pytorch實現yolo-v3 (原始碼閱讀和復現) -- 005
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-26
前面已經搭建了YOLO V3的網路, 只需要在此基礎上提供輸入,並對預測結果過濾,就可以輸出了,完整工程程式碼已分享.
1. 影象預處理部分preprocess.py
給定影象路徑以及期望的尺寸, 進行整體縮放後, 居中放置在畫布上,並返回,
返回值值包括 : 處理後圖像, 原圖, 原圖尺寸
def letterbox_image(img, input_dim):
"""
調整影象尺寸
將影象按照比例進行縮放,此時 某個邊正好可以等於目標長度,另一邊小於等於目標長度
將縮放後的資料拷貝到畫布中心,返回完成縮放
"""
ori_w, ori_h = img.shape[1 2. 檢測指令碼
detect.py
from __future__ import division
import time
import torch
from torch.autograd import Variable
import cv2
from util import *
import argparse
import os
import os.path as osp
from darknet import Darknet
from preprocess import preprocess_image, inp_to_image
import random
import pickle as pkl
def arg_parse():
"""
檢測模組的引數轉換
"""
# 格式: 引數名, 目標引數(dest是字典的key),幫助資訊,型別, 預設值
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Yolo v3 檢測模型")
parser.add_argument("--images", dest="images", help="待檢測影象目錄", type=str, default="imgs")
parser.add_argument("--dets", dest="dets", help="檢測結果儲存目錄", type=str, default="det")
parser.add_argument("--bs", dest="bs", help="Batch 大小, 預設為 1", default=1)
parser.add_argument("--confidence", dest="confidence", help="目標檢測結果置信度閾值", default=0.5)
parser.add_argument("--nms_thresh", dest="nms_thresh", help="NMS非極大值抑制閾值", default=0.4)
parser.add_argument("--cfg", dest="cfg", help="配置檔案", default="cfg/yolov3.cfg", type=str)
parser.add_argument("--weights", dest="weights", help="模型權重", default="yolov3.weights", type=str)
parser.add_argument("--resize", dest="resize", help="網路輸入解析度. 解析度越高,則準確率越高; 反之亦然.", \
default="416", type=str)
parser.add_argument("--scales", dest="scales", help="縮放尺度用於檢測", default="1,2,3", type=str)
# 返回轉換好的結果
return parser.parse_args()
if __name__ == '__main__':
args = arg_parse() # 型別: argparse.Namespace, 可以像easydict一樣使用
print(args)
scales = args.scales
images = args.images
batch_size = args.bs
confidence = args.confidence
nms_thresh = args.nms_thresh
# GPU環境是否可用
CUDA = torch.cuda.is_available()
# coco 資料集
num_class, classes = load_classes("data/coco.names")
# 建立神經網路
print("載入神經網路...")
model = Darknet(args.cfg)
model.load_weights(args.weights)
print("模型載入成功.")
# 網路輸入資料大小
model.net_info["height"] = int(args.resize)
input_dim = model.net_info["height"]
assert input_dim > 0 and input_dim % 32 == 0
# 如果GPU可用, 模型切換到cuda中執行
if CUDA:
model.cuda()
# 評估模式
model.eval()
# 載入待檢測影象列表
try:
imlist = [os.path.join(images, img) for img in os.listdir(images) if os.path.splitext(img)[1] in [".png", ".jpg", ".jpeg"]]
except NotADirectoryError:
imlist = []
imlist.append(os.path.join(images))
except FileNotFoundError:
print("%s 不是有效的目錄或者檔案" % (images,))
exit()
# 儲存結果目錄
if not os.path.exists(args.dets):
os.mkdir(args.dets)
load_batch = time.time()
# 載入全部待檢測影象
# map: 轉換函式prep_image, 兩個陣列 imlist [input_dim for x in imlist] 為其提供引數
batches = list(map(preprocess_image, imlist, [input_dim for x in imlist]))
ptt_images = [x[0] for x in batches] # ptt: pytorch_tensor
ori_images = [x[1] for x in batches]
ori_images_dim_list = [x[2] for x in batches]
# repeat(*size), 沿著指定維度複製資料
# 注: size維度必須和資料本身維度要一致
ori_images_dim_list = torch.FloatTensor(ori_images_dim_list).repeat(1, 2) # (11,4) 原始影象尺寸
if CUDA:
ori_images_dim_list = ori_images_dim_list.cuda()
