Log日誌框架-對原生Log進行簡單封裝
閒來無事,對以前專案中使用的對Log的封裝使用抽取出來,寫成一個Demo供博友參考。
Demo是以Gradle構建的專案。其中涉及到打Release包跟Debug包的時候對於日誌輸出的控制,由gradle指令碼進行控制,下文我再細說。
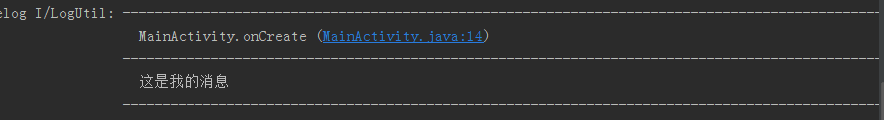
先看下日誌的輸出效果:
效果比較簡潔,主要展示日誌的具體來源及日誌訊息,並提供點選快速定位程式碼的功能。
下面直接看程式碼:
package com.csf.simplelog.utils; import android.text.TextUtils; import android.util.Log; /** * ClassName: LogUtil * Description:日誌工具類 * Created by chensf on 2016-7-27 9:53. */ public class LogUtil { private static final String TAG = LogUtil.class.getSimpleName(); /** * 日誌輸出等級 */ private static int LOG_LEVEL = Log.VERBOSE; /** * 是否顯示日誌 */ private static boolean isShowLog = true; private static final String DOUBLE_DIVIDER = "-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------"; public static void init(boolean isShowLog) { LogUtil.isShowLog = isShowLog; } public static void init(boolean isShowLog, int logLevel) { LogUtil.isShowLog = isShowLog; LogUtil.LOG_LEVEL = logLevel; } public static int v(Object msg) { return v(TAG, msg); } public static int v(String tag, Object msg) { return v(tag, msg, null); } public static int v(String tag, Object msg, Throwable tr) { return printLog(Log.VERBOSE, tag, msg, tr); } public static int d(Object msg) { return d(TAG, msg); } public static int d(String tag, Object msg) { return d(tag, msg, null); } public static int d(String tag, Object msg, Throwable tr) { return printLog(Log.DEBUG, tag, msg, tr); } public static int i(Object msg) { return i(TAG, msg); } public static int i(String tag, Object msg) { return i(tag, msg, null); } public static int i(String tag, Object msg, Throwable tr) { return printLog(Log.INFO, tag, msg, tr); } public static int w(Object msg) { return w(TAG, msg); } public static int w(String tag, Object msg) { return w(tag, msg, null); } public static int w(String tag, Object msg, Throwable tr) { return printLog(Log.WARN, tag, msg, tr); } public static int e(Object msg) { return e(TAG, msg); } public static int e(String tag, Object msg) { return e(tag, msg, null); } public static int e(String tag, Object msg, Throwable tr) { return printLog(Log.ERROR, tag, msg, tr); } private static int printLog(int type, String tag, Object msgObj, Throwable tr) { if (!isShowLog) { return 0; } String msg; StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(DOUBLE_DIVIDER).append('\n').append(getFunctionName()) .append(DOUBLE_DIVIDER).append('\n').append(" "); if (msgObj == null) { msg = ""; } else { msg = msgObj.toString(); } if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(msg)) { builder.append(msg); } if (tr != null) { builder.append('\n').append(Log.getStackTraceString(tr)); } builder.append('\n').append(DOUBLE_DIVIDER); switch (type) { case Log.VERBOSE: if (LOG_LEVEL <= Log.VERBOSE) { return Log.v(tag, builder.toString()); } break; case Log.DEBUG: if (LOG_LEVEL <= Log.DEBUG) { return Log.d(tag, builder.toString()); } break; case Log.INFO: if (LOG_LEVEL <= Log.INFO) { return Log.i(tag, builder.toString()); } break; case