Shiro學習筆記(2)——身份驗證之Realm
環境準備
建立java工程
需要的jar包
- 大家也可以使用maven,參考官網
什麼是Realm
在我所看的學習資料中,關於Realm的定義,寫了整整一長串,但是對於初學者來說,看定義實在是太頭疼了。
對於什麼是Realm,我使用過之後,個人總結一下:shiro要進行身份驗證,就要從realm中獲取相應的身份資訊來進行驗證,簡單來說,我們可以自行定義realm,在realm中,從資料庫獲取身份資訊,然後和 使用者輸入的身份資訊進行匹配。這一切都由我們自己來定義。
為什麼要用Realm
在Shiro學習筆記(1)——shiro入門中,我們將身份資訊(使用者名稱/密碼/角色/許可權)寫在配置檔案中,但是實際開發中,這些身份資訊應該儲存在資料中,因此我們需要自定義Realm來從資料中獲取身份資訊,進行驗證。
自定義Realm
- 定義一個MyRealm,繼承
AuthorizingRealm
package com.shiro.realm;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import - 讓我們定義的Realm起作用,就要在配置檔案中配置(shiro-realm.ini)
#宣告一個realm
MyRealm1=com.shiro.realm.MyRealm1
#指定securityManager的realms實現
securityManager.realms=$MyRealm1- 測試
package com.shiro.realm;
import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.IncorrectCredentialsException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.LockedAccountException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UnknownAccountException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken;
import org.apache.shiro.config.IniSecurityManagerFactory;
import org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject;
import org.apache.shiro.util.Factory;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class Main {
private static final transient Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Main.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
//獲取SecurityManager的例項
Factory<SecurityManager> factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro-realm.ini");
SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance();
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
Subject currenUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//如果還未認證
if(!currenUser.isAuthenticated()){
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("admin","123");
token.setRememberMe(true);
try {
currenUser.login(token);
} catch (UnknownAccountException uae) {
log.info("沒有該使用者: " + token.getPrincipal());
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice) {
log.info( token.getPrincipal() + " 的密碼不正確!");
} catch (LockedAccountException lae) {
log.info( token.getPrincipal() + " 被鎖定 ,請聯絡管理員");
}catch (AuthenticationException ae) {
//其他未知的異常
}
}
if(currenUser.isAuthenticated())
log.info("使用者 "+currenUser.getPrincipal() +" 登入成功");
//是否有role1這個角色
if(currenUser.hasRole("role1")){
log.info("有角色role1");
}else{
log.info("沒有角色role1");
}
//是否有對印表機進行列印操作的許可權
if(currenUser.isPermitted("printer:print")){
log.info("可以對印表機進行列印操作");
}else {
log.info("不可以對印表機進行列印操作");
}
}
}
- 測試結果
從結果截圖中,我們可以看到,自定義的Realm中的
doGetAuthorizationInfo方法被呼叫了兩次,並且分別在currenUser.hasRole()和currenUser.isPermitted方法呼叫時呼叫
雜湊演算法支援
一般我們存入資料庫的密碼都是通過加密的,比如將“原密碼+鹽”進行一次或多次MD5計算,shiro提供了對雜湊演算法的支援
package com.shiro.realm;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection;
import org.apache.shiro.util.ByteSource;
public class UserRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
private String salt = "hehe";//鹽
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(
AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
//使用者輸入的使用者名稱
String username = (String) token.getPrincipal();
//如果資料庫中沒有這個使用者,則返回null,登入失敗
if(!username.equals("xiaozhou"))
return null;
//從資料庫中查詢密碼
String password = "42029a889cc26562c986346114c02367";
SimpleAuthenticationInfo info = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(username,
password, ByteSource.Util.bytes(salt), getName());
return info;
}
}
使用MD5的realm和一般的realm沒有太多區別,唯一的區別在於:不使用雜湊演算法(即對密碼加密)的話,從資料庫查詢出來的密碼是明文,否則查詢出來的是密文,我們沒法使用密文來直接比對判斷密碼是否正確,為了讓shiro自動幫我們先加密再比對,我們要在配置檔案ini中告訴shiro使用什麼演算法
[main]
#密碼匹配器
credentialsMatcher=org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.HashedCredentialsMatcher
#匹配器使用md5
credentialsMatcher.hashAlgorithmName=md5
#進行幾次雜湊(用md5演算法做幾次運算)
credentialsMatcher.hashIterations=1
#realm
userRealm=com.shiro.realm.UserRealm
#該realm使用的匹配器是哪個
userRealm.credentialsMatcher=$credentialsMatcher
#使用哪個realm
securityManager.realms=$userRealm多個Realm
有時候,我們需要進行多次身份驗證,我們可以定義多個Realm,如同流水線一樣,shiro會依次呼叫Realm
MyRealm1
package com.shiro.mutilrealm;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.IncorrectCredentialsException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UnknownAccountException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.SimpleAuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.Realm;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import com.shiro.realm.Main;
public class MyRealm1 extends AuthorizingRealm{
private static final transient Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Main.class);
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
String username = (String) getAvailablePrincipal(principals);
//通過使用者名稱從資料庫獲取許可權字串
SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
//許可權
Set<String> s = new HashSet<String>();
s.add("printer:print");
s.add("printer:query");
info.setStringPermissions(s);
//角色
Set<String> r = new HashSet<String>();
r.add("role1");
info.setRoles(r);
return info;
}
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(
AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
log.info("MyRealm1開始認證。。。。。。");
//使用者名稱
String username = (String) token.getPrincipal();
log.info("username:"+username);
//密碼
String password = new String((char[])token.getCredentials());
log.info("password:"+password);
//從資料庫獲取使用者名稱密碼進行匹配,這裡為了方面,省略資料庫操作
if(!"admin".equals(username)){
throw new UnknownAccountException();
}
if(!"123".equals(password)){
throw new IncorrectCredentialsException();
}
//身份驗證通過
AuthenticationInfo aInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(username,password,getName());
return aInfo;
}
}
- MyRealm2和MyRealm1 程式碼其實基本上是一樣的,直接複製一份即可。當然,如果有需求,我們可以自由地定義修改Realm。這裡只做個示例而已。
配置Authenticator和AuthenticationStrategy
這兩個東東是啥玩意?