# 所有檢測結果
# objs = []
# 第i個影象批次
i = 0
# 批處理 ...
write = False
# batch >1 支援實現
if batch_size>1:
num_batches = int(len(imlist)/batch_size + 0.5)
ptt_images = [torch.cat(
(ptt_images[ i * batch_size: min((i + 1) * batch_size, len(ptt_images)) ]) )
for i in range(num_batches)]
# 暫未支援batch>1
for batch in ptt_images:
start = time.time()
if CUDA:
batch = batch.cuda()
with torch.no_grad():
predictions = model(Variable(batch), CUDA)
# 結果過濾
predictions = write_results(predictions, confidence, num_class, nms=True, nms_thresh=nms_thresh)
if type(predictions) == int:
i += 1
continue
end = time.time()
print(end - start, predictions.shape) # 單位 秒
predictions[:, 0] += i * batch_size # [0]表示影象索引
if not write:
output = predictions
write = True
else:
output = torch.cat((output, predictions))
for im_num, image in enumerate(imlist[i*batch_size: min((i+1)*batch_size, len(imlist))]):
im_ind = i*batch_size + im_num # 影象編號
objs = [ classes[int(x[-1])] for x in output if int(x[0]) == im_ind] # 輸出第im_ind影象結果
print("{0:20s} predicted in {1:6.3f} seconds".format(osp.split(image)[-1], (end-start)/batch_size))
print("{0:20s} {1:s}".format("Objects detected", " ".join(objs)))
print("----------------------------------------------------------")
i += 1
# 對所有的輸入的檢測結果
try:
output
except:
print("沒有檢測到任何目標")
exit()
# 0: 影象索引 1-4: 座標(在縮放後圖像中的位置) 5:score 6: ??? 7(-1):類別
# print(output)
# 對output結果按照dim=0維度分組?
ori_images_dim_list = torch.index_select(ori_images_dim_list, 0, output[:, 0].long()) # pytorch 切片torch.index_select(data, dim, indices)
scaling_factor = torch.min(input_dim/ori_images_dim_list, 1)[0].view(-1, 1)
# 座標換算,將居中的位置座標轉換為以(0,0)為起點的座標 x-x'soffset, y-y'soffset
output[:, [1,3]] -= (input_dim - scaling_factor*ori_images_dim_list[:, 0].view(-1,1))/2 # x416 - (縮放後x<=416長度/2 )
output[:, [2,4]] -= (input_dim - scaling_factor*ori_images_dim_list[:, 1].view(-1,1))/2
output[:, 1:5] /= scaling_factor # 縮放至原圖大小尺寸
# 繪圖
colors = pkl.load(open("pallete", "rb"))
def draw(x, batch, results):
# batch 轉換後的影象, 沒用到這裡
c1 = tuple(x[1:3].int()) # x1,y1
c2 = tuple(x[3:5].int()) # x2,y2
img = results[int(x[0])] # 影象索引
cls = int(x[-1])
label = "%s" % classes[cls]
color = random.choice(colors) # 隨機選擇顏色
# 繪圖(繪製一條結果)
cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, 1)
t_size = cv2.getTextSize(label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 1, 1)[0]
c2 = c1[0] + t_size[0] + 3, c1[1] + t_size[1] + 4
cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, -1)
cv2.putText(img, label, (c1[0], c1[1] + t_size[1] + 4), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 1, [225, 255, 255], 1)
return img
# 開始逐條繪製output中結果
list(map(lambda x: draw(x, ptt_images, ori_images), output))
# 儲存檔案路徑
det_names = ["{}/det_{}".format(args.dets, osp.split(x)[-1]) for x in imlist]
list(map(cv2.imwrite, det_names, ori_images))主時鐘對程式碼已經做了很細緻的解釋, 下面只陳述下主要過程:
搭建網路,並初始化權重
預處理輸入影象,並依據batch size引數調整, 預處理函式的輸出是batch為1的tensor
分批次進行預測, 將預測結果進行nms過濾, 並剔除掉置信度不夠的區域, 列印最終的檢測結果到控制檯
output中儲存所有的檢測結果, 利用其中資訊,展開視覺化,將結果儲存在了det目錄下.
