常用集合之LinkedHashMap原始碼淺析
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-27
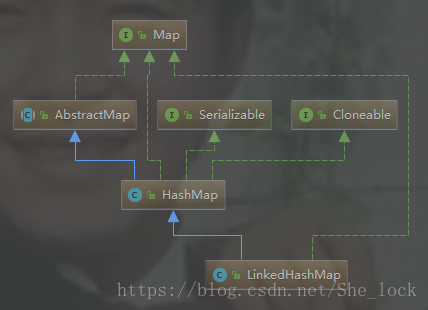
眾所周知 HashMap 是一個無序的 Map,因為每次根據 key 的 hashcode對映到Entry陣列上,所以遍歷出來的順序並不是寫入的順序。
因此 JDK 推出一個基於 HashMap 但具有順序的 LinkedHashMap 來解決有排序需求的場景。
它的底層是繼承於 HashMap實現的,由一個雙向連結串列所構成。
類圖
原始碼
資料結構
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V>
extends HashMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>
{
//繼承了HashMap 的靜態內部類HashMap.Node 其中HashMap.Node原始碼如下:
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { //單向連結串列
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
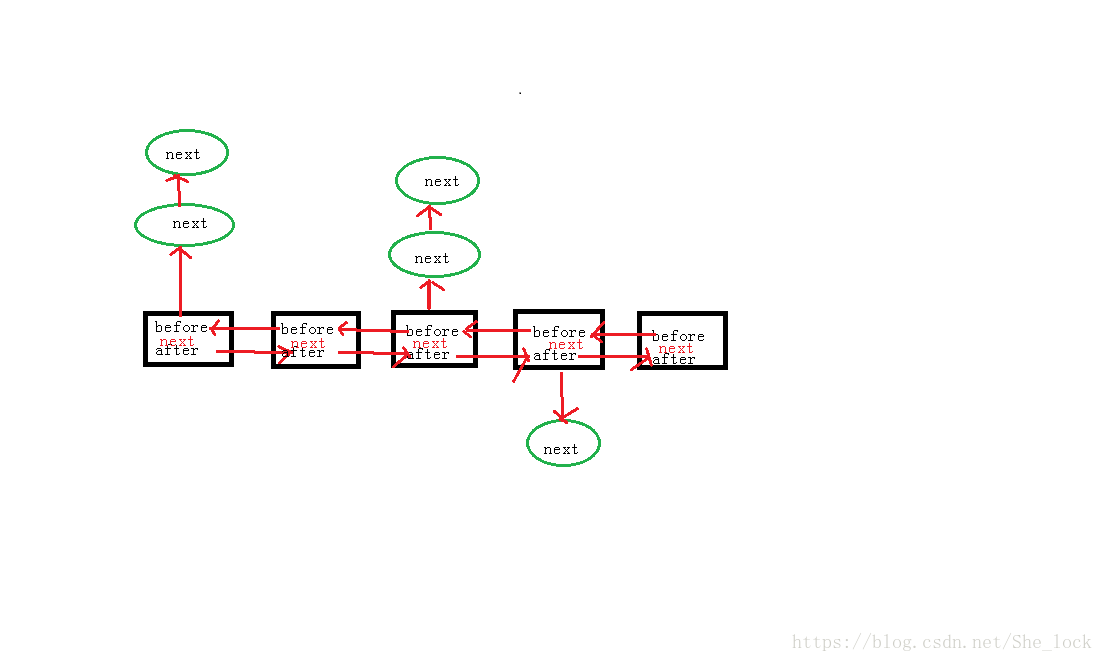
Node<K,V> next; //下一個節點 由原始碼可知,LinkedHashMap原本是一個雙向連結串列,但是,由於連結串列中裝有單向連結串列的節點HashMap.Node,所以就變成了雙向鏈中存放著單向鏈。
由此可得如下資料模型:
構造方法
public LinkedHashMap() {
super(); //這裡的super實際上就是HashMap的構造方法
accessOrder = false; //排序欄位預設為false
}
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
super(initialCapacity);
accessOrder = false;
}
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
accessOrder = false;
}
put方法
put方法依然繼承至HashMap。
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e); //排序,這個由子類實現
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}子類LinkedHashMap重寫afterNodeAccess方法,從而實現了排序功能:
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) { // move node to last
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last;
if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
p.after = null;
if (b == null)
head = a;
else
b.after = a;
if (a != null)
a.before = b;
else
last = b;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
tail = p;
++modCount;
}
}總的來說 LinkedHashMap 其實就是對 HashMap 進行了拓展,使用了雙向連結串列來保證了順序性。
因為是繼承與 HashMap 的,所以一些 HashMap 存在的問題 LinkedHashMap 也會存在,比如不支援併發等。
ps: 文末推薦其他幾篇有關集合的文章: