線性表資料結構解讀(六)鏈式雜湊表結構-LinkedHashMap
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-22
上一篇文章我和大家一起解讀了HashMap的原理原始碼,各位童鞋可以點選連結檢視線性表資料結構解讀(五)雜湊表結構-HashMap
這次我們一起來看一下LinkedHashMap,它保留插入的順序,如果需要輸出的順序和輸入時的相同,那麼就選用LinkedHashMap。就LinkedHashMap而言,它繼承了HashMap,底層使用雜湊表與雙向連結串列來儲存所有元素。其基本操作與父類HashMap相似,它通過重寫父類相關的方法,來實現自己的連結列表特性。
LinkedHashMap是Map介面的雜湊表和連結列表實現,具有可預知的迭代順序。此實現提供所有可選的對映操作,並允許使用null值和null鍵。此類不保證對映的順序,特別是它不保證該順序恆久不變。
LinkedHashMap實現與HashMap的不同之處在於,後者維護著一個運行於所有條目的雙重連結列表。此連結列表定義了迭代順序,該迭代順序可以是插入順序或者是訪問順序。
- 第一種和佇列一樣預設是按插入順序排序,先進來的是最老的元素,放在隊頭,將來會被先移出去,最後進來的是新的元素。
- 第二種,基於訪問排序,那麼呼叫get方法後,會將每次訪問的元素移至隊尾,將來移除的時候移除的是隊頭,最先訪問的元素最後才被移除,不斷訪問可以形成按訪問順序排序的連結串列。
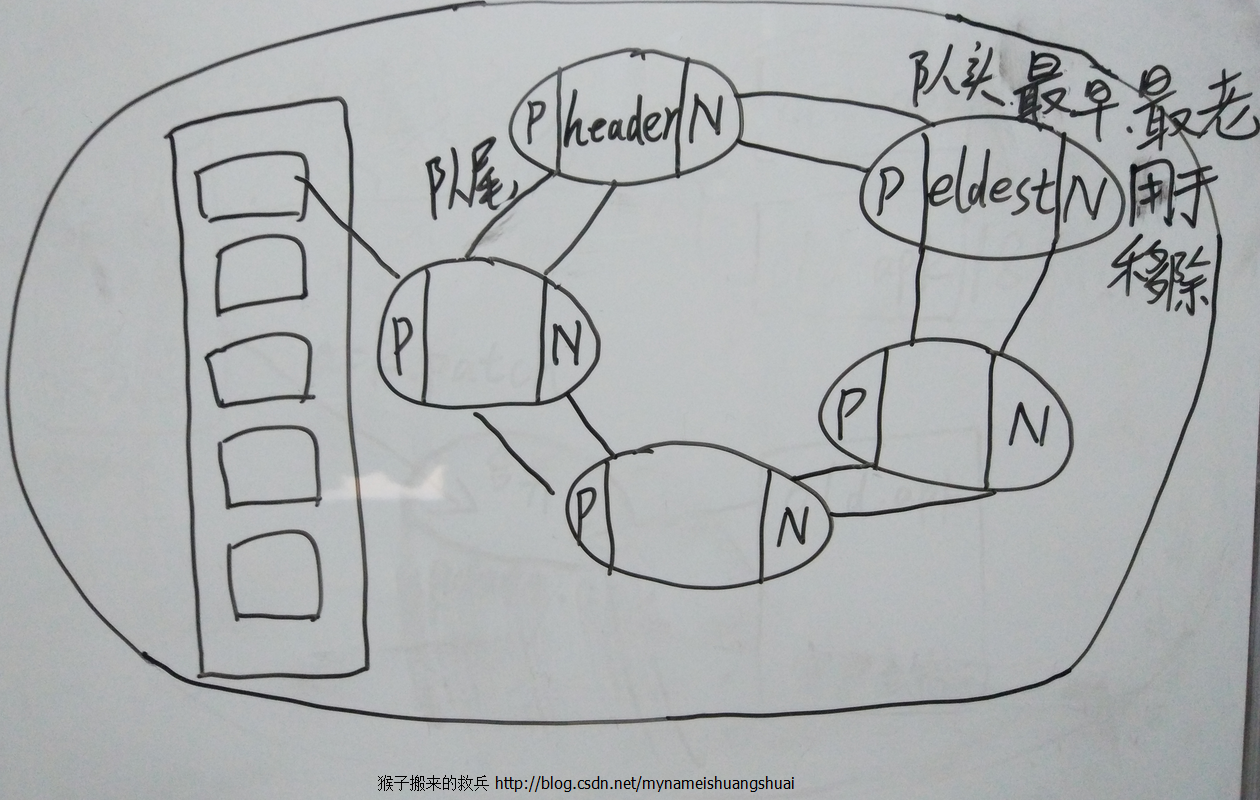
下圖是我在小黑板手繪的雙鏈迴環迴圈連結串列
下面我們一起來分析一下LinkedHashMap的原始碼:
初始化及構造方法
/**
* 雙鏈迴環迴圈連結串列
*/
public class LinkedHashMap<K, V> extends HashMap<K, V> { addNewEntry方法
/**
* 重寫了HashMap中的新增新元素方法
*/
@Override
void addNewEntry(K key, V value, int hash, int index) {
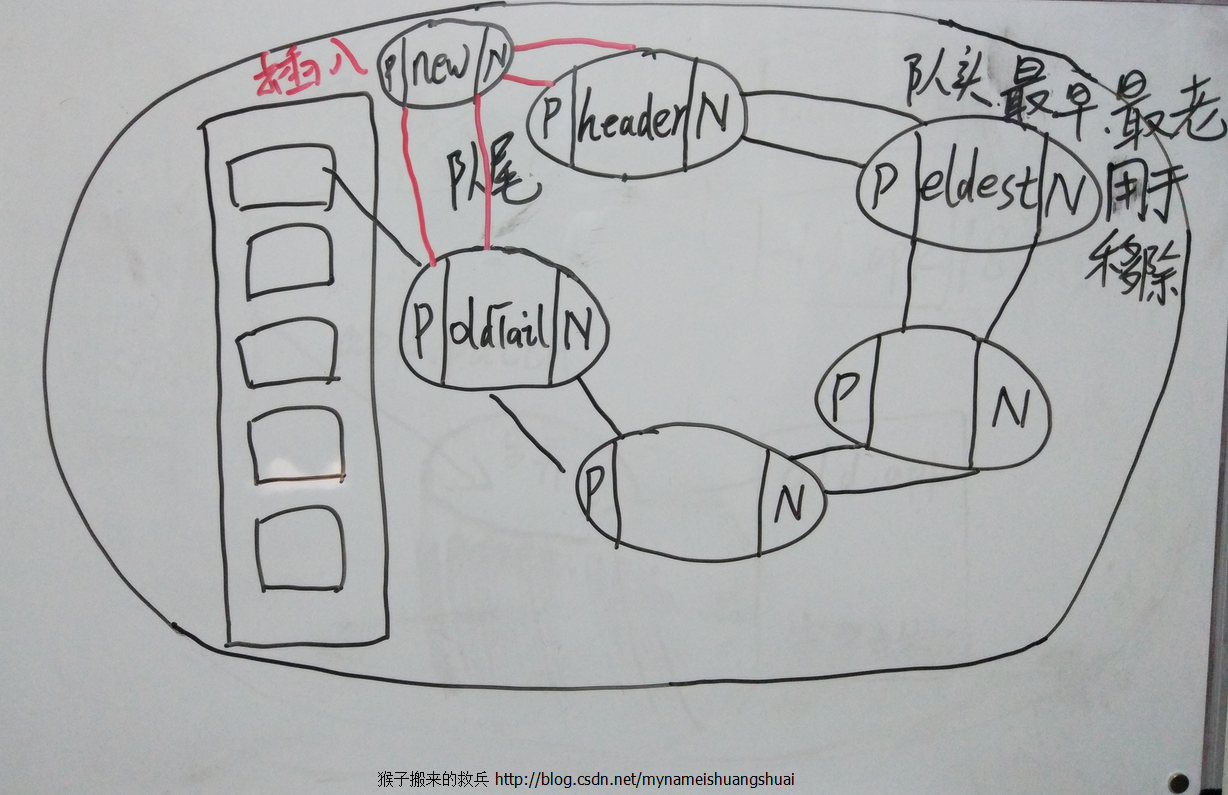
// 找到頭結點
LinkedEntry<K, V> header = this.header;
// 找到用於移除的隊頭的最老結點
LinkedEntry<K, V> eldest = header.nxt;
// 如果最老的結點不等於頭結點(有元素存在)且removeEldestEntry為true
if (eldest != header && removeEldestEntry(eldest)) {
remove(eldest.key);// 移除最老元素key
}
// Create new entry, link it on to list, and put it into table
// 使用雙向連結串列的套路實現插入,基於訪問排序