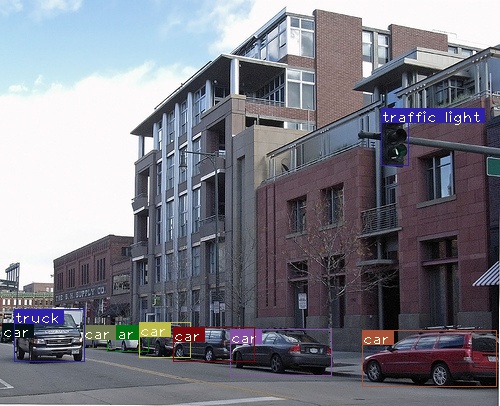
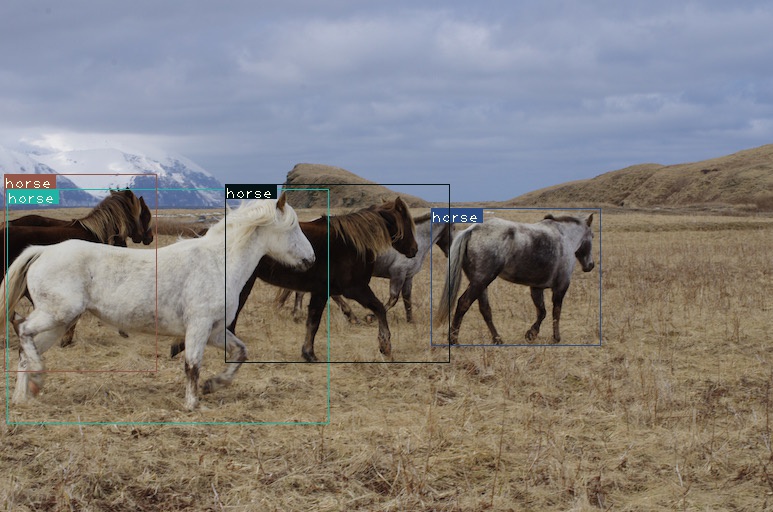
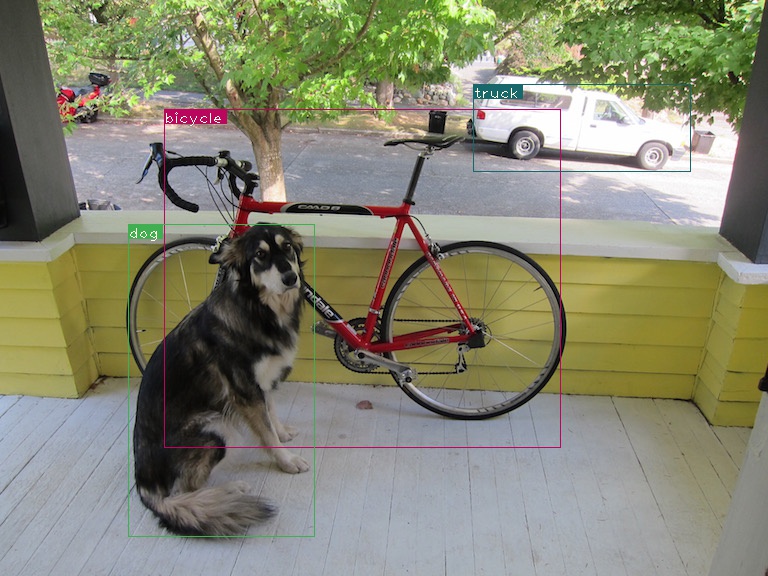
檢測結果示例如圖: