冒泡、插入、選擇、快速排序演算法
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-03
氣泡排序:原理是臨近的數字兩兩進行比較,按照從小到大或者從大到小的順序進行交換,這樣一趟過去後,最大或最小的數字被交換到了最後一位,然後再從頭開始進行兩兩比較交換,直到倒數第二位時結束。
插入排序:它的工作原理是通過構建有序序列,對於未排序資料,在已排序序列中從後向前掃描,找到相應位置並插入;假設第一個元素排好,之後的元素對排好的部分從後向前比較並逐一移動。
選擇排序:從未排好的部分的第一個作為最小(最大)的,然後依次和剩餘的比較,如果有更小(更大)的,記下下標,以此作為新的最小(最大)值,繼續比較,一趟結束後,然後和第一個進行交換。
快速排序:快速排序採用了分而治之的思想,利用遞迴方法把大量資料劃分成多分小量資料進行排序;而涉及到的基準關鍵字是關鍵。
基準關鍵字的選取,基準關鍵字的選取是決定快速排序演算法的關鍵,常用的基準關鍵字的選取方式如下:
第一種:三者取中。將序列首、尾和中間位置上的記錄進行比較,選擇三者中值作為基準關鍵字。
第二種:取left和right之間的一個隨機數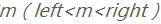
package com.kingcom.test; /** * @author CQling * @version 2017年10月17日 * */ public class MianSort { public static int[] bubbleSort(int[] sort) { int len=sort.length; int[] temp=sort; for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { for (int j = i+1; j < len; j++) { if (temp[i]<temp[j]) { int t = sort[i]; temp[i] = temp[j]; temp[j] = t; } } } return temp; } public static int[] insertSort(int[] sort) { int len=sort.length; int i,j,t; for (i = 1; i < len; i++) { t = sort[i]; for (j = i-1; j >=0&&t > sort[j]; j--) { sort[j+1] = sort[j]; } sort[j+1] = t; } return sort; } public static int[] selectSort(int[] sort) { int i,j,k,t; for (i = 0; i < sort.length; i++) { k=i; for (j = i+1; j < sort.length; j++) { if (sort[k]<sort[j]) { k=j; } } if (k!=i) { t=sort[i]; sort[i]=sort[k]; sort[k]=t; } } return sort; } public static int[] quickSort(int[] sort) { int low=0; int hight=sort.length-1; quickSort(low, hight, sort); return sort; } private static void quickSort(int low,int hight,int[] sort) { if (low>hight) { return; } int i=low,j=hight; int index = sort[i]; while (i<j) { while (i<j&&index>=sort[j]) { j--; } if (i<j) { sort[i++]=sort[j]; } while (i<j&&index<=sort[i]) { i++; } if (i<j) { sort[j--]=sort[i]; } } sort[i]=index; quickSort(low, i-1, sort); quickSort(i+1, hight, sort); } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] s = {2,1,4,5,3}; System.out.print("Sort Before:"); for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) { System.out.print(s[i]+" "); } System.out.println(""); System.out.print("InsertSort:"); int[] t = insertSort(s); for (int i = 0; i < t.length; i++) { System.out.print(t[i]+" "); } System.out.println(""); System.out.print("BubbleSort:"); int[] t1 = bubbleSort(s); for (int i = 0; i < t1.length; i++) { System.out.print(t1[i]+" "); } System.out.println(""); System.out.print("SelectSort:"); int[] t2 = selectSort(s); for (int i = 0; i < t2.length; i++) { System.out.print(t2[i]+" "); } System.out.println(""); System.out.print("QuickSort :"); int[] t3 = quickSort(s); for (int i = 0; i < t3.length; i++) { System.out.print(t3[i]+" "); } } }
