
2. Exercises
3. UploadResults from Monitor
Unit 5: MicroProject
1. Knowyour environment
2. Whatyou have to edit and create
3. Use theEnvironment just created to learn
Unit 6: FinalObservations
1. KeepLearning
RTAB-MAP IN ROS 101
Learnhow to use the rtabmap_ros package for performing RGB-D SLAM
Abrief summary
RTAB-Map(Real-Time Appearance-Based Mapping) is a RGB-D SLAM approach based on a loopclosure detector.
Theloop closure detector uses a bag-of-words approach in order to determinate if anew image detected by an RGB-D sensor it is from a new location or from alocation that it has been already visited.
Ofcourse, this is a very summarized explanation, you will get more details on howthis loop closure detector works inside this Course.
Whatyou will learn
Duringthis Course you will address the following topics:
1. Basicsof RTAB-Map.
2. How touse the rtabmap_ros package.
3. Howdoes loop closure detection work internally.
4. How tocreate a 3D Map of an environment.
5. AutonomousNavigation using RGB-D SLAM.
Unit 1:Introduction to the Course
1. What isRTAB-Map
2. Demo
3. Whatyou will learn with this Course
4. Minimumrequirements for the Course
5. SpecialThanks
Unit 2: BasicConcepts
1. SystemRequirements
2. DataVisualization - RViz
3. LaunchingRTAB-Map
4. SubscribedTopics
5. Arguments
Unit 3: AutonomousNavigation with rtabmap_ros
1. Brief Introduction
2. MappingMode
3. LocalizationMode
4. AutonomousNavigation
Unit 4: FinalRecommendations
1. KeepLearning
TF ROS 101
Tofinally understand TF and Robot State Publisher in ROS
Abrief summary
Anyphysical system, specially robotics systems, have many coordinate frames thatchange over time.
Arobotic arm, for example, has many different physical parts, each one with itsown coordinate frame, that can move at the same time.
WithTF, you will know how a hand "knows" the position of an object basedon the position of the camera, for example.
Whatyou will learn
Thiscourse will centre on hands on experience, making you able to:
1. Publishand Subscribe to TF data topics
2. Use thetools necessary to visualize TF data
3. Publishfixed TF transforms
4. UseRobotStatePublisher to generate TF data for robots to complex to publish itmanually
5. Understandthe use of JointStatePublisher and how it relates to RobotMovement Controllers
Unit 1: Intro toTF
1. What'sin the ROS TF Course
2. How youwill learn all that
3. Minimumrequirements for this course
Unit 2: TF Basics
1. Whatyou will be able to do after this Unit
2. Whatthis have to do with TF anyway
3. Get anidea of what is happening
Unit 3: TF Publishand Subscribe
1. TFPublisher
2. TFSubscriber
3. Addingmore frames
Unit 4:RobotStatePublisher
1. Knowhow Pi-Robot works
2. Createyour own robot_state_publisher launch
3. JointState Publisher
Unit 5: StaticTransforms
1. Introduction
2. Howit's done in launch files and command line
3. PracticalApplication
Unit 6:MicroProject
1. Spawn aURDF model
2. Removea model from Gazebo
3. Guidelinesand the project itself
Unit 7: What to donext
1. KeepLearning
ROS-INDUSTRIAL 101
Introductionof some basic ROS tools to control industrial robots with ROS
Abrief summary
ROS-Industrialis a project which main goal is to bring ROS closer to the robotics industrialworld. It is a HUGE project, composed of many packages and tools.
ThisCourse is not meant to make you learn all the things you can achieve withROS-Industrial, but just to introduce you to some basic concepts you need toknow if you want to begin exploring all the ROS-Industrial capabilities.
