spring-session簡介、使用及實現原理
一:spring-session 介紹
1.簡介
session一直都是我們做叢集時需要解決的一個難題,過去我們可以從serlvet容器上解決,比如開源servlet容器-tomcat提供的tomcat-redis-session-manager、memcached-session-manager。
或者通過nginx之類的負載均衡做ip_hash,路由到特定的伺服器上..
但是這兩種辦法都存在弊端。
spring-session是spring旗下的一個專案,把servlet容器實現的httpSession替換為spring-session,專注於解決 session管理問題。可簡單快速且無縫的整合到我們的應用中。
2.支援功能
1)輕易把session儲存到第三方儲存容器,框架提供了redis、jvm的map、mongo、gemfire、hazelcast、jdbc等多種儲存session的容器的方式。
2)同一個瀏覽器同一個網站,支援多個session問題。
3)Restful API,不依賴於cookie。可通過header來傳遞jessionID
4)WebSocket和spring-session結合,同步生命週期管理。
<context:annotation-config/>
/** 初始化一切spring-session準備,且把springSessionFilter放入IOC **/ 3)xml方式配置 web.xml ,配置 springSessionFilter到 filter chain中
<filter 二:spring-session框架內部剖析
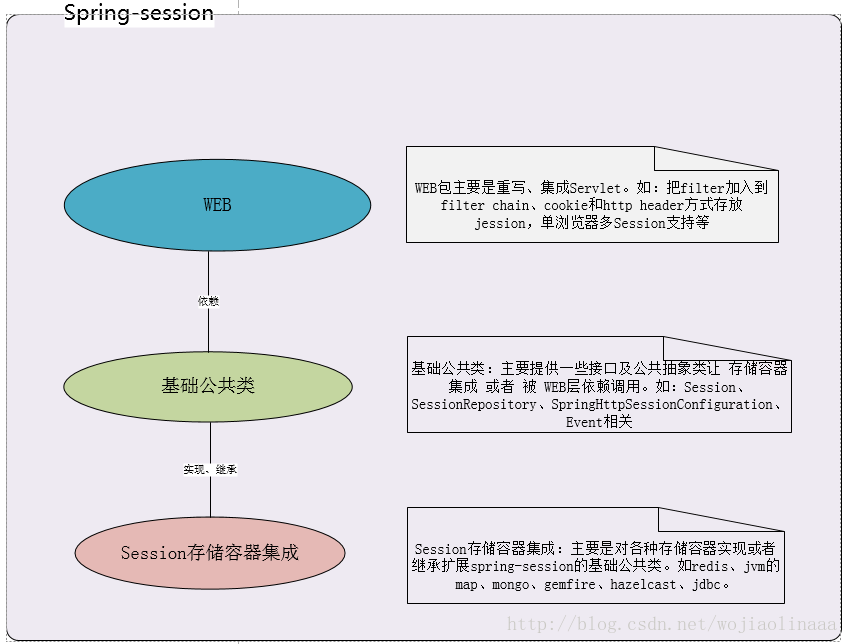
1.框架高層抽象結構圖
2.spring-session重寫servlet request 及 redis實現儲存相關問題
spring-session無縫替換應用伺服器的request大概原理是:
1.自定義個Filter,實現doFilter方法
2.繼承 HttpServletRequestWrapper 、HttpServletResponseWrapper 類,重寫getSession等相關方法(在這些方法裡呼叫相關的 session儲存容器操作類)。
3.在 第一步的doFilter中,new 第二步 自定義的request和response的類。並把它們分別傳遞 到 過濾器鏈
4.把該filter配置到 過濾器鏈的第一個位置上
/** 這個類是spring-session的1.30原始碼,也是實現上面第一到第三步的關鍵類 **/
public class SessionRepositoryFilter<S extends ExpiringSession>
extends OncePerRequestFilter {
/** session儲存容器介面,redis、mongoDB、genfire等資料庫都是實現該介面 **/
private final SessionRepository<S> sessionRepository;
private ServletContext servletContext;
/**
sessionID的傳遞方式介面。目前spring-session自帶兩個實現類
1.cookie方式 :CookieHttpSessionStrategy
2.http header 方式:HeaderHttpSessionStrategy
當然,我們也可以自定義其他方式。
**/
private MultiHttpSessionStrategy httpSessionStrategy = new CookieHttpSessionStrategy();
public SessionRepositoryFilter(SessionRepository<S> sessionRepository) {
if (sessionRepository == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("sessionRepository cannot be null");
}
this.sessionRepository = sessionRepository;
}
public void setHttpSessionStrategy(HttpSessionStrategy httpSessionStrategy) {
if (httpSessionStrategy == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("httpSessionStrategy cannot be null");
}
/**
通過前面的spring-session功能介紹,我們知道spring-session可以支援單瀏覽器多
session, 就是通過MultiHttpSessionStrategyAdapter來實現的。
每個瀏覽器擁有一個sessionID,但是這個sessionID擁有多個別名(根據瀏覽器的tab)。如:
別名1 sessionID
別名2 sessionID
...
