Linux:使用多執行緒程式設計和訊息佇列,實現兩個程序之間的聊天
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-23
思路:
一個檔案:建立一個執行緒和主函式,或者建立兩個執行緒主函式呼叫(我用這種)。
建立兩個訊息佇列,
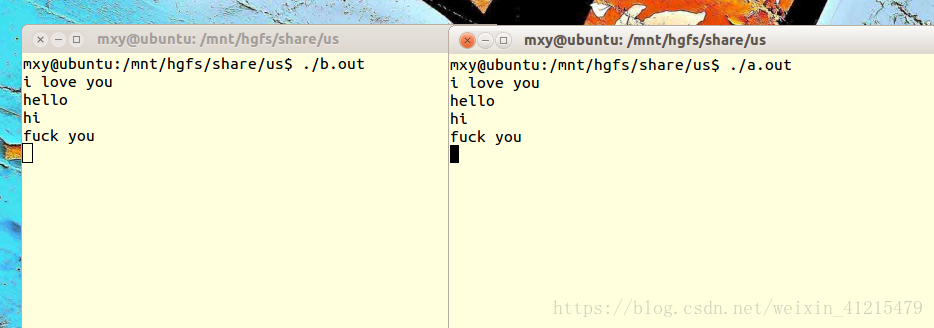
一共兩個檔案,兩個佇列,四個程序
a.c 一個程序寫(訊息型別為1) ---->>佇列 一個程序讀(訊息型別為2)
b.c 一個程序寫(訊息型別為2) ---->>佇列 一個程序讀(訊息型別為1)
a.c
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/ipc.h> #include <sys/msg.h> struct MSG{ long mtype;//訊息型別 char buf[100];//訊息資料 }; struct MSG_read{ long mtype_read;//訊息型別 char buf_read[100];//訊息資料 }; void *write1(void *arg) { //1.獲取key key_t key = ftok("/",'a'); if(key==-1) { perror("ftok"); exit(-1); } int msqid = msgget(key,IPC_CREAT|0666); //2.通過key建立訊息佇列 if(msqid==-1) { perror("msgget"); exit(-2); } //3.傳送訊息 struct MSG msg1; while(1) { msg1.mtype = 1; fgets(msg1.buf,100,stdin); int res = msgsnd(msqid,&msg1,sizeof(msg1.buf),0); } } void *read1(void *arg) { key_t key = ftok("/",'b'); if(key==-1) { perror("ftok"); exit(-1); } int msqid = msgget(key,IPC_CREAT|0666); //2.通過key建立訊息佇列 if(msqid==-1) { perror("msgget"); exit(-2); } struct MSG_read msg; while(1) { int res = msgrcv(msqid,&msg,sizeof(msg.buf_read),2,0); //收型別為2 的資訊 if(res==-1){ perror("msgrcv"); exit(-3); } printf("%s",msg.buf_read); } } int main() { pthread_t id1; pthread_t id2; //建立執行緒 int res = pthread_create(&id1,0,write1,0); if(res){ printf("%s\n",strerror(res)); //exit(-1); } int res2 = pthread_create(&id2,0,read1,0); if(res2){ printf("%s\n",strerror(res2)); //exit(-1); } pthread_join(id1,0); pthread_join(id2,0); return 0; }
b.c
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/ipc.h> #include <sys/msg.h> struct MSG{ long mtype;//訊息型別 char buf[100];//訊息資料 }; struct MSG_read{ long mtype_read;//訊息型別 char buf_read[100];//訊息資料 }; void *read2(void *arg) { //1.獲取key key_t key = ftok("/",'a'); if(key==-1) { perror("ftok"); exit(-1); } int msqid = msgget(key,IPC_CREAT|0666); //2.通過key建立訊息佇列 if(msqid==-1) { perror("msgget"); exit(-2); } struct MSG msg1; while(1) { int res = msgrcv(msqid,&msg1,sizeof(msg1.buf),1,0); //收型別為2 的資訊 if(res==-1){ perror("msgrcv"); exit(-3); } printf("%s",msg1.buf); } } void *write2(void *arg) { key_t key = ftok("/",'b'); if(key==-1) { perror("ftok"); exit(-1); } int msqid = msgget(key,IPC_CREAT|0666); //2.通過key建立訊息佇列 if(msqid==-1) { perror("msgget"); exit(-2); } struct MSG_read msg1; msg1.mtype_read = 2; while(1) { fgets(msg1.buf_read,100,stdin); int res = msgsnd(msqid,&msg1,sizeof(msg1.buf_read),0); } } int main() { pthread_t id1; pthread_t id2; //建立執行緒 int res = pthread_create(&id1,0,write2,0); if(res){ printf("%s\n",strerror(res)); //exit(-1); } int res2 = pthread_create(&id2,0,read2,0); if(res2){ printf("%s\n",strerror(res2)); //exit(-1); } pthread_join(id1,0); pthread_join(id2,0); return 0; }
gcc a.c -pthread -o b.out
gcc b.c -pthread