上面我們配置了多個Realm進行身份驗證,假設一下:MyRealm1 驗證通過了,MyRealm2驗證不通過怎麼辦,這就需要定義一個驗證策略來處理這種情況。Strategy的意思就是策略。Authenticator就是驗證器
配置檔案(shiro-mutil-realm.ini)
#宣告一個realm
MyRealm1=com.shiro.mutilrealm.MyRealm1
MyRealm2=com.shiro.mutilrealm.MyRealm2
#配置驗證器
authenticator = org.apache.shiro.authc.pam.ModularRealmAuthenticator
#配置策略
# AllSuccessfulStrategy 表示 MyRealm1和MyRealm2 認證都通過才算通過
authcStrategy = org.apache.shiro.authc.pam.AllSuccessfulStrategy
#將驗證器和策略關聯起來
authenticator.authenticationStrategy = $authcStrategy
#配置驗證器所使用的Realm
authenticator.realms=$MyRealm2,$MyRealm1
#把Authenticator設定給securityManager
securityManager.authenticator = $authenticator
##########################################################################
# 1. AtLeastOneSuccessfulStrategy :如果一個(或更多)Realm 驗證成功,則整體的嘗試被認
# 為是成功的。如果沒有一個驗證成功,則整體嘗試失敗。
# 2. FirstSuccessfulStrategy 只有第一個成功地驗證的Realm 返回的資訊將被使用。所有進一步
# 的Realm 將被忽略。如果沒有一個驗證成功,則整體嘗試失敗
# 3. AllSucessfulStrategy 為了整體的嘗試成功,所有配置的Realm 必須驗證成功。如果沒有一
# 個驗證成功,則整體嘗試失敗。
# ModularRealmAuthenticator 預設的是AtLeastOneSuccessfulStrategy
###########################################################################
- 驗證的策略有三種,在配置檔案中我用註釋都寫好了,就不再詳細說明了
- 測試
package com.shiro.mutilrealm;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.IncorrectCredentialsException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.LockedAccountException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UnknownAccountException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken;
import org.apache.shiro.config.IniSecurityManagerFactory;
import org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject;
import org.apache.shiro.util.Factory;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class Main {
private static final transient Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Main.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
//獲取SecurityManager的例項
Factory<SecurityManager> factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro-mutil-realm.ini");
SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance();
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
Subject currenUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//如果還未認證
if(!currenUser.isAuthenticated()){
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("admin","123");
token.setRememberMe(true);
try {
currenUser.login(token);
} catch (UnknownAccountException uae) {
log.info("沒有該使用者: " + token.getPrincipal());
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice) {
log.info( token.getPrincipal() + " 的密碼不正確!");
} catch (LockedAccountException lae) {
log.info( token.getPrincipal() + " 被鎖定 ,請聯絡管理員");
}catch (AuthenticationException ae) {
//其他未知的異常
}
}
if(currenUser.isAuthenticated())