Whatyou will learn
Duringthis Course you will address the following topics:
1. Overviewof how to create an URDF file for an industrial robot.
2. How tocreate a MoveIt! package for your industrial robot.
3. How toperform motion planning using Python.
Unit 1:Introduction to the Course
1. What isROS-Industrial
2. Whatyou will learn with this Course
3. How youwill learn it
4. Minimumrequirements for the Course
5. SpecialThanks
Unit 2: Creatingthe URDF
1. Buildingthe URDF
2. Buildingthe Xacro
Unit 3: Building aMoveIt package
1. Buildinga MoveIt! package
2. BasicMotion Planning
3. Movingthe robot in the simulation
Unit 4: MotionPlanning through code (Python)
1. Planninga trajectory
2. Planningto a joint space goal
3. Gettingsome useful data
4. Executinga trajectory
Unit 5: FinalProject
1. Buildthe URDF
2. Buildthe MoveIt! package
3. Connectthe MoveIt! package with the simulation
4. PythonScript
Unit 6: FinalRecommendations
1. KeepLearning
ROS CONTROL 101
Learnhow to ROSify the control of your robot
Abrief summary
ROSControl are a set of packages and tools that allow you to send commands andcommunicate with the joints of your robot in order to be able to control them.
Themain goal of this Course is to teach you how to integrate this ros_controlutility within a simulated environment, so you can apply the same concepts touse this tool to control the joints of your real robot.
Whatyou will learn
Duringthis Course you will address the following topics:
1. Basicsof ROS Control.
2. How toconfigure ROS Control to work with your robot simulation.
3. How tocreate a custom controller.
Unit 1:Introduction to the Course
1. What isROS Control
2. Whatyou will learn with this Course
3. How youwill learn it
4. Minimumrequirements for the Course
5. SpecialThanks
Unit 2: BasicConcepts
1. Theros_control packages
Unit 3:Configuring the controllers
1. Configuringthe URDF - Transmissions
2. Configuringthe URDF - Plugin
3. Interactingwith the joints in a graphical way
Unit 4: Create acontroller
1. Creatingthe package
2. Creatingthe source code
3. Updatingthe package.xml file
4. Updatingthe CMakeLists.txt file
5. Buildthe controller
6. Writethe configuration file
7. Createa launch file
Unit 5: CourseProject
1. Examinethe simulation
2. Buildthe control package
3. Testyour package
4. Createa controller
Unit 6: FinalRecommendations
1. KeepLearning
ROBOT CREATIONWITH URDF
Learnhow to create the URDF files to control your robot with ROS
Abrief summary
Inthis course you will learn how to go from a physical robot or even a robotdrawing to a full fledged simulation with physics, actuators and sensors.
Whatyou will learn
Duringthis course you will learn:
1. How tocreate a URDF file that defines your robot in the Gazebo-ROS ecosystem.
2. Definitionof weights, inertias, joints, links, sensor plugins and all that is needed tosimulate a robot.
3. XACROfiles.
Unit 1: URDF Intro
1. Introductionwith demo
2. Why youneed to simulate robots
3. How youwill learn about URDF files
4. Requirements
5. SpecialThanks
Unit 2: Creatingthe Visual Robot Model with URDF
1. Introduction
2. Learnhow to use the URDF creation tools and the creation procedure
3. Linksand Joints
4. See theURDF
5. Learnabout the morphology of your robot
6. Learnhow to import your 3D CAD models to Gazebo
Unit 3: Adapt URDFfor Gazebo Simulator
1. AddCollisions
2. Spawn arobot in Gazebo Through URDF Files
3. AddInertias
4. Addcontrollers
5. AddingSensors
Unit 4: GurdyRobot
1. Createthe Gurdy Robot
Unit 5: XACROfiles
1. Basicson using XACRO
2. Createyour own XACRO
Unit 6: MicroProject: Create your own Jibo
1. Instructionsand the Project itself
Unit 7: What to donext
1. KeepLearning
ROS RVIZ ADVANCEDMARKERS
Learnhow to use RViz Advanced Markers for debugging and visualization
Abrief summary
Visualizingdata in the correct way is vital to extract meaningful conclusions. This isspecially true in Robotics.
Oneof the problems you always tend to have in robotics is to know what the robotis actually seeing, what is the virtual representation of the world in hismind. Its also very important to represent visually complex data in one placeonly.
That'swhy RViz and all its markers and plugins have made robotics much user friendlyand powerful than ever before!
