[UnityShader2]頂點片段著色器例項(五)
官方文件:http://docs.unity3d.com/Manual/SL-VertexFragmentShaderExamples.html
相關連結:http://blog.csdn.net/candycat1992/article/details/41605257
1.
a.cg內建函式:tex2D(sample2D tex, float2 s) //s為紋理(uv)座標
b.UnityCG.cginc:TRANSFORM_TEX,其定義為:
// Transforms 2D UV by scale/bias property
#define TRANSFORM_TEX(tex,name) (tex.xy * name##_ST.xy + name##_ST.zw)
##是字串連線符,同時需要定義一個帶有_ST的變數。其中name##_ST.xy是縮放倍數,name##_ST.zw是偏移值
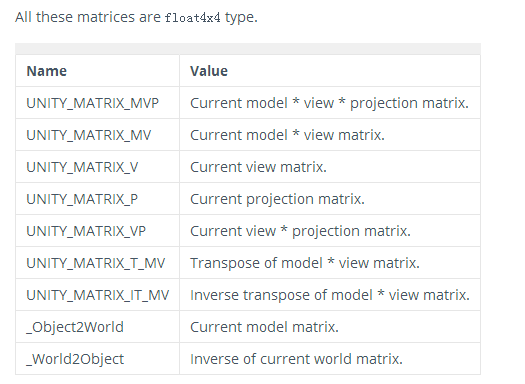
Shader "Unlit/NewUnlitShader" { Properties { _MainTex ("Texture", 2D) = "white" {} } SubShader { Tags { "RenderType"="Opaque" } LOD 100 Pass { CGPROGRAM #pragma vertex vert #pragma fragment frag // make fog work #pragma multi_compile_fog #include "UnityCG.cginc" struct appdata { float4 vertex : POSITION; float2 uv : TEXCOORD0; }; struct v2f { float2 uv : TEXCOORD0; UNITY_FOG_COORDS(1) float4 vertex : SV_POSITION; }; sampler2D _MainTex; float4 _MainTex_ST; v2f vert (appdata v) { v2f o; o.vertex = mul(UNITY_MATRIX_MVP, v.vertex); o.uv = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.uv, _MainTex); UNITY_TRANSFER_FOG(o,o.vertex); return o; } fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target { // sample the texture fixed4 col = tex2D(_MainTex, i.uv); // apply fog UNITY_APPLY_FOG(i.fogCoord, col); return col; } ENDCG } } }
2.
a.UnityCG.cginc:UnityObjectToWorldNormal,其定義為:
// Transforms normal from object to world space
inline float3 UnityObjectToWorldNormal( in float3 norm )
{
// Multiply by transposed inverse matrix, actually using transpose() generates badly optimized code
return normalize(_World2Object[0].xyz * norm.x + _World2Object[1].xyz * norm.y + _World2Object[2].xyz * norm.z);
}
一般來說,需要將模型空間的法線轉換為世界空間的法線,法線是float3型別的,與4x4的矩陣是不能直接相乘的
Shader "Unlit/WorldSpaceNormals"
{
// no Properties block this time!
SubShader
{
Pass
{
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
// include file that contains UnityObjectToWorldNormal helper function
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
struct v2f {
// we'll output world space normal as one of regular ("texcoord") interpolators
half3 worldNormal : TEXCOORD0;
float4 pos : SV_POSITION;
};
// vertex shader: takes object space normal as input too
v2f vert (float4 vertex : POSITION, float3 normal : NORMAL)
{
v2f o;
o.pos = mul(UNITY_MATRIX_MVP, vertex);
// UnityCG.cginc file contains function to transform
// normal from object to world space, use that
o.worldNormal = UnityObjectToWorldNormal(normal);
return o;
}
fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target
{
fixed4 c = 0;
// normal is a 3D vector with xyz components; in -1..1
// range. To display it as color, bring the range into 0..1
// and put into red, green, blue components
c.rgb = i.worldNormal*0.5+0.5;
return c;
}
ENDCG
}
}
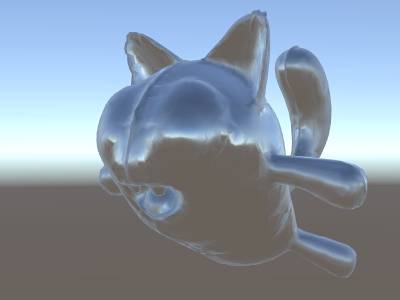
}3.使用世界空間的法線進行環境反射(天空盒)
a.HDR:http://www.ceeger.com/Manual/HDR.html
b.cg內建函式:reflect(I, N),根據入射光線方向I和表面法向量N計算反射向量,僅對三元向量有效,一般來說都統一在世界空間中進行計算
c.cg內建函式:normalize(v),返回一個指向與向量v一樣,長度為1的向量
d.UnityCG.cginc:UnityWorldSpaceViewDir,其定義為:
// Computes world space view direction, from object space position
inline float3 UnityWorldSpaceViewDir( in float3 worldPos )
{
return _WorldSpaceCameraPos.xyz - worldPos;
}
e.當天空盒在場景中使用時,會被當作為一個反射源,然後unity內部會建立一個預設的反射探頭(Reflection Probe),這個探頭包含了天空盒的資料。因為天空盒本質上可以看作為一個Cubemap(6個面),即探頭包含了一個Cubemap的資料。
Shader "Unlit/SkyReflection"
{
SubShader
{
Pass
{
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
struct v2f {
half3 worldRefl : TEXCOORD0;
float4 pos : SV_POSITION;
};
v2f vert (float4 vertex : POSITION, float3 normal : NORMAL)
{
v2f o;
o.pos = mul(UNITY_MATRIX_MVP, vertex);
// compute world space position of the vertex
float3 worldPos = mul(_Object2World, vertex).xyz;
// compute world space view direction
float3 worldViewDir = normalize(UnityWorldSpaceViewDir(worldPos));
// world space normal
float3 worldNormal = UnityObjectToWorldNormal(normal);
// world space reflection vector
o.worldRefl = reflect(-worldViewDir, worldNormal);
return o;
}
fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target
{
// sample the default reflection cubemap, using the reflection vector
half4 skyData = UNITY_SAMPLE_TEXCUBE(unity_SpecCube0, i.worldRefl);
// decode cubemap data into actual color
half3 skyColor = DecodeHDR (skyData, unity_SpecCube0_HDR);
// output it!
