android佈局優化的三大標籤
1、佈局重用 <include />
- 標籤能夠重用佈局檔案,簡單的使用如下:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width=”match_parent”
android:layout_height=”match_parent”
android:background="@color/app_bg"
android:gravity="center_horizontal" - 1)
<include />標籤可以使用單獨的layout屬性,這個也是必須使用的。 - 2)可以使用其他屬性。
<include />標籤若指定了ID屬性,而你的layout也定義了ID,則你的layout的ID會被覆蓋,解決方案。 - 3)在include標籤中所有的android:layout_*都是有效的,前提是必須要寫layout_width和layout_height兩個屬性。
- 4)佈局中可以包含兩個相同的include標籤,引用時可以使用如下方法解決(參考):
View bookmarks_container_2 = findViewById(R.id.bookmarks_favourite); 2、減少檢視層級 <ViewStub />
顧名思義,就是合併、融合的意思。使用它可以有效的將某些符合條件的多餘的層級優化掉。使用merge的場合主要有兩處:
(1) 自定義View中使用,父元素儘量是FrameLayout,當然如果父元素是其他佈局,而且不是太複雜的情況下也是可以使用的
(2) Activity中的整體佈局,根元素需要是FrameLayout
下面這個例子將融合這兩種情況,來展示如何縮減佈局層次。
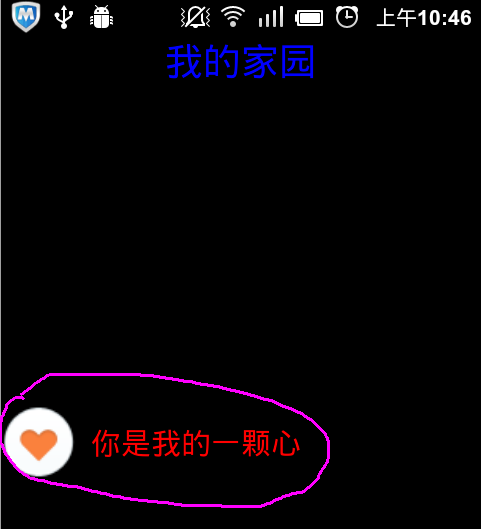
總體顯示介面如圖所示:
其中粉紅色圈住的部分為我們的自定義View。
整個介面的佈局layout_mergedemo.xml如下:
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="25sp"
android:textColor="#FF0000FF"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="我的家園"/>
<com.example.myandroiddemo.MyItemView
android:id="@+id/myitem_view"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center" />
</FrameLayout> - 自定義佈局view_item.xml如下:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/view_item_img"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:scaleType="fitXY"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/view_item_txt"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:textColor="#FFFF0000"/>
</LinearLayout> - 自定義View中使用下面來解析佈局:
public class MyItemView extends LinearLayout {
......
private void initView(Context context) {
mContext = context;
View view = LayoutInflater.from(mContext).inflate(R.layout.view_item, this, true);
mMyItemImg = (ImageView)view.findViewById(R.id.view_item_img);
mMyItemText = (TextView)view.findViewById(R.id.view_item_txt);
}
......
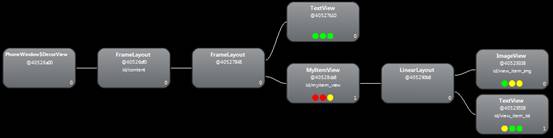
} - 整個功能開發完成之後,使用hierarchyviewer來看一下佈局層次:
我們發現簡單的一個功能竟然使用了六層佈局,包括每個Window自動新增的PhoneWindow$DecorView和FrameLayout(id/content)。明顯可以看到這個佈局存在冗餘,比如第二層和第三層的FrameLayout,比如第四層的MyItemView(LinearLayout子類)和第五層的LinearLayout,都可以縮減。
- 好了,該我們的merge標籤大顯身手了。將佈局這樣修改:
- 簡化layout_mergedemo.xml:
<merge xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="25sp"
android:textColor="#FF0000FF"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="我的家園"/>
<com.example.myandroiddemo.MyItemView
android:id="@+id/myitem_view"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center" />
</merge> - 簡化view_item.xml:
<merge xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" >
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/view_item_img"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:scaleType="fitXY"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/view_item_txt"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:textColor="#FFFF0000"/>
</merge> 因為這裡merge代替的佈局元素為LinearLayout,而不是FrameLayout,所以我們需要在自定義佈局程式碼中將LinearLayout的屬性新增上,比如垂直或者水平佈局,比如背景色等,此處設定為水平佈局:
private void initView(Context context) {
setOrientation(LinearLayout.HORIZONTAL);
……
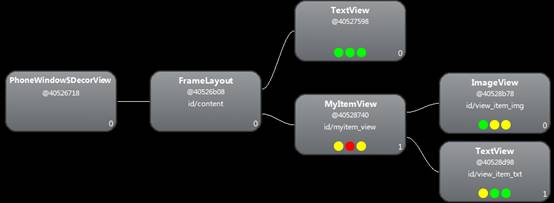
} - OK,就是這麼簡單,再來看看佈局層次吧:
哈哈,只有四層了,載入速度也明顯加快,特別是如果佈局比較複雜,子View較多的情況下,合理使用merge能大大提高程式的速度和流暢性。
但是使用merge標籤還是有一些限制的,具體有以下幾點:
(1)merge只能用在佈局XML檔案的根元素
(2)使用merge來inflate一個佈局時,必須指定一個ViewGroup作為其父元素,並且要設定inflate的attachToRoot引數為true。(參照inflate(int, ViewGroup, boolean))
(3)不能在ViewStub中使用merge標籤。最直觀的一個原因就是ViewStub的inflate方法中根本沒有attachToRoot的設定
說到這兒,merge的使用也就講完了。還想嘮叨一下做的演出專案,因為本人水平有限,並且產品提的這個顯示需求確實比較BT,所以整個專案的顯示框架做了很多巢狀,具體點就是ActivityGroup中巢狀ViewFlipper,然後再巢狀TabHost,然後再巢狀自己的Activity,大體數了一下,最多竟然有20幾層,My God!知道Android佈局設計的原則是什麼嗎?最好是10層以下,儘量不要超過15層,如果再多效能就會下降,也可能會出現問題,就是我們看到的StackOverFlow,這個專案被證實也確實在某些低端機上發生了這種錯誤,比如HTC的某某機型,OPPO的某某機型,(不要聲討我,沒有惡意貶低的意思<_>),最終我使用merge縮呀縮呀,把大部分的佈局都縮減到了15層以下,一測試,通過!