log.info("使用者 "+currenUser.getPrincipal() +" 登入成功");
//得到一個身份集合
PrincipalCollection principalCollection = currenUser.getPrincipals();
}
}
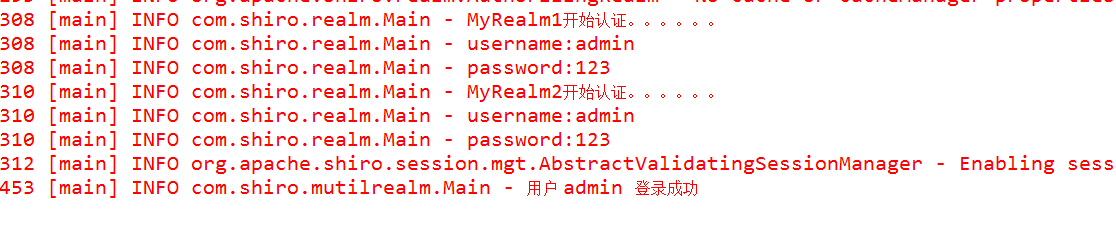
- 執行結果
結果很明顯,MyRealm1和MyRealm2依次執行
自定義AuthenticationStrategy(驗證策略)
- 上面我們使用了shiro自帶的AuthenticationStrategy,其實我們也可以自己定義。
package com.shiro.authenticationstrategy;
import java.util.Collection;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.pam.AbstractAuthenticationStrategy;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.Realm;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import com.shiro.realm.Main;
public class MyAuthenticationStrategy extends AbstractAuthenticationStrategy{
private static final transient Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyAuthenticationStrategy.class);
/**
* 所有Realm驗證之前呼叫
*/
@Override
public AuthenticationInfo beforeAllAttempts(
Collection<? extends Realm> realms, AuthenticationToken token)
throws AuthenticationException {
log.info("===============beforeAllAttempts方法被呼叫==================");
return super.beforeAllAttempts(realms, token);
}
/**
* 每一個Realm驗證之前呼叫
*/
@Override
public AuthenticationInfo beforeAttempt(Realm realm,
AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo aggregate)
throws AuthenticationException {
log.info("===============beforeAttempt方法被呼叫==================");
return super.beforeAttempt(realm, token, aggregate);
}
/**
* 每一個Realm驗證之後呼叫
*/
@Override
public AuthenticationInfo afterAttempt(Realm realm,
AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo singleRealmInfo,
AuthenticationInfo aggregateInfo, Throwable t)
throws AuthenticationException {
log.info("===============afterAttempt方法被呼叫==================");
return super.afterAttempt(realm, token, singleRealmInfo, aggregateInfo, t);
}
/**
* 所有Realm驗證之後呼叫
*/
@Override
public AuthenticationInfo afterAllAttempts(AuthenticationToken token,
AuthenticationInfo aggregate) throws AuthenticationException {
log.info("===============afterAllAttempts方法被呼叫==================");
return super.afterAllAttempts(token, aggregate);
}
}
我們所繼承的 AbstractAuthenticationStrategy 中,各個方法並不是抽象的,也就是說並一定要重寫,我們可以根據需求重寫需要的方法即可
配置檔案
要讓我們自定義的AuthenticationStrategy起作用,只要將上面配置檔案(shiro-mutil-realm.ini)中
authcStrategy = org.apache.shiro.authc.pam.AllSuccessfulStrategy
改為authcStrategy = com.shiro.authenticationstrategy.MyAuthenticationStrategy即可測試程式碼不變
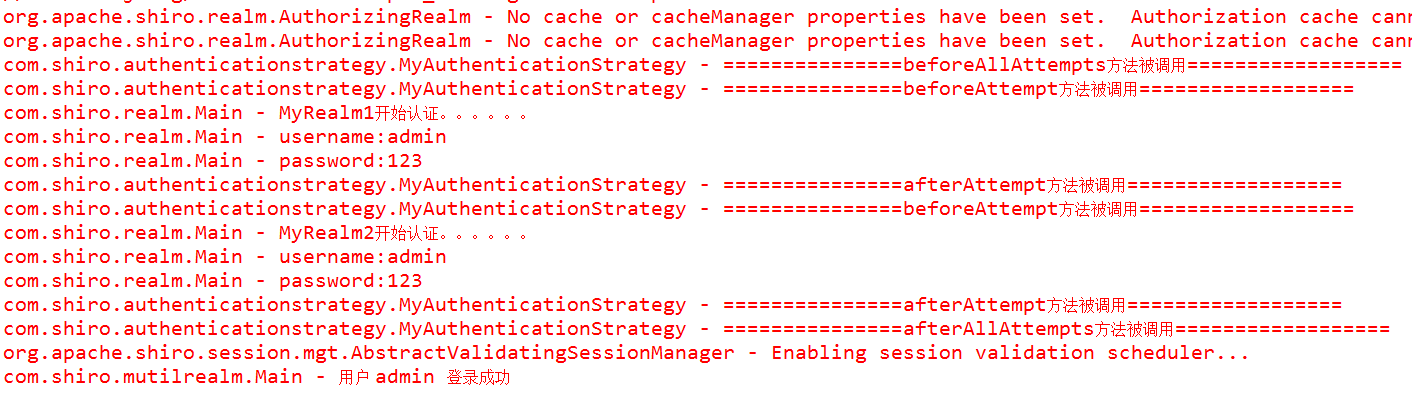
結果
從截圖中也可以清除的看到自定義的策略中,各個方法被呼叫的順序。有了這些,我們就可以隨心所欲的根據需求進行操作了
多個Realm驗證順序
隱式排列
- 當你配置多個realm的時候,處理的順序預設就是你配置的順序。
- 這種情況通常就是隻定義了realm,而沒有配置securityManager的realms
顯式排列
- 也就是顯示的配置securityManager.realms,那麼執行的順序就是你配置該值的realm的順序。
- 通常更推薦顯示排列。
我們可以簡單的理解為,多個Realm驗證的順序,就是我們配置的順序