dijkstra演算法、Bellman_Ford演算法、SPFA模板、Floyd演算法
尋找最短路徑指的是找出從圖中某個結點出發到達另一個結點所經過的邊的權重之和最小的那條路徑。這裡的最短路不僅僅指一般意義上的距離最短,還可以引申到時間,費用等最小。
演算法中的最短路問題型別:
1:單源最短路:給定一個源結點,求出這個點到其他所有點的最短路徑,有Dijkstra和Bellman-ford兩種演算法,Dijkstra只能求解所有邊權都為正的情況,Bellman-ford可以求解邊權為正或為負但沒有負環的情況。
2:多源最短路:求出圖中每個結點到其他所有結點的最短路,可用Floyd演算法解,Floyd同樣可求解有負邊無負環的情況。
3:點對點最短路:給定起點和終點,求這兩點間的最短路徑
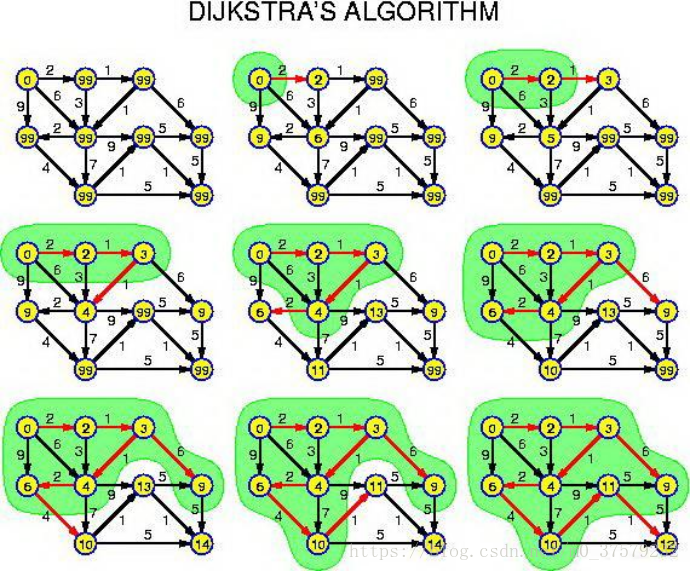
dijkstra演算法
需要設的變數:
1:cost陣列,cost[i][j]代表從i到j的距離(或費用等任意權值)。
2:d陣列,d[i]代表源點到結點i的最短路,初始值為無限大。
3:used陣列,used[i]表示結點i是否被使用,初始為0,表示沒被使用
演算法步驟
初始化cost陣列為INF,然後讀入邊的值
初始化d陣列為INF,設d[s]=0,s為原點
初始化used陣列為0,表示都沒用過
1:將源點s的d值設定為0,used[s]=1,遍歷與s有邊相連的所有結點i,並將他們的d值設定為u,i之間的距離cost[u][i]。
2:在used[i]=0的結點中找一個到源點的距離最小的點v,並把它的used值設為1。
3:遍歷與v有邊相連的所有結點i,如果源點到i的距離d[i]大於從源點到v的距離d[v]與i,v之間的距離cost[i][v]的加和,那麼將d[i]設定為d[v]+cost[i][v](這個步驟稱為邊的鬆弛,等於從源點到i時多走了一步,變成先到v再到i,鬆弛操作即鬆弛點,經過的點數變多,縮小距離)。
4:重複步驟2+3 n-1次,直到最後一個結點被加入,結束。
圖解:
例題:
在每年的校賽裡,所有進入決賽的同學都會獲得一件很漂亮的t-shirt。但是每當我們的工作人員把上百件的衣服從商店運回到賽場的時候,卻是非常累的!所以現在他們想要尋找最短的從商店到賽場的路線,你可以幫助他們嗎?