而這個別名通過url來傳遞,這就是單瀏覽器多session原理了
**/
this.httpSessionStrategy = new MultiHttpSessionStrategyAdapter(
httpSessionStrategy);
}
public void setHttpSessionStrategy(MultiHttpSessionStrategy httpSessionStrategy) {
if (httpSessionStrategy == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("httpSessionStrategy cannot be null");
}
this.httpSessionStrategy = httpSessionStrategy;
}
/**
該方法相當於重寫了doFilter,只是spring-session又做了多一層封裝。
在這個方法裡建立自定義的 request和response,然後傳遞到過濾器鏈filterChain
**/
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
request.setAttribute(SESSION_REPOSITORY_ATTR, this.sessionRepository);
/**
spring-session重寫的ServletRequest。這個類繼承了HttpServletRequestWrapper
**/
SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper wrappedRequest = new SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper(
request, response, this.servletContext);
SessionRepositoryResponseWrapper wrappedResponse = new SessionRepositoryResponseWrapper(
wrappedRequest, response);
HttpServletRequest strategyRequest = this.httpSessionStrategy
.wrapRequest(wrappedRequest, wrappedResponse);
HttpServletResponse strategyResponse = this.httpSessionStrategy
.wrapResponse(wrappedRequest, wrappedResponse);
try {
/**
傳遞自定義 request和response到鏈中,想象下如果
該spring-sessionFilter位於過濾器鏈的第一個,那麼後續的Filter,
以及到達最後的控制層所獲取的 request和response,是不是就是我們自定義的了?
**/
filterChain.doFilter(strategyRequest, strategyResponse);
}
finally {
wrappedRequest.commitSession();
}
}
public void setServletContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
this.servletContext = servletContext;
}
/**
這個就是Servlet response的重寫類了
*/
private final class SessionRepositoryResponseWrapper
extends OnCommittedResponseWrapper {
private final SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper request;
SessionRepositoryResponseWrapper(SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
super(response);
if (request == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("request cannot be null");
}
this.request = request;
}
/**
這步是持久化session到儲存容器,我們可能會在一個控制層裡多次呼叫session的操作方法
如果我們每次對session的操作都持久化到儲存容器,必定會帶來效能的影響。比如redis
所以我們可以在整個控制層執行完畢了,response返回資訊到瀏覽器時,才持久化session
**/
@Override
protected void onResponseCommitted() {
this.request.commitSession();
}
}
/**
spring-session 的request重寫類,這幾乎是最重要的一個重寫類。裡面重寫了獲取getSession,Session等方法以及類
*/
private final class SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper
extends HttpServletRequestWrapper {
private Boolean requestedSessionIdValid;
private boolean requestedSessionInvalidated;
private final HttpServletResponse response;
private final ServletContext servletContext;
private SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, ServletContext servletContext) {
super(request);
this.response = response;
this.servletContext = servletContext;
}
/**
* Uses the HttpSessionStrategy to write the session id to the response and
* persist the Session.
