Cartographer原始碼閱讀(9):圖優化的前端——閉環檢測
約束計算
閉環檢測的策略:搜尋閉環,通過匹配檢測是否是閉環,採用了分支定界法。
前已經述及PoseGraph的內容,此處繼續。位姿圖類定義了pose_graph::ConstraintBuilder constraint_builder_物件。
1.ConstraintBuilder類圖
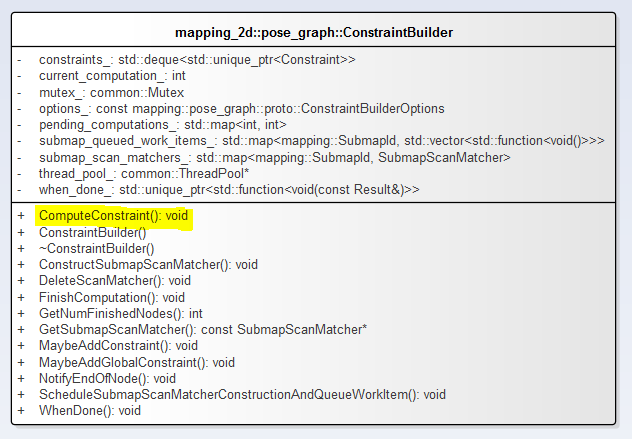
定義了SubmapScanMatcher的鍵值對。
1 // Map of already constructed scan matchers by 'submap_id'. 2 std::map<mapping::SubmapId, SubmapScanMatcher> submap_scan_matchers_ GUARDED_BY(mutex_);
SubmapScanMatcher結構體定義如下:
1 struct SubmapScanMatcher 2 { 3 const ProbabilityGrid* probability_grid; 4 std::unique_ptr<scan_matching::FastCorrelativeScanMatcher> 5 fast_correlative_scan_matcher; 6 };
注意ConstraintBuilder::ComputeConstraint方法,MaybeAddConstraint和MaybeAddGlobalConstraint都呼叫了該方法。
1 void ConstraintBuilder::ComputeConstraint( 2 const mapping::SubmapId& submap_id, const Submap* const submap, 3 const mapping::NodeId& node_id, bool match_full_submap, 4 const mapping::TrajectoryNode::Data* const constant_data, 5 const transform::Rigid2d& initial_relative_pose,6 std::unique_ptr<ConstraintBuilder::Constraint>* constraint) { 7 const transform::Rigid2d initial_pose = 8 ComputeSubmapPose(*submap) * initial_relative_pose; 9 const SubmapScanMatcher* const submap_scan_matcher = 10 GetSubmapScanMatcher(submap_id); 11 12 // The 'constraint_transform' (submap i <- node j) is computed from: 13 // - a 'filtered_gravity_aligned_point_cloud' in node j, 14 // - the initial guess 'initial_pose' for (map <- node j), 15 // - the result 'pose_estimate' of Match() (map <- node j). 16 // - the ComputeSubmapPose() (map <- submap i) 17 float score = 0.; 18 transform::Rigid2d pose_estimate = transform::Rigid2d::Identity(); 19 20 // Compute 'pose_estimate' in three stages: 21 // 1. Fast estimate using the fast correlative scan matcher. 22 // 2. Prune if the score is too low. 23 // 3. Refine. 24 if (match_full_submap) { 25 if (submap_scan_matcher->fast_correlative_scan_matcher->MatchFullSubmap( 26 constant_data->filtered_gravity_aligned_point_cloud, 27 options_.global_localization_min_score(), &score, &pose_estimate)) { 28 CHECK_GT(score, options_.global_localization_min_score()); 29 CHECK_GE(node_id.trajectory_id, 0); 30 CHECK_GE(submap_id.trajectory_id, 0); 31 } else { 32 return; 33 } 34 } else { 35 if (submap_scan_matcher->fast_correlative_scan_matcher->Match( 36 initial_pose, constant_data->filtered_gravity_aligned_point_cloud, 37 options_.min_score(), &score, &pose_estimate)) { 38 // We've reported a successful local match. 39 CHECK_GT(score, options_.min_score()); 40 } else { 41 return; 42 } 43 } 44 { 45 common::MutexLocker locker(&mutex_); 46 score_histogram_.Add(score); 47 } 48 49 // Use the CSM estimate as both the initial and previous pose. This has the 50 // effect that, in the absence of better information, we prefer the original 51 // CSM estimate. 