LinkedEntry<K, V> oldTail = header.prv;
LinkedEntry<K, V> newTail = new LinkedEntry<K,V>(
key, value, hash, table[index], header, oldTail);
table[index] = oldTail.nxt = header.prv = newTail;// 把新的加入到table陣列中
}下圖是我在小黑板手繪的插入方法實現原理圖,注意其中指標的變化:
remove方法
// 移除最老的元素
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K, V> eldest) {
return false;
}get方法
/**
* Returns the value of the mapping with the specified key.
* @param key the key.
* @return the value of the mapping with the specified key, or {@code null}
* if no mapping for the specified key is found.
*/
@Override public V get(Object key) {
/*
* This method is overridden to eliminate the need for a polymorphic
* invocation in superclass at the expense of code duplication.
*/
if (key == null) {
HashMapEntry<K, V> e = entryForNullKey;
if (e == null)
return null;
if (accessOrder)// 判斷排序模式
makeTail((LinkedEntry<K, V>) e);
return e.value;
}
int hash = Collections.secondaryHash(key);
HashMapEntry<K, V>[] tab = table;
for (HashMapEntry<K, V> e = tab[hash & (tab.length - 1)];
e != null; e = e.next) {
K eKey = e.key;
if (eKey == key || (e.hash == hash && key.equals(eKey))) {
if (accessOrder)
makeTail((LinkedEntry<K, V>) e);
return e.value;
}
}
return null;
}下面博文,我將為大家帶來LinkedHashMap的最佳實踐:LruCache快取演算法的解析,敬請查閱LinkedHashMap最佳實踐:LruCache