*/
private void commitSession() {
HttpSessionWrapper wrappedSession = getCurrentSession();
if (wrappedSession == null) {
// session失效,刪除cookie或者header
if (isInvalidateClientSession()) {
SessionRepositoryFilter.this.httpSessionStrategy
.onInvalidateSession(this, this.response);
}
}
else {
S session = wrappedSession.getSession();
SessionRepositoryFilter.this.sessionRepository.save(session);
if (!isRequestedSessionIdValid()
|| !session.getId().equals(getRequestedSessionId())) {
// 把cookie或者header寫回給瀏覽器儲存
SessionRepositoryFilter.this.httpSessionStrategy.onNewSession(session,
this, this.response);
}
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private HttpSessionWrapper getCurrentSession() {
return (HttpSessionWrapper) getAttribute(CURRENT_SESSION_ATTR);
}
private void setCurrentSession(HttpSessionWrapper currentSession) {
if (currentSession == null) {
removeAttribute(CURRENT_SESSION_ATTR);
}
else {
setAttribute(CURRENT_SESSION_ATTR, currentSession);
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
public String changeSessionId() {
HttpSession session = getSession(false);
if (session == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot change session ID. There is no session associated with this request.");
}
// eagerly get session attributes in case implementation lazily loads them
Map<String, Object> attrs = new HashMap<String, Object>();
Enumeration<String> iAttrNames = session.getAttributeNames();
while (iAttrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = iAttrNames.nextElement();
Object value = session.getAttribute(attrName);
attrs.put(attrName, value);
}
SessionRepositoryFilter.this.sessionRepository.delete(session.getId());
HttpSessionWrapper original = getCurrentSession();
setCurrentSession(null);
HttpSessionWrapper newSession = getSession();
original.setSession(newSession.getSession());
newSession.setMaxInactiveInterval(session.getMaxInactiveInterval());
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> attr : attrs.entrySet()) {
String attrName = attr.getKey();
Object attrValue = attr.getValue();
newSession.setAttribute(attrName, attrValue);
}
return newSession.getId();
}
// 判斷session是否有效
@Override
public boolean isRequestedSessionIdValid() {
if (this.requestedSessionIdValid == null) {
String sessionId = getRequestedSessionId();
S session = sessionId == null ? null : getSession(sessionId);
return isRequestedSessionIdValid(session);
}
return this.requestedSessionIdValid;
}
private boolean isRequestedSessionIdValid(S session) {
if (this.requestedSessionIdValid == null) {
this.requestedSessionIdValid = session != null;
}
return this.requestedSessionIdValid;
}
private boolean isInvalidateClientSession() {
return getCurrentSession() == null && this.requestedSessionInvalidated;
}
private S getSession(String sessionId) {
// 從session儲存容器中根據sessionID獲取session
S session = SessionRepositoryFilter.this.sessionRepository
.getSession(sessionId);
if (session == null) {
return null;
}
// 設定sesison的最後訪問時間,以防過期
session.setLastAccessedTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
return session;