52 ceres::Solver::Summary unused_summary; 53 ceres_scan_matcher_.Match(pose_estimate.translation(), pose_estimate, 54 constant_data->filtered_gravity_aligned_point_cloud, 55 *submap_scan_matcher->probability_grid, 56 &pose_estimate, &unused_summary); 57 58 const transform::Rigid2d constraint_transform = 59 ComputeSubmapPose(*submap).inverse() * pose_estimate; 60 constraint->reset(new Constraint{submap_id, 61 node_id, 62 {transform::Embed3D(constraint_transform), 63 options_.loop_closure_translation_weight(), 64 options_.loop_closure_rotation_weight()}, 65 Constraint::INTER_SUBMAP}); 66 67 if (options_.log_matches()) { 68 std::ostringstream info; 69 info << "Node " << node_id << " with " 70 << constant_data->filtered_gravity_aligned_point_cloud.size() 71 << " points on submap " << submap_id << std::fixed; 72 if (match_full_submap) { 73 info << " matches"; 74 } else { 75 const transform::Rigid2d difference = 76 initial_pose.inverse() * pose_estimate; 77 info << " differs by translation " << std::setprecision(2) 78 << difference.translation().norm() << " rotation " 79 << std::setprecision(3) << std::abs(difference.normalized_angle()); 80 } 81 info << " with score " << std::setprecision(1) << 100. * score << "%."; 82 LOG(INFO) << info.str(); 83 } 84 }
這裡出現了scan_matching::FastCorrelativeScanMatcher,另一種掃描匹配的方法。論文中介紹的分支定界法就在這個類中實現。
以上FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::Match和FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::MatchFullSubmap方法都呼叫了FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::MatchWithSearchParameters方法。
FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::MatchWithSearchParameters呼叫了FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::BranchAndBound方法。
|
Tips:總結一下出現的幾種掃描匹配的方法? RealTimeCorrelativeScanMatcher FastCorrelativeScanMatcher |
1 bool FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::MatchWithSearchParameters( 2 SearchParameters search_parameters, 3 const transform::Rigid2d& initial_pose_estimate, 4 const sensor::PointCloud& point_cloud, float min_score, float* score, 5 transform::Rigid2d* pose_estimate) const 6 { 7 CHECK_NOTNULL(score); 8 CHECK_NOTNULL(pose_estimate); 9 10 const Eigen::Rotation2Dd initial_rotation = initial_pose_estimate.rotation(); 11 const sensor::PointCloud rotated_point_cloud = sensor::TransformPointCloud( 12 point_cloud, 13 transform::Rigid3f::Rotation(Eigen::AngleAxisf( 14 initial_rotation.cast<float>().angle(), Eigen::Vector3f::UnitZ()))); 15 const std::vector<sensor::PointCloud> rotated_scans = 16 GenerateRotatedScans(rotated_point_cloud, search_parameters); 17 const std::vector<DiscreteScan> discrete_scans = DiscretizeScans( 18 limits_, rotated_scans, 19 Eigen::Translation2f(initial_pose_estimate.translation().x(), 20 initial_pose_estimate.translation().y())); 21 search_parameters.ShrinkToFit(discrete_scans, limits_.cell_limits()); 22 23 const std::vector<Candidate> lowest_resolution_candidates = 24 ComputeLowestResolutionCandidates(discrete_scans, search_parameters); 25 const Candidate best_candidate = BranchAndBound( 26 discrete_scans, search_parameters, lowest_resolution_candidates, 27 precomputation_grid_stack_->max_depth(), min_score);//分支定界法 28 if (best_candidate.score > min_score) { 29 *score = best_candidate.score; 30 *pose_estimate = transform::Rigid2d( 31 {initial_pose_estimate.translation().x() + best_candidate.x, 32 initial_pose_estimate.translation().y() + best_candidate.y}, 33 initial_rotation * Eigen::Rotation2Dd(best_candidate.orientation)); 34 return true; 35 } 36 return false; 37 }
2.分支定界法
FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::BranchAndBound,......
