HashMap和HashSet原理及底層實現
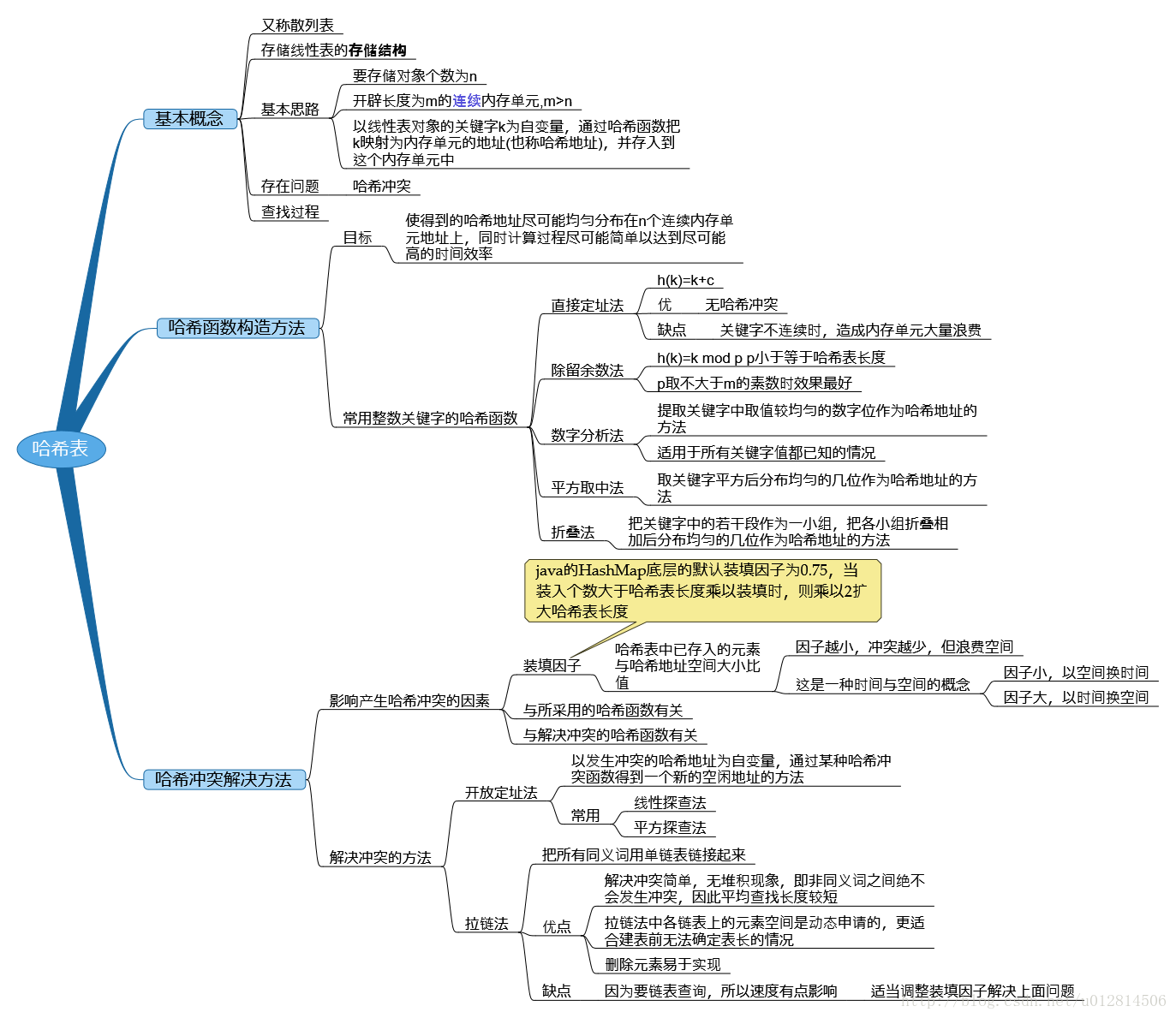
HashMap底層用雜湊演算法實現,下面看一下雜湊算表的整體概括:
當map.put(“key”,”values”);的時候,底層是這樣的:
static final Entry<?,?>[] EMPTY_TABLE = {}; transient Entry<K,V>[] table = (Entry<K,V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE; /** * The number of key-value mappings contained in this map. */ transient int size; int threshold; // 臨界值 它等於HashMap的容量乘以負載因子 final float loadFactor;// 負載因子 public V put(K key, V value) { // 如果table為空,則使其不為空 if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) { inflateTable(threshold); } // 如果key為null,呼叫putForNullKey處理 if (key == null) return putForNullKey(value); int hash = hash(key); // 搜尋指定hash值對應的索引 int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; // 如果hash值相同,並且equals比較返回true,則覆蓋,然後返回被覆蓋的 if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) { V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; e.recordAccess(this); return oldValue; } } // 如果i索引處的entry為null,表明此處還沒有entry modCount++; addEntry(hash, key, value, i); return null; } // 新增entry void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) { resize(2 * table.length);//原來長度的2倍 hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0; bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length); } createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex); } void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex]; // 頭插法建立鏈 table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e); size++; } void resize(int newCapacity) { Entry[] oldTable = table;//先記錄下來table int oldCapacity = oldTable.length; if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; //static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; return; } Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];//這個是原來長度的2倍 transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity)); table = newTable; threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1); } /** * Transfers all entries from current table to newTable. */ void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {// rehash 是否重新hash int newCapacity = newTable.length; for (Entry<K,V> e : table) { while(null != e) { Entry<K,V> next = e.next; if (rehash) { e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key); } int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity); e.next = newTable[i]; newTable[i] = e; e = next; } } } /** * Initialize the hashing mask value. We defer(延遲) initialization until we * really need it. */ final boolean initHashSeedAsNeeded(int capacity) { boolean currentAltHashing = hashSeed != 0; boolean useAltHashing = sun.misc.VM.isBooted() && (capacity >= Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD); boolean switching = currentAltHashing ^ useAltHashing; if (switching) { hashSeed = useAltHashing ? sun.misc.Hashing.randomHashSeed(this) : 0; } return switching; } // 內部類 entry static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final K key; V value; Entry<K,V> next;// 指向下一個entry int hash; /** * Creates new entry. */ Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) { value = v; next = n; key = k; hash = h; }
說明:
對於HashMap及其子類而言,它們採用Hash演算法來決定集合中元素的儲存位置。當系統開始初始化HashMap時,系統會建立一個長度為capacity的Entry陣列,這個數組裡可以儲存元素的位置被稱為“桶(bucket)”,每個bucket都有其指定索引,系統可以根據其索引快速訪問該bucket裡儲存的元素。當每個bucket只儲存一個元素時,HashMap效能最好。當解決衝突而產生的鏈越長,效能越差。
裝填因子load factor,預設值是0.75,這個是空間和時間的折衷,增大裝填因子,可以減小Hash表所佔用的空間,但會增加查詢時間,減小裝填因子,會提高資料查詢效能,但會增加
在new 一個hashMap的時候,可以適當的傳入要建立的大小,傳入的應該是2的n次冪。
HashSet的底層實現
HashSet底層是通過HashMap實現的,看如下的建構函式,構造HashSet的時候底層就構造了一個HashMap
public HashSet() { map = new HashMap<>(); } private static final Object PRESENT = new Object(); public boolean add(E e) { return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null; }
add的時候呼叫map的put方法,value始終是PRESENT。
The general contract of hashCode is:
· Whenever it is invoked on the same object more than once during an execution of a Java application, the hashCode method must consistently return the same integer, provided no information used in equals comparisons on the object is modified. This integer need not remain consistent from one execution of an application to another execution of the same application.
· If two objects are equal according to the equals(Object) method, then calling the hashCode method on each of the two objects must produce the same integer result.
· It is not required that if two objects are unequal according to the equals(java.lang.Object) method, then calling the hashCode method on each of the two objects must produce distinct integer results. However, the programmer should be aware that producing distinct integer results for unequal objects may improve the performance of hash tables.