fixed4 c = 0;
c.rgb = skyColor;
return c;
}
ENDCG
}
}
}
4.使用法線貼圖進行環境反射
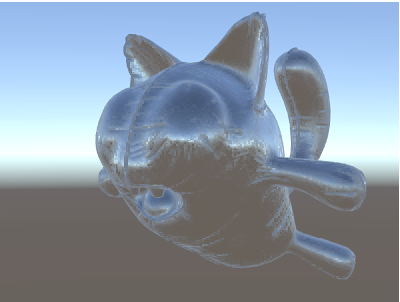
a.通常來說,法線貼圖用來為物體新增細節(凹凸感),而不會增添額外的幾何體。上面的shader,反射方向是逐頂點計算的;而如果我們要使用法線貼圖,那麼貼圖表面上的法線就需要逐畫素計算(對於與貼圖相關的計算,一般要放在片段程式進行逐畫素計算)。
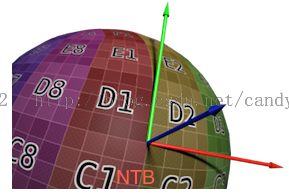
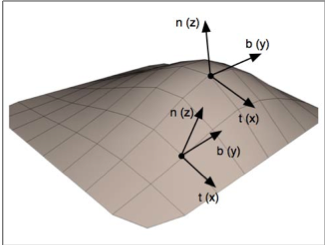
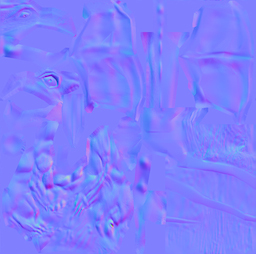
b.切線空間:在切線空間中,原點就是頂點的位置,z軸就是該頂點法線的方向,另外兩個軸就是與該頂點相切的兩條切線。理論上切線是有無數條的,但模型一般會給定該頂點的一條切線方向,這個切線方向一般是使用和紋理座標方向相同的那條切線。而另一個座標軸的方向就可以通過normal和tangent的叉乘得到。這三個座標軸依次稱為normal、tangent、bitangent,簡寫為N、T、B。在頂點程式的輸入中,我們就已經可以得到法線和切線這兩個值了(模型空間下的)。
法線貼圖一般就是像這樣一片藍色的貼圖了:
c.法線貼圖儲存的是在切線空間下的法線值,並且該值是一個"壓縮值"。因為法線在(-1,1)範圍,要對映到(0,1)範圍,要進行"壓縮"。那麼,如果我們使用tex2D函式進行取樣,對取樣之後的值就要進行"解壓",使用的就是UnityCG.cginc下的UnpackNormal函式:inline fixed3 UnpackNormal(fixed4 packednormal)。得到這個"解壓"後的切線空間下的法線值,我們需要把它轉換為世界空間,這樣就能進行統一的計算了。說道轉換空間,那麼就要搞一個矩陣,能將向量從切線空間轉到世界空間。
Shader "Unlit/SkyReflection Per Pixel"
{
Properties {
// normal map texture on the material,
// default to dummy "flat surface" normalmap
_BumpMap("Normal Map", 2D) = "bump" {}
}
SubShader
{
Pass
{
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
struct v2f {
float3 worldPos : TEXCOORD0;
// these three vectors will hold a 3x3 rotation matrix
// that transforms from tangent to world space
half3 tspace0 : TEXCOORD1; // tangent.x, bitangent.x, normal.x
half3 tspace1 : TEXCOORD2; // tangent.y, bitangent.y, normal.y
half3 tspace2 : TEXCOORD3; // tangent.z, bitangent.z, normal.z
// texture coordinate for the normal map
float2 uv : TEXCOORD4;
float4 pos : SV_POSITION;
};
// vertex shader now also needs a per-vertex tangent vector.