1 Candidate FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::BranchAndBound( 2 const std::vector<DiscreteScan>& discrete_scans, 3 const SearchParameters& search_parameters, 4 const std::vector<Candidate>& candidates, const int candidate_depth, 5 float min_score) const 6 { 7 if (candidate_depth == 0) 8 { 9 // Return the best candidate. 10 return *candidates.begin(); 11 } 12 13 Candidate best_high_resolution_candidate(0, 0, 0, search_parameters); 14 best_high_resolution_candidate.score = min_score; 15 for (const Candidate& candidate : candidates) 16 { 17 if (candidate.score <= min_score) { break; } 18 std::vector<Candidate> higher_resolution_candidates; 19 const int half_width = 1 << (candidate_depth - 1); 20 for (int x_offset : {0, half_width}) 21 { 22 if (candidate.x_index_offset + x_offset > 23 search_parameters.linear_bounds[candidate.scan_index].max_x) { 24 break; 25 } 26 for (int y_offset : {0, half_width}) { 27 if (candidate.y_index_offset + y_offset > 28 search_parameters.linear_bounds[candidate.scan_index].max_y) { 29 break; 30 } 31 higher_resolution_candidates.emplace_back( 32 candidate.scan_index, candidate.x_index_offset + x_offset, 33 candidate.y_index_offset + y_offset, search_parameters); 34 } 35 } 36 ScoreCandidates(precomputation_grid_stack_->Get(candidate_depth - 1), 37 discrete_scans, search_parameters, 38 &higher_resolution_candidates); 39 best_high_resolution_candidate = std::max( 40 best_high_resolution_candidate, 41 BranchAndBound(discrete_scans, search_parameters, 42 higher_resolution_candidates, candidate_depth - 1, 43 best_high_resolution_candidate.score)); 44 } 45 return best_high_resolution_candidate; 46 }
相關推薦
Cartographer原始碼閱讀(9):圖優化的前端——閉環檢測
約束計算 閉環檢測的策略:搜尋閉環,通過匹配檢測是否是閉環,採用了分支定界法。 前已經述及PoseGraph的內容,此處繼續。位姿圖類定義了pose_graph::ConstraintBuilder constraint_builder_物件。 1.ConstraintBuilder類圖 定義了S
Cartographer源碼閱讀(8):圖優化的前端——閉環檢測
tips 閱讀 psc style con 總結 rap mapi tex 約束計算 閉環檢測的策略:搜索閉環 分支定界法 通過匹配檢測是否是閉環 前已經述及PoseGraph的內容,此處繼續。位姿圖類定義了pose_graph::ConstraintBuilder
Cartographer原始碼閱讀(5):PoseGraph位姿圖
PoseGraph位姿圖 mapping2D::PoseGraph類的註釋: // Implements the loop closure method called Sparse Pose Adjustment (SPA) from// Konolige, Kurt, et al. "E
Cartographer原始碼閱讀(8):imu_tracker
1 /* 2 * Copyright 2016 The Cartographer Authors 3 * 4 * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); 5 * you may not use
Cartographer原始碼閱讀(1):程式入口
1 [email protected]:~$ sudo apt-get install kdevelop 2 [sudo] password for yhexie: 3 Reading package lists... Done 4 Building dependency
Cartographer原始碼閱讀(2):Node和MapBuilder物件
