Java IO系列4 位元組流之PushbackInputStream
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-29
PushbackInputStream
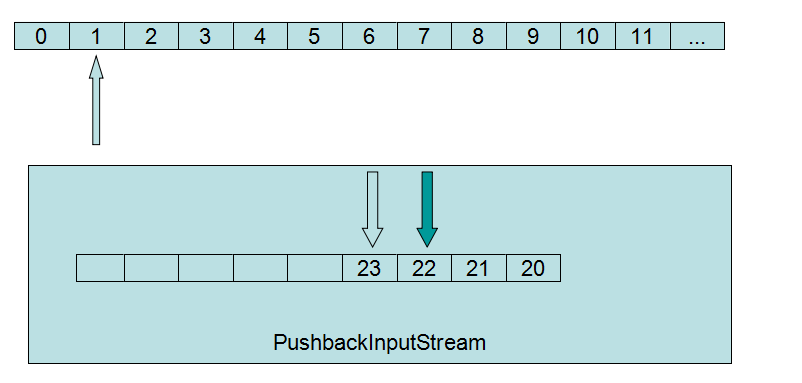
原理是在內部儲存一個位元組緩衝區,如果unRead一個位元組,就會向這個緩衝區倒著寫入資料,下一次read的時候,就會把該緩衝區裡的位元組讀取出來。
當緩衝區裡沒資料時,跟別的位元組輸入流一樣
但是當有資料時
例如:我們現在讀取1資料,這個時候unRead 4個位元組,順序是20、21、22、23
當我們再次read的時候順序是23、22、21、20、2
public class PushbackInputStream extends FilterInputStream { //回退緩衝區,預設1位元組 protected byte[] buf; //回退區中最前面一個數據的位置,回退是倒著來的buf[--pos] = X protected int pos; private void ensureOpen() throws IOException { if (in == null) throw new IOException("Stream closed"); } public PushbackInputStream(InputStream in, int size) { super(in); if (size <= 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("size <= 0"); } this.buf = new byte[size]; this.pos = size; } //預設1位元組的回退區 public PushbackInputStream(InputStream in) { this(in, 1); } //如果回退區中沒有資料,跟平常的位元組輸入流沒什麼兩樣。 //如果回退區中有資料,先把回退區的資料讀出來 public int read() throws IOException { ensureOpen(); if (pos < buf.length) { return buf[pos++] & 0xff; } return super.read(); } //最多讀取len個位元組資料到b[]位元組數組裡,起始位置off //返回最多讀到的資料 public int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException { ensureOpen(); if (b == null) { throw new NullPointerException(); } else if (off < 0 || len < 0 || len > b.length - off) { throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); } else if (len == 0) { return 0; } //檢查回退區是否還有位元組資料 int avail = buf.length - pos; if (avail > 0) { if (len < avail) { //如果回退區裡的可用資料比需要的len還多 //直接avail = len avail = len; } System.arraycopy(buf, pos, b, off, avail); pos += avail; off += avail; len -= avail; } //如果回退區裡的可用資料比需要的len還少,例如回退區裡有5個位元組可用,現在len是20, //那麼現在len == 15;就是說還要在資料流裡最多再讀取15個位元組(注意“最多”) if (len > 0) { len = super.read(b, off, len); if (len == -1) { return avail == 0 ? -1 : avail; } return avail + len; } return avail; } //把資料推到回退區中,注意是倒著的 public void unread(int b) throws IOException { ensureOpen(); if (pos == 0) { throw new IOException("Push back buffer is full"); } buf[--pos] = (byte)b; } public void unread(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException { ensureOpen(); if (len > pos) { throw new IOException("Push back buffer is full"); } pos -= len; System.arraycopy(b, off, buf, pos, len); } public void unread(byte[] b) throws IOException { unread(b, 0, b.length); } public int available() throws IOException { ensureOpen(); int n = buf.length - pos; int avail = super.available(); return n > (Integer.MAX_VALUE - avail) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : n + avail; } //跳過最多n個位元組,如果回退區中有資料,把回退區裡的資料也算上 public long skip(long n) throws IOException { ensureOpen(); if (n <= 0) { return 0; } long pskip = buf.length - pos; if (pskip > 0) { if (n < pskip) { pskip = n; } pos += pskip; n -= pskip; } if (n > 0) { pskip += super.skip(n); } return pskip; } public boolean markSupported() { return false; } public synchronized void mark(int readlimit) { } //不許重置,流裡的資料一旦讀取後,指標再也回不去了 public synchronized void reset() throws IOException { throw new IOException("mark/reset not supported"); } public synchronized void close() throws IOException { if (in == null) return; in.close(); in = null; buf = null; } }
String data = "PushbackInputStream"; ByteArrayInputStream in = new ByteArrayInputStream(data.getBytes()); PushbackInputStream inputStream = new PushbackInputStream(in, 4); int d; int count = 0; try { while ((d = inputStream.read())!=-1) { count++; if(count == 5){ inputStream.unread("push".getBytes()); } System.out.print((char)d); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
輸出結果:PushbpushackInputStream