還要說一下,因為Window窗體(比如Activity)載入時會自動新增PhoneWindow$DecorView和FrameLayout(id/content)兩層佈局,所以如果我們在Activity的自定義佈局根元素中使用merge,而且想設定總體背景什麼的,可以用(id/content)將FrameLayout取出來,再設定屬性,可以這樣實現:
//setContentView(R.layout.layout_showset);
FrameLayout frameLayout = (FrameLayout)this.getWindow().getDecorView().findViewById(android.R.id.content);
frameLayout.setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.bg_repeated_main);
LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.layout_showset, frameLayout, true); 3、需要時使用 <merge />
這是什麼玩應兒呢?其實就是一個輕量級的頁面,我們通常使用它來做預載入處理,來改善頁面載入速度和提高流暢性,ViewStub本身不會佔用層級,它最終會被它指定的層級取代。
還是說說演出專案吧,還說?對了,實踐才能發現問題嘛,在哪兒發現問題就在那兒改進。由於專案中用到了比較多的動畫,而且巢狀佈局比較複雜,所以在Android低端機上進行頁面切換時候經常讓人感覺卡卡的,不怎麼流暢,因為頁面切換動畫和標題旋轉動畫是同時進行的,所以為了達到更好的體驗就需要使用一種方法,在動畫進行時儘量的減少其他操作,特別是頁面載入重繪。趕緊想辦法,起初我想先將要載入的頁面所有的元件都初始為gone顯示狀態,整個頁面只留一下載入滾動條,後來發現這是不行滴,因為在Android的機制裡,即使是將某一個控制元件的visibility屬性設定為不可見的gone,在整個頁面載入過程中還是會載入此控制元件的。再後來就用到了ViewStub,在做頁面切換動畫時,只在頁面中放一個loading載入圖示和一個ViewStub標籤,像下面這樣:
> layout_loading.xml佈局檔案:
<merge xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<ViewStub
android:id="@+id/viewstub"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"/>
<NetErrAndLoadView
android:id="@+id/start_loading_lay"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" />
</merge>這個頁面是相當輕量級的,所以導致動畫載入速度非常快、而且流暢。等頁面切換動畫完成之後,我們再指定ViewStub的資源,來載入實際的頁面,這個資源就是實際要載入的頁面的佈局檔案。比如要載入MainActivity的佈局檔案layout_main.xml,onCreate實現如下:
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.layout_loading);
mLoadHandler = new Handler();
mLoadingView = (NetErrAndLoadView)findViewById(R.id.start_loading_lay);
mLoadingView.startLoading();
mViewStub = (ViewStub)findViewById(R.id.viewstub);
mViewStub.setLayoutResource(R.layout.layout_main);
mLoadHandler.postDelayed(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
mViewStub.inflate();
mLoadingView.hide();
}
},500);
} 上面的500單位是ms,就是延遲載入的時間。上面使用的是動態新增ViewStub指向佈局資源的方法(mViewStub.setLayoutResource(R.layout.layout_main)),當然根據需要可以直接在ViewStub的佈局塊兒中設定,需要設定ViewStub標籤下的layout屬性(android:layout=”@layout/ layout_main”)。
ViewStub也是有少許缺點的,下面所說:
1、 ViewStub只能Inflate一次,之後ViewStub物件會被置為空。按句話說,某個被ViewStub指定的佈局被Inflate後,就不能夠再通過ViewStub來控制它了。所以它不適用 於需要按需顯示隱藏的情況。
2、 ViewStub只能用來Inflate一個佈局檔案,而不是某個具體的View,當然也可以把View寫在某個佈局檔案中。如果想操作一個具體的view,還是使用visibility屬性吧。
3、 VIewStub中不能巢狀merge標籤。(前面好像說過)
不過這些確定都無傷大雅,我們還是能夠用ViewStub來做很多事情。
有時候真的不得不佩服google的Android團隊的遠見性和架構性,這種細微的設計都能考慮的到,想用就有。