Log.WARN: if (LOG_LEVEL <= Log.WARN) { return Log.w(tag, builder.toString()); } break; case Log.ERROR: if (LOG_LEVEL <= Log.ERROR) { return Log.e(tag, builder.toString()); } break; } return 0; } private static String getFunctionName() { StackTraceElement[] elements = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace(); if (elements == null) { return ""; } for (StackTraceElement ste : elements) { if (ste.isNativeMethod()) { continue; } if (ste.getClassName().equals(Thread.class.getName())) { continue; } if (ste.getClassName().equals(LogUtil.class.getName())) { continue; } return " " + ste.getFileName().substring(0, ste.getFileName().indexOf(".")) + "." + ste.getMethodName() + " (" + ste.getFileName() + ":" + ste.getLineNumber() + ")\n"; } return ""; } }
167行的程式碼,其中提供快速定位功能的程式碼在getFunctionName這個方法中,通過迴圈獲取Stack Trace Element中的element,分析獲取到具體的呼叫類方法及對應行數。程式碼如下:
private static String getFunctionName() { StackTraceElement[] elements = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace(); if (elements == null) { return ""; } for (StackTraceElement ste : elements) { if (ste.isNativeMethod()) { continue; } if (ste.getClassName().equals(Thread.class.getName())) { continue; } if (ste.getClassName().equals(LogUtil.class.getName())) { continue; } return " " + ste.getFileName().substring(0, ste.getFileName().indexOf(".")) + "." + ste.getMethodName() + " (" + ste.getFileName() + ":" + ste.getLineNumber() + ")\n"; } return "";
下面我們將目光回到對Log的封裝類LogUtil上,LogUtil只是對原生Log類進行簡單的封裝,通過增加屬性isShowLog及LOG_LEVEL對我們的log進行控制,方便在釋出Release包的時候快速關閉日誌輸出。
LogUtil提供兩個初始函式,
public static void init(boolean isShowLog) { LogUtil.isShowLog = isShowLog; } public static void init(boolean isShowLog, int logLevel) { LogUtil.isShowLog = isShowLog; LogUtil.LOG_LEVEL = logLevel; }
這兩個函式二選一,最好是在應用的入口進行初始化,一般我們會自定義一個Application的繼承類。在其方法onCreate中就能進行應用的初始工作。
程式碼如下:
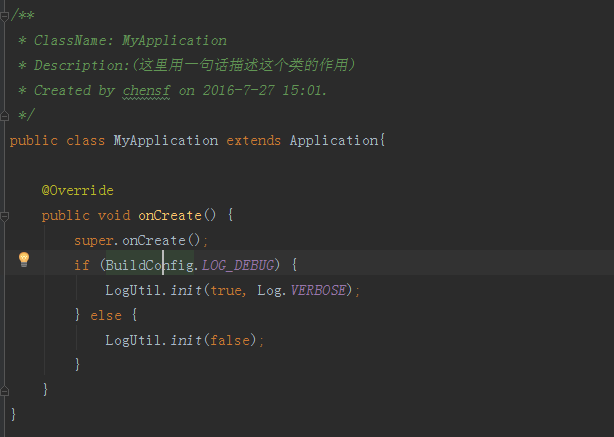
然後在AndroidManifest中引用這個MyApplication類
<application
android:name=".config.MyApplication"
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >在MyApplication的onCreate方法中,我們看到,我這裡通過
BuildConfig.LOG_DEBUG這個值來控制日誌是否輸出。
我們來看這個語句LogUtil.init(true, Log.VERBOSE);其中參一是是否開啟日誌輸出,參二顧名思義,就是日誌的級別,這裡我將級別控制設定為最低的VERBOSE,意思就是所有的日誌資訊,VERBOSE,DEBUG,INFO,WARN,ERROR這些級別的資訊都會輸出。如果傳遞引數Log.ERROR,那就只會輸出錯誤日誌,因為我們的Log.ERROR的級別比VERBOSE,DEBUG,INFO,WARN都要高。具體的大家去看到Demo的效果。
回到上面的BuildConfig.LOG_DEBUG,機智的小夥伴會發現BuildConfig中並沒有LOG_DEBUG這個屬性,那麼我們來講下開文提到
“涉及到打Release包跟Debug包的時候對於日誌輸出的控制,由gradle指令碼進行控制”
通過Gradle指令碼來進行控制日誌的輸出,這樣我們就不用在打包的時候手動去修改程式碼。
下面貼出部分Gradle指令碼:
buildTypes {
debug {
//顯示日誌
buildConfigField("boolean","LOG_DEBUG","true");
}
release {
//不顯示日誌
buildConfigField("boolean","LOG_DEBUG","false");
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
在主工程的Gradle指令碼的buildTypes下,在debug跟release中增加buildConfigField(“boolean”,”LOG_DEBUG”,”true”);
這個語句的意思是在BuildConfig中增加欄位LOG_DEBUG,debug下LOG_DEBUG的值為true,release下則為false.然後再通過該值去初始化LogUtil,達到控制日誌輸出。