// in Unity tangents are 4D vectors, with the .w component used to
// indicate direction of the bitangent vector.
// we also need the texture coordinate.
v2f vert (float4 vertex : POSITION, float3 normal : NORMAL, float4 tangent : TANGENT, float2 uv : TEXCOORD0)
{
v2f o;
o.pos = mul(UNITY_MATRIX_MVP, vertex);
o.worldPos = mul(_Object2World, vertex).xyz;
half3 wNormal = UnityObjectToWorldNormal(normal);
half3 wTangent = UnityObjectToWorldDir(tangent.xyz);
// compute bitangent from cross product of normal and tangent
half tangentSign = tangent.w * unity_WorldTransformParams.w;
half3 wBitangent = cross(wNormal, wTangent) * tangentSign;
// output the tangent space matrix
o.tspace0 = half3(wTangent.x, wBitangent.x, wNormal.x);
o.tspace1 = half3(wTangent.y, wBitangent.y, wNormal.y);
o.tspace2 = half3(wTangent.z, wBitangent.z, wNormal.z);
o.uv = uv;
return o;
}
// normal map texture from shader properties
sampler2D _BumpMap;
fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target
{
// sample the normal map, and decode from the Unity encoding
half3 tnormal = UnpackNormal(tex2D(_BumpMap, i.uv));
// transform normal from tangent to world space
half3 worldNormal;
worldNormal.x = dot(i.tspace0, tnormal);
worldNormal.y = dot(i.tspace1, tnormal);
worldNormal.z = dot(i.tspace2, tnormal);
// rest the same as in previous shader
half3 worldViewDir = normalize(UnityWorldSpaceViewDir(i.worldPos));
half3 worldRefl = reflect(-worldViewDir, worldNormal);
half4 skyData = UNITY_SAMPLE_TEXCUBE(unity_SpecCube0, worldRefl);
half3 skyColor = DecodeHDR (skyData, unity_SpecCube0_HDR);
fixed4 c = 0;
c.rgb = skyColor;
return c;
}
ENDCG
}
}
}
5.進一步改進
Shader "Unlit/More Textures"
{
Properties {
// three textures we'll use in the material
_MainTex("Base texture", 2D) = "white" {}
_OcclusionMap("Occlusion", 2D) = "white" {}
_BumpMap("Normal Map", 2D) = "bump" {}
}
SubShader
{
Pass
{
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
// exactly the same as in previous shader
struct v2f {
float3 worldPos : TEXCOORD0;
half3 tspace0 : TEXCOORD1;
half3 tspace1 : TEXCOORD2;
half3 tspace2 : TEXCOORD3;
float2 uv : TEXCOORD4;
float4 pos : SV_POSITION;
};
v2f vert (float4 vertex : POSITION, float3 normal : NORMAL, float4 tangent : TANGENT, float2 uv : TEXCOORD0)
{
v2f o;
o.pos = mul(UNITY_MATRIX_MVP, vertex);
o.worldPos = mul(_Object2World, vertex).xyz;
half3 wNormal = UnityObjectToWorldNormal(normal);
half3 wTangent = UnityObjectToWorldDir(tangent.xyz);
half tangentSign = tangent.w * unity_WorldTransformParams.w;
half3 wBitangent = cross(wNormal, wTangent) * tangentSign;
o.tspace0 = half3(wTangent.x, wBitangent.x, wNormal.x);
o.tspace1 = half3(wTangent.y, wBitangent.y, wNormal.y);
o.tspace2 = half3(wTangent.z, wBitangent.z, wNormal.z);
o.uv = uv;
return o;
}
// textures from shader properties
sampler2D _MainTex;
sampler2D _OcclusionMap;
sampler2D _BumpMap;
fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target
{
// same as from previous shader...
half3 tnormal = UnpackNormal(tex2D(_BumpMap, i.uv));
half3 worldNormal;
worldNormal.x = dot(i.tspace0, tnormal);
worldNormal.y = dot(i.tspace1, tnormal);
worldNormal.z = dot(i.tspace2, tnormal);
half3 worldViewDir = normalize(UnityWorldSpaceViewDir(i.worldPos));
half3 worldRefl = reflect(-worldViewDir, worldNormal);
half4 skyData = UNITY_SAMPLE_TEXCUBE(unity_SpecCube0, worldRefl);
half3 skyColor = DecodeHDR (skyData, unity_SpecCube0_HDR);
fixed4 c = 0;
c.rgb = skyColor;
// modulate sky color with the base texture, and the occlusion map
fixed3 baseColor = tex2D(_MainTex, i.uv).rgb;
fixed occlusion = tex2D(_OcclusionMap, i.uv).r;
c.rgb *= baseColor;
c.rgb *= occlusion;
return c;
}
ENDCG
}
}
}