求解二維和三維法向量的方法
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-30
二維曲線法向量的求解示例:
Here's an example using an analytic curve of y
= x^2
x = 0:0.1:1;
y = x.*x;
dy = gradient(y);
dx = gradient(x);
quiver(x,y,-dy,dx)
hold on; plot( x, y)
which gives:

三維三角面片頂點法向量的求解:頂點相鄰各個三角面片單位法向量的疊加。
The normal at a vertex should be computed as the normalised sum of all the unit length normals for each face the vertex shares. Consider the following image:
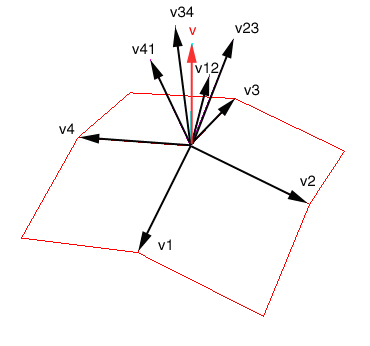
In the above image, v represents the normal at the center vertex. Each vij represents a normal for each face that shares the center vertex. So for instance v12 is the unit lenght normal for the bottom right face.
The vertex normal v is computed as the normalised sum of all vij vectors:
v = normalised(sum(v12, v23, v34, v41)) where vij = normalised(vi x vj) // normalised cross product