Whatyou will learn
1. How touse Basic RViz Markers.
2. How toCreate BoundingBoxes Arrays that change dynamically.
3. How toadd Overlay text, graphs and menus in RViz.
4. DrawTFTRajectories, RobotFootsteps and occupancy grids that change based on realrobot data.
5. Drawpictograms from FontAwsome to represent detections and real object in the world
6. RepresentTwistStamped commands issued to the robot
7. CreateInteractive displays in RViz that allow to execute programs from RViz withcustom icons.
8. Recordvideos of Rviz
Unit 1:RvizMarkers Unit 0: Presentation in ROS
1. Intro
2. Let'sPlay
3. Whatyou will learn with this Course
4. How youwill learn all this
5. Requirements
6. SpecialThanks
Unit 2:RvizMarkers Unit 1: Basic Markers
1. Firstget the feeling of the simulation
2. Createyour first basic Marker
3. Createa Custom Mesh Marker
Unit 3:RvizMarkers Unit 2: BoundingBoxes, RobotFootsteps, PolygonArray ,Ocupancygrids, Pictograms
1. Whereto find all this elements in RViz
2. BoundingBoxes
3. RobotFootsteps
4. PolygonArray
5. OccupancyGrids
6. Pictograms
Unit 4:RvizMarkers Unit3: Add Overlays
1. Addingplots, piecharts and menus
2. Plotsand PieCharts
3. Menusand Text Overlay
4. Completedemo
Unit 5:RvizMarkers Unit 4: Add Custom Panels to RVIZ and Extras
1. Add aYES or NO interactive panel
2. Add acustom GUI
3. Drawtrajectories and TwistStaped in RViz
4. RecordRViz Sessions
Unit 6:RvizMarkers What to do Next
1. KeepLearning
MASTERING WITHROS: SUMMIT XL
Masterthe robot SUMMIT XL from Robotnik. Learn all the basics to work with the realrobot.
Abrief summary
Whatyou will learn
1. How toset up the navigation stack to make it navigate in an indoor environment,generating maps by its own.
2. How tocreate a program to navigate in outdoors environments through GPS data.
3. How todetect persons with the Hokuyo laser sensor.
4. How todetect person with its PTZ RGB camera.
5. How torecognise person with its PTZ RGB camera and tell if it has permission to bethere or not.
6. How toSet WayPoints in a map to make it follow that path to patrole.
7. Createa reactive programs based on all previously mentioned and create a patrolingprogram that reacts to person detections.
Unit 0: Unit 0:Robotniks Summit XL platform
Unit0: Summit XL Intro
Unit 1: Unit 1:Set Indoor Navigation Stack
Unit1: Set Indoor Navigation Stack
Unit 2: Unit 2:Set Outdoors Navigation
Unit2: Set Outdoors Navigation
Unit 3: Unit 3: Detectand localise person
Unit3: Detect and localise person
Unit 4: Patrolewith Summit XL Micro Project
Patrolewith Summit XL Micro Project
Unit 5: I havefinished, now what?
Ihave finished, now what?
MASTERING WITHROS: JACKAL
Learnhow to create real world applications for a real robot. In this case Jackalrobot from ClearPathRobotics.
Abrief summary
Learnhow to create real world applications for a real robot. In this case Jackalrobot from ClearPathRobotics.
Whatyou will learn
1. How toset up the navigation stack to make it navigate in an indoor environment,generating maps by its own.
2. How tocreate a program to navigate in outdoors environments through GPS data.
3. How todetect persons with the laser sensor.
4. How todetect person with its RGB stereo camera.
5. How togenerate waypoints and make jackal patrole.
6. Use theStereoCam to generate PointCloud Data
7. Createa reactive programs based on all previously mentioned and create a patrolingprogram that reacts to person detections.
Unit 0: Unit 0:Introducing ClearPath Jackal Robot
IntroducingClearPath Jackal Robot
Unit 1: Unit 1:Navitaion Indoor
NavigationIndoor
Unit 2: Unit 2:Set Outdoors Navigation
SetOutdoors Navigation
Unit 3: Unit 3:Detect and localise a person
Detectand localise a person
Unit 4: Patrolwith Jackal Micro Project
Patrolwith Jackal Micro Project
Unit 5: I havefinished, now what?
Ihave finished, now what?
MASTERING WITHROS: SMART GRASPING SYSTEM
Learnhow to work with a robotic hand from Shadow Robot, including their SmartGrasping System.
Abrief summary
Withinthis Course, you are going to learn how you can start working with one of therobotic hands developed by the Shadow Robot Company, as well as how to usetheir Smart Grasping System.
Whatyou will learn
1. BasicUsage and control of a Shadow Hand.
2. How toattach a robotic hand to a manipulated arm.
3. How tocreate a MoveIt package for a manipulated robot.
4. How tointeract with the Smart Grasping System
5. How tointegrate Perception with the Smart Grasping System
Unit 1:Introduction to the Course
Introductionto the Course
Unit 2: BasicUsage
BasicUsage
Unit 3: Attach thehand to a robotic arm
Attachthe hand to a robotic arm
Unit 4: MotionPlanning with MoveIt
MotionPlanning with MoveIt
Unit 5: SmartGrasping System
SmartGrasping System
Unit 6: Perceptionand Object Recognition
Perceptionand Object Recognition
Unit 7: Project
Project
Unit 8: FinalRecommendations
FinalRecommendations
MASTERING WITHROS: TURTLEBOT3
Learnhow to work with a Turtlebot3 robot.
Abrief summary
Withinthis Course, you are going to learn how you can start working with a Turtlebot3robot using its both versions, Burger and Waffle.
Whatyou will learn
1. BasicUsage and control of the Turtlebot3 robot.
2. How toperform Navigation with Turtlebot3.
3. Followa line with Turtlebot3.
4. ObjectRecognition with Turtlebot3
5. MotionPlanning in Moveit with Turtlebot3
Unit 1:Introduction to the Course
Abrief introduction to the Course, including a demo.
Unit 2: BasicUsage
BasicConcepts and Usage of the Turtlebot3 robot
Unit 3: Navigationwith Burger
Howto make Turtlebot3 robot navigate
Unit 4: Follow aline
Howto create a script in order to make Turtlebot3 follow a line in the floor
Unit 5: BlobTracking
Blobtracking with RGBD camera
Unit 6: ObjectRecognition
Detectobjects with RGBD camera
Unit 7: MotionPlanning with MoveIt
Howto perform Motion Planning with MoveIt and the Open Simulator arm
Unit 8: ProjectPart 1
1stpart of the Project, involving Navigation
Unit 9: ProjectPart 2
2ndpart of the project, involving Motion Planning
Unit 10: FinalRecommendations
Whatto do after finishing the course
MASTERING WITHROS: TIAGO
Learnhow to work with a TIAGo robot from PAL Robotics.
Abrief summary
Withinthis Course, you are going to learn how you can start working with a TIAGorobot from PAL Robotics.
Whatyou will learn
1. Controlof TIAGos joints.
2. Navigationwith TIAGo.
3. MotionPlanning with MoveIt!
4. Perceptionwith OpenCV
5. Perceptionwith PCL
Unit 1:Introduction to the Course
Abrief introduction to the Course, including a demo.
Unit 2: Control
Howto control the different joints of TIAGo robot
Unit 3: Navigation
Howto Navigate in indoor environments with TIAGo robot
Unit 4: MotionPlanning with MoveIt: Part 1
MotionPlanning with MoveIt and TIAGo
Unit 5: MotionPlanning with MoveIt: Part 2
MotionPlanning with Octomap
Unit 6: MotionPlanning with MoveIt: Part 3
Executea Pick and Place task with TIAGo
Unit 7: Perceptionwith OpenCV
Howto perform Perception with TIAGo using the OpenCV library
Unit 8: Perceptionwith PCL
Howto perform Perception with TIAGo using the PCL library
Unit 9: MicroProject
AMicro Project to apply the knowledge acquired during the course
Unit 10: FinalRecommendations
Whatto do after finishing the Course
ROS PROJECTS:TURTLEBOT3
Thisis a ROS Project where you will have to apply different ROS knowledge in orderto solve all the exercises.
Abrief summary
Thisis a full ROS Project where you will have to apply different ROS concepts inorder to solve all the exercises that are presented. This project is based onthe Turtlebot3 robot.
Whatyou will need for the project
1. BasicROS knowledge
2. BasicPython knowledge
3. ROSNavigation knowledge
4. ROSPerception basic knowledge (Object Recognition)
5. ROSManipulation knowledge (MoveIt and Python API)
Unit 2: Part 1:Navigation
Makethe Turtlebot3 robot navigate applying ROS Navigation concepts
Unit 3: Part 2:Perception
Makethe Turtlebot3 robot be able to detect objects applying some ROS Perceptionconcepts
Unit 4: Part 3:Motion Planning
Makethe Open Manipulator arm perform motions applying some ROS ManipulationConcepts
PROGRAMMING DRONESWITH ROS
Inthis Course, you are going to learn all the basics you need in order to startprogramming autnomous drones.
Abrief summary
Inthis Course, you are going to learn all the basics you need in order to startprogramming autnomous drones. You are going to use a Parrot AR Drone.
1. Whatyou will learn
2. BasicControl of a drone.
3. Droneexploration
4. DroneNavigation
5. SimulationIn The Loop
Unit 1:Introduction to the Course
Abrief introduction to the Course, including a demo.
Unit 2: BasicControl of a drone
Our6th ROS Summer School took place at the Aachen UAS from 14th August - 25thAugust, 2017.
The ROS Summer Schoolcovered common topics regarding mobile robotics:
1. Introductionto Mobile Robotics
2. ROSFile System
3. ROSCommunication
4. Hardwareand Sensors
5. ROSSerialand Teleoperation
6. ImageProcessing with OpenCV & ROS
7. LandmarkDetection
8. Localizationand Navigation
9. Mapping
10. Introductionto SLAM Algorithms
11. Participationat Urban Challenge Competition
Visitto Paris, France
Weused the Middleware ROS (Robot Operating System) as standard Operating Systemfor Robots. After having learnt the theory all topics were experienced on realhardware using our mobile robots developed at the Aachen UAS. In the end we hada competition where participants had to use their skills to program the robotto drive around a course.
Agendaof the 6. ROS Summer School, 14th-25th August, 2017:
Monday,August 14th: ROS-Demo / Show, welcome BBQ
Tuesday,August 15th: ROS Basics: Navigating in Linux and ROS file system
Wednesday,August 16th: ROS Basics: ROS internal communication
Thursday,August 17th: Hardware interfaces, Transforms in ROS
Friday,August 18th: Introduction to GAZEBO simulator, AR tag recognition
Saturday,August 19th: Day trip to Paris (France)
Sunday,August 20th: Day at leisure
Monday,August 21st: Localization & Mapping
Tuesday,August 22nd: ROS control, Path planning
Wednesday,August 23rd: Industrial exhibition
Thursday,August 24th: Exam, free hacking
Friday,August 25th: Free hacking, competition, farewell BBQ
Additionally,we offer excursions during the week to explore Aachen and other nearby cities(e.g. Cologne, Maastricht or Bonn).
Option:UAV Workshop on August 26-27th, 2017
Saturday,August 26th: Basic principles of UAV design, components and functions, examplesetup of a multicopter, first flight setup guide
Sunday,August 27th: Flight modes, GPS based behaviours, Interfacing with ROS, AR_tagsand UAVs, autonomous flying
Programming forRobotics - ROS
Maincontent
Abstract:This course gives an introduction to the Robot Operating System (ROS) includingmany of the available tools that are commonly used in robotics. With the helpof different examples, the course should provide a good starting point forstudents to work with robots. They learn how to create software includingsimulation, to interface sensors and actuators, and to integrate controlalgorithms.
Objective:
1. ROSarchitecture: Master, nodes, topics, messages, services, parameters and actions
2. Consolecommands: Navigating and analyzing the ROS system and the catkin workspace
3. CreatingROS packages: Structure, launch-files, and best practices
4. ROS C++client library (roscpp): Creating your own ROS C++ programs
5. Simulatingwith ROS: Gazebo simulator, robot models (URDF) and simulation environments(SDF)
6. Workingwith visualizations (RViz) and user interface tools (rqt)
7. InsideROS: TF transformation system, time, bags
Content:This course consists of a guided tutorial and exercises with increasing levelof difficulty when working with an autonomous robot. You learn how to setupsuch a system from scratch using ROS, how to interface the individual sensorsand actuators, and finally how to implement first closed loop control systems.
