實現Hello,World!的方式
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-01
實現Hello, world! 的方式:
先來幾個python的
(注:使用的是python3.6版本):
方式1:
使用python + reportlab庫 生成PDF檔案
from reportlab.graphics.shapes import Drawing, String from reportlab.graphics import renderPDF d = Drawing(860, 480) s = String(430, 240, 'Hello, world!', textAnchor='middle') s.fontSize = 100 d.add(s) renderPDF.drawToFile(d, 'hello.pdf', 'A simple PDF file')
執行後得到檔案 hello.pdf
開啟後看到:
方式2:
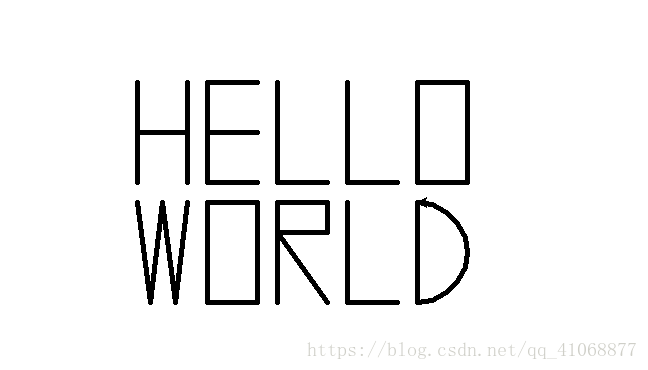
python + turtle庫(turtle是很好用的1個圖形庫)
注:執行此程式可看到畫圖的過程
import turtle as t #移動筆,而不在路徑中畫 def move_pen_to(t,x,y): t.up() t.goto(x,y) t.down() #畫H def drawH(x,y): move_pen_to(t, x, y) t.goto(x, y-100) move_pen_to(t, x, y-50) t.goto(x+50, y-50) move_pen_to(t,x+50,y) t.goto(x+50,y-100) #E def drawE(x,y): move_pen_to(t, x, y) t.goto(x+50, y) move_pen_to(t, x, y) t.goto(x, y-100) move_pen_to(t, x, y-50) t.goto(x+50, y-50) move_pen_to(t,x, y-100) t.goto(x+50, y-100) #畫L def drawL(x, y): move_pen_to(t,x,y) t.goto(x, y-100) t.goto(x+50, y-100) #畫O def drawO(x, y): move_pen_to(t,x,y) t.goto(x, y-100) t.goto(x+50, y-100) t.goto(x+50, y) t.goto(x,y) def drawW(x, y): move_pen_to(t, x, y) t.goto(x+(50/4),y-100) t.goto(x+(50/4)*2,y) t.goto(x+ (50/4)*3, y-100) t.goto(x+ (50/4)*4, y) def drawR(x,y): move_pen_to(t, x, y) t.goto(x+50,y) t.goto(x+50,y-30) t.goto(x, y-30) move_pen_to(t, x, y) t.goto(x, y-100) move_pen_to(t, x, y-30) t.goto(x+50, y-100) def drawD(x, y): move_pen_to(t, x, y) t.goto(x, y-100) t.circle(50,180) #設定寬度和速度 t.width(5) t.speed(2) #起點x,y x =-200 y = 200 drawH(x, y) drawE(x+50+20, y) drawL(x+50*2+20*2, y) drawL(x+50*3+20*3, y) drawO(x+50*4+20*4, y) line2 = y -100-20 drawW(x, line2) drawO(x+50+20, line2) drawR(x+50*2+20*2, line2) drawL(x+50*3+20*3, line2) drawD(x+50*4+20*4, line2)
方式3:python print()
print("Hello, world")方式4:C語言 printf()
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("Hello, world");
return 0;
}方式5:C++ cout
#include<iostream>
int main()
{
std::cout << "Hello, world";
return 0;
}方式6:C++ cout
#include<iostream> int main() { using std::cout; cout<< "HH HH\t" << "EEEEEEEEEE\t" << "LL \t" << "LL \t" << "OOOOOOOOOO\n" << "HH HH\t" << "EE \t" << "LL \t" << "LL \t" << "OO OO\n" << "HH HH\t" << "EE \t" << "LL \t" << "LL \t" << "OO OO\n" << "HHHHHHHHHH\t" << "EEEEEEEEEE\t" << "LL \t" << "LL \t" << "OO OO\n" << "HH HH\t" << "EE \t" << "LL \t" << "LL \t" << "OO OO\n" << "HH HH\t" << "EE \t" << "LL \t" << "LL \t" << "OO OO\n" << "HH HH\t" << "EEEEEEEEEE\t" << "LLLLLLLLLL\t" << "LLLLLLLLLL\t" << "OOOOOOOOOO\n"; cout<< "\n\n"; cout<< "WW WW WW\t" << "OOOOOOOOOO\t" << "RRRRRRRRRR\t" << "LL \t" << "DDDDDD\n" << "WW WW WW\t" << "OO OO\t" << "RR RR\t" << "LL \t" << "DD DD\n" << "WW WW WW\t" << "OO OO\t" << "RRRRRRRRRR\t" << "LL \t" << "DD DD\n" << "WW WW WW\t" << "OO OO\t" << "R RRR \t" << "LL \t" << "DD DD\n" << "WW WW WW\t" << "OO OO\t" << "R RRR \t" << "LL \t" << "DD DD\n" << "WW WW WW\t" << "OO OO\t" << "R RRR \t" << "LL \t" << "DD DD\n" << "WWWWWWWWWW\t" << "OOOOOOOOOO\t" << "R RRR\t" << "LLLLLLLLLL\t" << "DDDDDD\n"; system("pause"); return 0; }
方式7
Qt5
#include <QApplication>
#include <QLabel>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QApplication app(argc, argv);
QLabel label("Hello, world");
label.show();
return app.exec();
}