Input輸入包括多組資料。每組資料第一行是兩個整數N、M(N<=100,M<=10000),N表示成都的大街上有幾個路口,標號為1的路口是商店所在地,標號為N的路口是賽場所在地,M則表示在成都有幾條路。N=M=0表示輸入結束。接下來M行,每行包括3個整數A,B,C(1<=A,B<=N,1<=C<=1000),表示在路口A與路口B之間有一條路,我們的工作人員需要C分鐘的時間走過這條路。
輸入保證至少存在1條商店到賽場的路線。
Output對於每組輸入,輸出一行,表示工作人員從商店走到賽場的最短時間Sample Input
2 1
1 2 3
3 3
1 2 5
2 3 5
3 1 2
0 0Sample Output
3
2程式碼如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N=105,INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
int d[N],w[N][N],vis[N],n,m;
void Dijkstra(int s){
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){//每個點到原點的最短距離
d[i]=INF;
}
d[s]=0;
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int v=-1;
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){//對於每一個點,找到最近的一個點
if(!vis[j]&&(v==-1||d[j]<d[v]))v=j;
}
vis[v]=1;
for(int k=1;k<=n;k++){
d[k]=min(d[k],d[v]+w[v][k]);
}
}
}
int main(){
int a,b,c;
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF){
if(n==0&&m==0)break;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){
w[i][j]=INF;
}
}
while(m--){
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c);
w[a][b]=w[b][a]=c;
}
Dijkstra(1);
printf("%d\n",d[n]);
}
}dijkstra演算法的優化:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> P;
const int N=105,INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
int d[N],n,m;
struct edge{
int to,cost;
};
vector<edge>G[N];
void Dijkstra(int s){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){//每個點到原點的最短距離
d[i]=INF;
}
d[s]=0;
priority_queue<P,vector<P>,greater<P> >q;
q.push(P(d[s],s));//按邊的權值排序
while(!q.empty()){
P p=q.top();q.pop();
int v=p.second;//頂點的編號
if(d[v]<p.first)continue;
for(int i=0;i<G[v].size();i++){
edge e=G[v][i];//點v到i的情況(點i的值和v到i的路徑)
if(d[e.to]>d[v]+e.cost){
d[e.to]=d[v]+e.cost;
q.push(P(d[e.to],e.to));
}
}
}
}
int main(){
int a,b,c;
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF){
if(n==0&&m==0)break;
memset(G,0,sizeof(G));
while(m--){
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c);
G[a].push_back({b,c});
G[b].push_back({a,c});
}
Dijkstra(1);
printf("%d\n",d[n]);
}
}
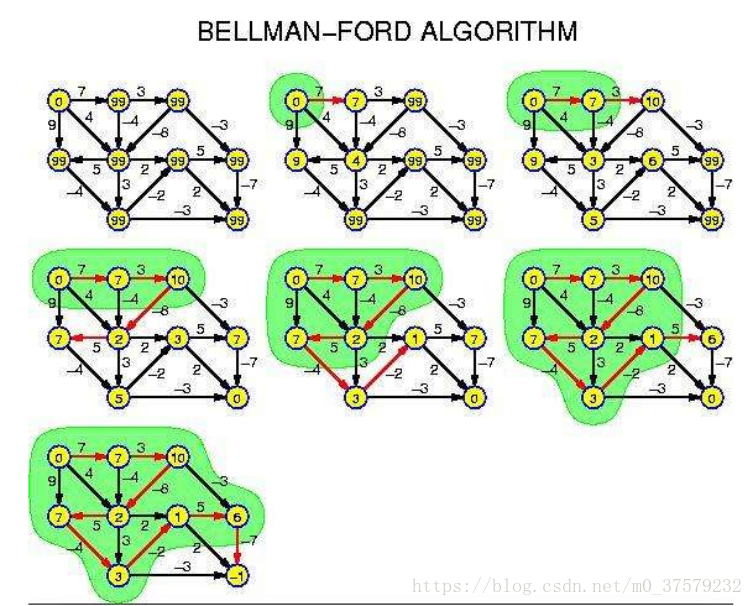
貝爾曼-福特演算法和狄克斯特拉演算法類似,只不過每次隨機尋找邊進行更新。
檢查是否存在負環:如果在進行過n-1次鬆弛操作後還存在可以鬆弛的邊,那麼說明有負環。
(如果沒有負環的話鬆弛操作完後,d[i]就表示點i到原點最小的長度,還能再鬆弛說明有一個邊是負的)
時間複雜度:O(VE),用佇列優化複雜度為O(kE),k為每個節點入隊次數,也就是SPFA演算法。
例題:
While exploring his many farms, Farmer John has discovered a number of amazing wormholes. A wormhole is very peculiar because it is a one-way path that delivers you to its destination at a time that is BEFORE you entered the wormhole! Each of FJ's farms comprises N (1 ≤ N ≤ 500) fields conveniently numbered 1..N, M (1 ≤ M≤ 2500) paths, and W (1 ≤ W ≤ 200) wormholes.
As FJ is an avid time-traveling fan, he wants to do the following: start at some field, travel through some paths and wormholes, and return to the starting field a time before his initial departure. Perhaps he will be able to meet himself :) .
To help FJ find out whether this is possible or not, he will supply you with complete maps to F (1 ≤ F ≤ 5) of his farms. No paths will take longer than 10,000 seconds to travel and no wormhole can bring FJ back in time by more than 10,000 seconds.
Input
Line 1: A single integer, F. F farm descriptions follow.
Line 1 of each farm: Three space-separated integers respectively: N, M, and W
Lines 2.. M+1 of each farm: Three space-separated numbers ( S, E, T) that describe, respectively: a bidirectional path between S and E that requires T seconds to traverse. Two fields might be connected by more than one path.
Lines M+2.. M+ W+1 of each farm: Three space-separated numbers ( S, E, T) that describe, respectively: A one way path from S to E that also moves the traveler backT seconds.
Output
Lines 1.. F: For each farm, output "YES" if FJ can achieve his goal, otherwise output "NO" (do not include the quotes).
Sample Input
2
3 3 1
1 2 2
1 3 4
2 3 1
3 1 3
3 2 1
1 2 3
2 3 4
3 1 8Sample Output
NO
YESHint
For farm 1, FJ cannot travel back in time.
For farm 2, FJ could travel back in time by the cycle 1->2->3->1, arriving back at his starting location 1 second before he leaves. He could start from anywhere on the cycle to accomplish this.