上文提到特別注意map_builder_bridge_.AddTrajectory(x,x),檢視其中的程式碼。兩點: 首先是map_builder_.AddTrajectoryBuilder(...),呼叫了map_builder_物件的方法。其次是sensor_bridges_鍵值對的賦值。
Cartographer原始碼閱讀(3):程式邏輯結構
Cartographer早期的程式碼在進行3d製圖的時候使用了UKF方法,檢視現有的tag版本,可以轉到0.1.0和0.2.0檢視,包含kalman_filter資料夾。 資料夾中的pose_tracker類檔案在mapping_3d的檔案加下有kalman_local_trajectory_builder
Cartographer原始碼閱讀(7):軌跡推算和位姿推算的原理
其實也就是包括兩個方面的內容:類似於運動模型的位姿估計和掃描匹配,因為需要計算速度,所以時間就有必要了! 1. PoseExtrapolator解決了IMU資料、里程計和位姿資訊進行融合的問題。 該類定義了三個佇列。 1 std::deque<TimedPose> timed_pose_
Cartographer原始碼閱讀(4):Node和MapBuilder物件2
MapBuilder的成員變數sensor::Collator sensor_collator_; 再次閱讀MapBuilder::AddTrajectoryBuilder方法。首先構造了mapping::GlobalTrajectoryBuilder例項,接著作為引數構造了CollatedTraj
Cartographer原始碼閱讀(6):LocalTrajectoryBuilder和PoseExtrapolator
LocalTrajectoryBuilder意思是區域性軌跡的構建,下面的類圖中方法的引數沒有畫進去。 注意其中的三個類:PoseExtrapolator類,RealTimeCorrelativeScanMatcher類和CeresScanMatcher類。 (1)PoseExtrapolator類(
論文閱讀9:在自適應輔導系統中保持和測量ZPD
參考論文:Toward Measuring and Maintaining the Zone of Proximal Development in Adaptive Instructional Systems 圖片出不來,請參見我的知乎連線:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/
Spring4.3.12原始碼閱讀系列:1-環境搭建
學習任務 近期想增加部分原始碼閱讀經驗,提高自己在造輪子方面的實力,增長些在設計模式應用方面的編碼能力,以及懷著向大佬們膜拜的心情,開始有計劃地閱讀Spring原始碼 前期準備 以下幾項準備事項,算是基本的日常開發環境,就算沒有,也是動動手很快安
Tensorflow object detection API 原始碼閱讀筆記:RPN
Update: 建議先看從程式設計實現角度學習Faster R-CNN,比較直觀。這裡由於原始碼抽象程度較高,顯得比較混亂。 faster_rcnn_meta_arch.py中這兩個對應知乎文章中RPN包含的3*3和1*1卷積: rpn_box_pred
資料結構實驗9:圖的相關操作(待填坑)
實驗9 姓名: 學號:班級: 8.1 實驗目的 (1) 掌握圖的基本概念。 (2) 掌握圖的儲存結構的設計與實現,基本運算的實現。 (3) 熟練掌握圖的兩種遍歷演算法、遍歷生成樹及遍歷演算法的應用。 8.2 實驗任務 分別設計圖(網)的鄰接矩陣、鄰接表儲存結構,編寫演算法實
原始碼閱讀系列:為什麼要閱讀原始碼?
一.為什麼要閱讀程式碼 養成閱讀高品質程式碼的習慣,可以提高編寫程式碼的能力。 電腦科學是一門實踐性很強的學科,很多內容在書本上根本學不到。就拿專案的組織來說,沒有什麼書籍專門論述應該如何組織與管理專案的目錄結構,因為這本身就是一種見仁見智的活動,要
Tensorflow object detection API 原始碼閱讀筆記:架構
在之前的博文中介紹過用tf提供的預訓練模型進行inference,非常簡單。這裡我們深入原始碼,瞭解檢測API的程式碼架構,每個部分的深入閱讀留待後續。 '''構建自己模型的介面是虛基類DetectionModel,具體有5個抽象函式需要實現。 ''' o
Tensorflow object detection API 原始碼閱讀筆記:RFCN
有了前面Faster R-CNN的基礎,RFCN就比較容易了。 """object_detection/meta_architectures/rfcn_meta_arch.py The R-FCN
Ethzasl MSF原始碼閱讀(1):程式入口和主題訂閱
Ethz的Stephen Weiss的工作,是一個IMU鬆耦合的方法。 1.程式入口:ethzasl_msf\msf_updates\src\pose_msf\main.cpp 1 #include "pose_sensormanager.h" 2 3 int main(int argc,
Ethzasl MSF原始碼閱讀(2):百川匯海
這裡有個感覺,就是百川匯海。即IMU資料和相機的訊息資料都彙集到msf_core進行處理。接上一篇, 1. 檢視IMUHandler_ROS::IMUCallback和IMUHandler_ROS::StateCallback回撥函式。 MUHandler_ROS::IMUCallback,傳入的訊息s
Ethzasl MSF原始碼閱讀(3):MSF_Core和PoseMeasurement
1.MSF_Core的三個函式:ProcessIMU、ProcessExternallyPropagatedState和AddMeasurement MSF_Core維護了狀態佇列和觀測值佇列,這裡需要結合論文思考這個狀態佇列的作用。 ProcessIMU方法: 1 template<