}
/**
這個方法是不是很熟悉,下面還有個getSession()才更加熟悉。沒錯,就是在這裡重新獲取session方法
**/
@Override
public HttpSessionWrapper getSession(boolean create) {
//快速獲取session,可以理解為一級快取、二級快取這種關係
HttpSessionWrapper currentSession = getCurrentSession();
if (currentSession != null) {
return currentSession;
}
//從httpSessionStratge裡面根據cookie或者header獲取sessionID
String requestedSessionId = getRequestedSessionId();
if (requestedSessionId != null
&& getAttribute(INVALID_SESSION_ID_ATTR) == null) {
//從儲存容器獲取session以及設定當次初始化屬性
S session = getSession(requestedSessionId);
if (session != null) {
this.requestedSessionIdValid = true;
currentSession = new HttpSessionWrapper(session, getServletContext());
currentSession.setNew(false);
setCurrentSession(currentSession);
return currentSession;
}
else {
if (SESSION_LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
SESSION_LOGGER.debug(
"No session found by id: Caching result for getSession(false) for this HttpServletRequest.");
}
setAttribute(INVALID_SESSION_ID_ATTR, "true");
}
}
if (!create) {
return null;
}
if (SESSION_LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
SESSION_LOGGER.debug(
"A new session was created. To help you troubleshoot where the session was created we provided a StackTrace (this is not an error). You can prevent this from appearing by disabling DEBUG logging for "
+ SESSION_LOGGER_NAME,
new RuntimeException(
"For debugging purposes only (not an error)"));
}
// 如果該瀏覽器或者其他http訪問者是初次訪問伺服器,則為他建立個新的session
S session = SessionRepositoryFilter.this.sessionRepository.createSession();
session.setLastAccessedTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
currentSession = new HttpSessionWrapper(session, getServletContext());
setCurrentSession(currentSession);
return currentSession;
}
@Override
public ServletContext getServletContext() {
if (this.servletContext != null) {
return this.servletContext;
}
// Servlet 3.0+
return super.getServletContext();
}
@Override
public HttpSessionWrapper getSession() {
return getSession(true);
}
@Override
public String getRequestedSessionId() {
return SessionRepositoryFilter.this.httpSessionStrategy
.getRequestedSessionId(this);
}
/**
HttpSession的重寫類
*/
private final class HttpSessionWrapper extends ExpiringSessionHttpSession<S> {
HttpSessionWrapper(S session, ServletContext servletContext) {
super(session, servletContext);
}
@Override
public void invalidate() {
super.invalidate();
SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper.this.requestedSessionInvalidated = true;
setCurrentSession(null);
SessionRepositoryFilter.this.sessionRepository.delete(getId());
}
}
}
}Redis儲存容器實現。
主要實現儲存公共基礎類->FindByIndexNameSessionRepository ,裡面主要有根據indexName從redis中查詢session、根據sessionID對redis中的session增刪改查的方法。
關於redis的session儲存容器,實際上spring-session是有些缺陷的。比如無法做到session的過期以及銷燬的實時釋出事件,以及getCurrentSession中可能存在的一些併發問題(小問題)。但整體來說還是可用性很高的,畢竟我們自己寫一套這類框架成本很高。
以上只是針對redis session的儲存容器,其他儲存容器可能會比redis更好,比如gemfire,至少在事件釋出上是完整了(根據它實現了事件猜的)
相關推薦
spring-session簡介、使用及實現原理
一:spring-session 介紹 1.簡介 session一直都是我們做叢集時需要解決的一個難題,過去我們可以從serlvet容器上解決,比如開源servlet容器-tomcat提供的tomcat-redis-session-m