Bellman_Ford
程式碼如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
struct proc{int from,to,cost;};
proc edge[6000];
int d[505],n,m,w,cnt;
void addEdge(int s,int e,int c){
edge[cnt].from=s;
edge[cnt].to=e;
edge[cnt++].cost=c;
}
int Bellman(){
int flag;
memset(d,INF,sizeof(d));
d[1]=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
flag=0;
for(int j=1;j<=cnt;j++){//存的邊的數量
if(d[edge[j].to]>d[edge[j].from]+edge[j].cost){
d[edge[j].to]=d[edge[j].from]+edge[j].cost;
flag=1;
}
}
if(!flag)break;
}
//尋找負環
for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++){
if(d[edge[i].to]>d[edge[i].from]+edge[i].cost)return 1;
}
return 0;
}
int main(){
int f,s,e,c;
scanf("%d",&f);
while(f--){
cnt=1;
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&w);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
scanf("%d%d%d",&s,&e,&c);
addEdge(s,e,c);
addEdge(e,s,c);
}
for(int i=1;i<=w;i++){
scanf("%d%d%d",&s,&e,&c);
addEdge(s,e,-c);
}
if(Bellman())printf("YES\n");
else printf("NO\n");
}
}
SPFA演算法:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
struct proc{int to,cost,next;};
proc edge[6000];
int d[505],vis[505],cnt[505],head[505];
int n,m,w,tot;
void init(){
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
memset(d,INF,sizeof(d));
memset(cnt,0,sizeof(cnt));
tot=0;
}
void addEdge(int from,int to,int cost){
edge[tot].to=to;
edge[tot].cost=cost;
edge[tot].next=head[from];
head[from]=tot;
tot++;
}
int spfa(){
queue<int>q;
q.push(1);
d[1]=0;
vis[1]=1;
cnt[1]=1;
while(!q.empty()){
int u=q.front();
q.pop();
vis[u]=0;
for(int p=head[u];p!=-1;p=edge[p].next){
int v=edge[p].to;
if(d[v]>d[u]+edge[p].cost){
d[v]=d[u]+edge[p].cost;
if(!vis[v]){
vis[v]=1;
cnt[v]++;
if(cnt[v]>n)return 1;
q.push(v);
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int main(){
int T,s,e,c;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--){
init();
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&w);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
scanf("%d%d%d",&s,&e,&c);
addEdge(s,e,c);
addEdge(e,s,c);
}
for(int i=1;i<=w;i++){
scanf("%d%d%d",&s,&e,&c);
addEdge(s,e,-c);
}
if(spfa())printf("YES\n");
else printf("NO\n");
}
return 0;
}Floyd演算法:
求解任意兩點的最短路問題,設陣列d[i][j]表示點i到j的最短路徑,初始值:d[i][j]=INF(沒有路徑,i!=j),d[i][i]=0;
核心程式碼:
void floyd(){
for(int k=1;k<=n;k++){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){
d[i][j]=min(d[i][j],d[i][k]+d[k][j]);
}
}
}
}例題:Floyd演算法解決傳遞閉包問題
Cow Contest
N (1 ≤ N ≤ 100) cows, conveniently numbered 1..N, are participating in a programming contest. As we all know, some cows code better than others. Each cow has a certain constant skill rating that is unique among the competitors.
The contest is conducted in several head-to-head rounds, each between two cows. If cow A has a greater skill level than cow B (1 ≤ A ≤ N; 1 ≤ B ≤ N; A ≠ B), then cow A will always beat cow B.
Farmer John is trying to rank the cows by skill level. Given a list the results of M(1 ≤ M ≤ 4,500) two-cow rounds, determine the number of cows whose ranks can be precisely determined from the results. It is guaranteed that the results of the rounds will not be contradictory.
Input
* Line 1: Two space-separated integers: N and M
* Lines 2..M+1: Each line contains two space-separated integers that describe the competitors and results (the first integer, A, is the winner) of a single round of competition: A and B
Output
* Line 1: A single integer representing the number of cows whose ranks can be determined
Sample Input
5 5
4 3
4 2
3 2
1 2
2 5
Sample Output
2題意:n個人m個回合,在m行中,給出a,b表示a能打敗b,問經過m個回合,n個人中,幾個人的等級可以確定
傳遞閉包即是:已知i能到j,j能到k,則i能到k
若1個人與其他n-1個人的關係可以確定,那麼他的等級就可以確定。
要注意的是這裡的d陣列初始化為0,表示還不知道i,j的關係,有關係則為1,這裡設為INF就不行啦吧啊哈哈。
程式碼如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
int n,m;
int d[103][103];
void floyd(){
for(int k=1;k<=n;k++){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){
d[i][j]=d[i][j]||(d[i][k]&&d[k][j]);
}
}
}
}
int main(){
int a,b;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
memset(d,0,sizeof(d));
while(m--){
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
d[a][b]=1;
}
floyd();
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int sum=0;
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){
if(d[i][j]||d[j][i])sum++;
}
if(sum==n-1)ans++;
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
}