Coursedates
Location:HG G1
Time:08.15-12.00
Dates:20.2.2017, 23.2.2017, 24.2.2017, 27.2.2017, 2.3.2017
Preparationbefore the course
Becausethe course will start already on the first day using ROS and Ubuntu, we expectyou to prepare your Laptop with a working environment before the course. Duringthe course, we will work with Ubuntu 14.04 and ROS Indigo Igloo. We highlyrecommend you to use a virtual machine and the provided image that alreadycontains a preinstalled environment with the following software:
Ubuntu14.04
ROSIndigo Igloo
EclipseNeon
Catkincommandline tools
Terminator
Git
Installvirtual machine
Torun the provided image you need the VMware Workstation 12 Pro (Windows, Linux)or VMware Fusion 8 (Mac OS X). This software can be ordered on the ETH Zurich’sIT Shop: https://idesnx.ethz.ch/
Pleasefollow the given instructions to download and install the software from VMware.
Downloadimage
Downloadthe complete folder “Ubuntu ROS-Course” from polybox:https://polybox.ethz.ch/index.php/s/kPQFsNrpDinWQJL
Werecommend you to have at least 20GB of available memory on your computer to runthe virtual machine.
Startup virtual machine
OpenVMware Workstation
Openfile Ubuntu ROS-Course.vmx in the downloaded folder Ubuntu ROS-Course
Startvirtual machine with “Power on this virtual machine”
Tologin under Ubuntu use the provided account ROS Course:
User:student
Password:Ros.2017
Coursematerial
VideoRecording of the Lectures
Topics Material
ROSarchitecture & philosophy
ROSmaster, nodes, and topics
Consolecommands
Catkinworkspace and build system
Launch-files
Gazebosimulator
Videorecording
Lecture1 (PDF, 3.2 MB)
Updated22.02.2017
Exercise1 (PDF, 290 KB)
Updated22.02.2017
ROSpackage structure
Integrationand programming with Eclipse
ROSC++ client library (roscpp)
ROSsubscribers and publishers
ROSparameter server
RVizvisualization
Videorecording
Lecture2 (PDF, 4.1 MB)
Updated24.02.2017
Exercise2 (PDF, 210 KB)
Updated22.02.2017
HuskyHighlevel Controller Template (ZIP, 3 KB)
Updated22.02.2017
TFTransformation System
rqtUser Interface
Robotmodels (URDF)
Simulationdescriptions (SDF)
Videorecording
Lecture3 (PDF, 5.5 MB)
Updated24.02.2017
Exercise3 (PDF, 218 KB)
Updated01.03.2017
ROSWorlds (ZIP, 1 KB)
Updated13.02.2017
ROSservices
ROSactions (actionlib)
ROStime
ROSbags
Debuggingstrategies
Videorecording
Lecture4 (PDF, 966 KB)
Updated26.02.2017
Exercise4 (PDF, 477 KB)
Updated02.03.2017
ROSBag (BAG, 158.9 MB)
Updated13.02.2017
Casestudy: Using ROS in complex real-world applications
Casestudy video recording
Casestudy slides (click on download)
Exercise5 (PDF, 145 KB)
Updated01.03.2017
Settingup a developer's PC (after the course)
Ifyou will later work on a project involving programming with ROS under Linux, werecommend a native installation (not recommended for this course). You caninstall the same installation as you found on the virtual machine with theseinstructions (PDF, 77 KB).
JustinHuang edited this page on 20 May · 18 revisions
Tutorials
C++crash course
ROSweb interfaces with Polymer
Touchscreeninterfaces
USBscale
ROSarchitectural tips
Simulatingpoint cloud locations
Controllingnavigation speed
Clonethis wiki locally
https://github.com/cse481sp17/cse481c.wiki.git
Clone in Desktop
Welcometo CSE 481C, Spring 2017! A list of labs for the class i