Spring 事務事件監控及實現原理
來源:https://my.oschina.net/zhangxufeng/blog/1976076 前面我們講到了Spring在進行事務邏輯織入的時候,無論是事務開始,提交或者回滾,都會觸發相應的事務事件。本文首先會使用例項進行講解Spring事務事件是如何使用的,
【dubbo基礎】dubbo學習過程、使用經驗分享及實現原理簡單介紹
multi spring配置 不同 影響 為什麽 exception 同事 sock services 一、前言 部門去年年中開始各種改造,第一步是模塊服務化,這邊初選dubbo試用在一些非重要模塊上,慢慢引入到一些稍微重要的功能上,半年時間,學習過程及線上使用遇到的些問
dubbo學習過程、使用經驗分享及實現原理簡單介紹
sum 使用 相同 應該 lib blog 組合 功能模塊 返回 一、前言 部門去年年中開始各種改造,第一步是模塊服務化,這邊初選dubbo試用在一些非重要模塊上,慢慢引入到一些稍微重要的功能上,半年時間,學習過程及線上使用遇到的些問題在此總結下。 整理這篇文章差不多花
HashMap、ConcurrentHashMap實現原理及原始碼分析
HashMap:https://www.cnblogs.com/chengxiao/p/6059914.html ConcurrentHashMap:https://blog.csdn.net/dingjianmin/article/details/79776646 遺留問
理解高併發(15).Future、Callable實現原理及用法
概述 jdk1.5推出的,使用它能帶來2個方便: 能夠獲得到執行緒執行後返回的結果 執行緒異常有效捕獲 簡單例子 輸出結果:result=hello public class ThreadLocal
JAVA集合框架的特點及實現原理簡介
1.集合框架總體架構 集合大致分為Set、List、Queue、Map四種體系,其中List,Set,Queue
TCP/IP協議的三次握手及實現原理
簡單 查找 32位 端口 包括 弱點 建立 成功 有效 TCP/IP是很多的不同的協議組成,實際上是一個協議組,TCP用戶數據報表協議(也稱作TCP傳輸控制協議,Transport Control Protocol。可靠的主機到主機層協議。這裏要先強調一下,傳輸控制協議是O
【Spring】27、JPA 實現樂觀鎖@Version註解的使用
線程並發 基礎上 nal where 本質 項目需求 得到 業務 -s 持久層使用jpa時,默認提供了一個註解@Version來實現樂觀鎖 簡單來說就是用一個version字段來充當樂觀鎖的作用。先來設計實體類 /** * Created by xujingfeng on
EJB2.0教程 詳解EJB技術及實現原理
tee nsa 普通 事情 println 配置 ransac 教程 聲明 EJB是什麽呢?EJB是一個J2EE體系中的組件.再簡單的說它是一個能夠遠程調用的javaBean.它同普通的javaBean有兩點不同.第一點,就是遠程調用.第二點,就是事務的功能,我們在EJB中
DNS簡介、DNS工作原理、DNS正反向解析的搭建、DNS主從備份、DNS子域創建
查找 art 技術分享 c51 找到 tex 文件權限 就會 查詢方式 一、DNS簡介DNS 域名系統(Domain Name System)萬維網上作為域名和IP地址相互映射的一個分布式數據庫,能夠使用戶更方便的訪問互聯網,而不用去記讓人頭疼的一大串數字。根服務器:13組
ThreadLocal的使用場景及實現原理
局部變量 運行 內部 然而 cal private 中間 pub new t 1. 什麽是ThreadLocal? 線程局部變量(通常,ThreadLocal變量是private static修飾的,此時ThreadLocal變量相當於成為了線程內部的全局變量) 2. 使用
Spring的簡介、使用特點
源碼 spa new 接口 nbsp 英文翻譯 弊端 aop 完成 Spring:英文翻譯為春天--->也是javaEE開發的春天 spring是開源的框架、輕量級的、javaEE一站式框架(對EE開發每一層都有解決方案) 主要特點:輕量級、控制反轉(IOC)、面向切
C++函式模板及實現原理
C++為我們提供了函式模板機制。所謂函式模板,實際上是建立一個通用函式,其函式型別和形參型別不具體指定,用一個虛擬的型別來代表。這個通用函式就稱為函式模板。 凡是函式體相同的函式都可以用這個模板來代替,不必定義多個函式,只需在模板中定義
springboot2整合spring-session-data-redis,實現session共享
1.新增Maven依賴 <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId> <artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
.NetCore 中介軟體之AddAuthentication服務說明及實現原理簡述
如果你使用過.NetCore開發過程序,你會很清楚,在其中我們經常會用到一些如下的程式碼 services.AddAuthentication(options => { options.DefaultAuthentic
java中代理,靜態代理,動態代理以及spring aop代理方式,實現原理統一彙總 Spring中AOP的兩種代理方式(Java動態代理和CGLIB代理)
若代理類在程式執行前就已經存在,那麼這種代理方式被成為 靜態代理 ,這種情況下的代理類通常都是我們在Java程式碼中定義的。 通常情況下, 靜態代理中的代理類和委託類會實現同一介面或是派生自相同的父類。 一、概述1. 什麼是代理我們大家都知道微商代理,簡單地說就是代替廠家賣商品,廠家“委託”代理為
Linux inotify功能及實現原理
分享一下我老師大神的人工智慧教程!零基礎,通俗易懂!http://blog.csdn.net/jiangjunshow 也歡迎大家轉載本篇文章。分享知識,造福人民,實現我們中華民族偉大復興!
Spring裡的aop實現方式和原始碼分析 java中代理,靜態代理,動態代理以及spring aop代理方式,實現原理統一彙總
使用"橫切"技術,AOP把軟體系統分為兩個部分:核心關注點和橫切關注點。業務處理的主要流程是核心關注點,與之關係不大的部分是橫切關注點。橫切關注點的一個特點是,他們經常發生在核心關注點的多處,而各處基本相似,比如許可權認證、日誌、事務。AOP的作用在於分離系統中的各種關注點,將核心關注點和橫切關注點分離開來。
Mybatis(四):MyBatis核心元件介紹原理解析和原始碼解讀 java中代理,靜態代理,動態代理以及spring aop代理方式,實現原理統一彙總
Mybatis核心成員 Configuration MyBatis所有的配置資訊都儲存在Configuration物件之中,配置檔案中的大部分配置都會儲存到該類中 SqlSession &