ListView動畫展開佈局 ExpandableLayout原始碼解析
專案結構
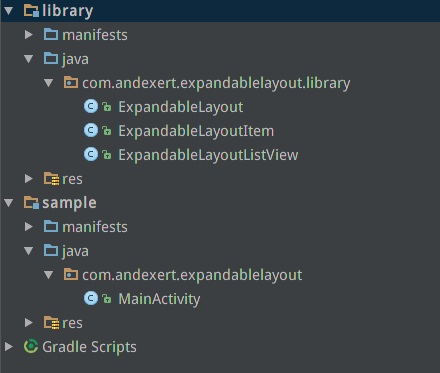
在library下面,定義了ExpandableLayout的原始碼。我們來看
ExpandableLayout: 繼承自RelativeLayout,實現了點選view向下出現要彈出的view的效果
ExpandableLayoutItem: ExpandableLayoutListView的item的view的型別
ExpandableLayoutListView: 實現了一個ListView,點選item會彈出一個下拉檢視,在點選一次檢視會收縮回去。
我們先來看ExpandableLayout.java的實現:
ExpandableLayout的實現
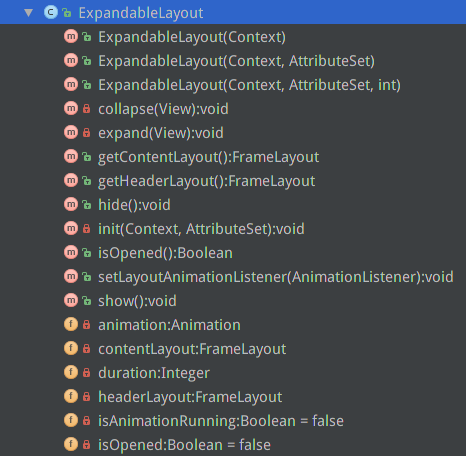
ExpandableLayout有幾個重要的方法:
1.collapse(final View v):下拉檢視消失
2.expand(final View v):展開下拉檢視
3.getContentLayout():得到下拉檢視
4.getHeaderLayout():得到item檢視
5.hide():隱藏下拉檢視,內部呼叫了collapse(final View v)函式
6.show():展開下拉檢視,內部呼叫了expand(final View v)函式
好了,現在我們從建構函式來一步一步的看
建構函式:
public ExpandableLayout(Context context)
{
super 可以看到,在構造中,呼叫了init()方法,我們來看一下init做了什麼
init()方法:
private void init(final Context context, AttributeSet attrs)
{
final View rootView = View.inflate(context, R.layout.view_expandable, this);
headerLayout = (FrameLayout) rootView.findViewById(R.id.view_expandable_headerlayout);
final TypedArray typedArray = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.ExpandableLayout);
final int headerID = typedArray.getResourceId(R.styleable.ExpandableLayout_el_headerLayout, -1);
final int contentID = typedArray.getResourceId(R.styleable.ExpandableLayout_el_contentLayout, -1);
contentLayout = (FrameLayout) rootView.findViewById(R.id.view_expandable_contentLayout);
if (headerID == -1 || contentID == -1)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("HeaderLayout and ContentLayout cannot be null!");
if (isInEditMode())
return;
duration = typedArray.getInt(R.styleable.ExpandableLayout_el_duration, getContext().getResources().getInteger(android.R.integer.config_shortAnimTime));
final View headerView = View.inflate(context, headerID, null);
headerView.setLayoutParams(new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT));
headerLayout.addView(headerView);
final View contentView = View.inflate(context, contentID, null);
contentView.setLayoutParams(new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT));
contentLayout.addView(contentView);
contentLayout.setVisibility(GONE);
headerLayout.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener()
{
@Override
public void onClick(View v)
{
if (!isAnimationRunning)
{
if (contentLayout.getVisibility() == VISIBLE)
collapse(contentLayout);
else
expand(contentLayout);
isAnimationRunning = true;
new Handler().postDelayed(new Runnable()
{
@Override
public void run()
{
isAnimationRunning = false;
}
}, duration);
}
}
});
typedArray.recycle();
}第一句
final View rootView = View.inflate(context, R.layout.view_expandable, this);載入R.layout.view_expandable佈局檔案到自己上,來看以下R.layout.view_expandable是怎麼定義的:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/view_expandable_headerlayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/view_expandable_contentLayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/view_expandable_headerlayout"/>
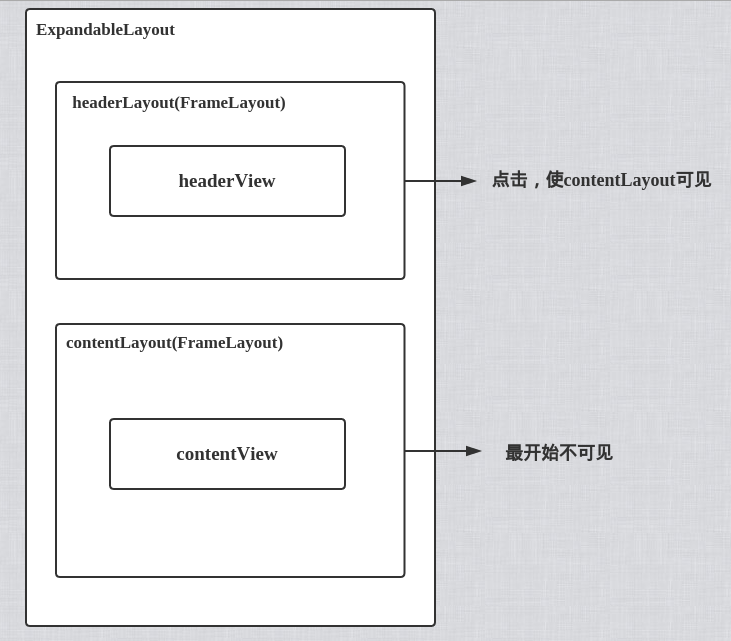
</RelativeLayout>一個RelativeLayout包裹了兩個FrameLayout,分別是headerLayout和contentLayout,其中,contentLayout在headerLayout的下面。
我們繼續看init()
headerLayout = (FrameLayout) rootView.findViewById(R.id.view_expandable_headerlayout);
final TypedArray typedArray = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.ExpandableLayout);
final int headerID = typedArray.getResourceId(R.styleable.ExpandableLayout_el_headerLayout, -1);
final int contentID = typedArray.getResourceId(R.styleable.ExpandableLayout_el_contentLayout, -1);
contentLayout = (FrameLayout) rootView.findViewById(R.id.view_expandable_contentLayout);分別通過findViewById得到headerLayout和contentLayout,
同時,如下,得到了headerID和contentID,headerID和contentID是在attr.xml中定義的。
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="ExpandableLayout">
<attr name="el_headerLayout" format="reference"/>
<attr name="el_contentLayout" format="reference" />
<attr name="el_duration" format="integer" />
</declare-styleable>
</resources>繼續init函式
duration = typedArray.getInt(R.styleable.ExpandableLayout_el_duration, getContext().getResources().getInteger(android.R.integer.config_shortAnimTime));得到duration,它表示下拉和收起下拉檢視時動畫執行的時間。
final View headerView = View.inflate(context, headerID, null);
headerView.setLayoutParams(new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT));
headerLayout.addView(headerView);
final View contentView = View.inflate(context, contentID, null);
contentView.setLayoutParams(new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT));
contentLayout.addView(contentView);
contentLayout.setVisibility(GONE);這一段程式碼,通過headerID和contentID得到headerView和contentView,並且把headerView新增到headerLayout中,把contentView新增到contentLayout中。設定contentLayout不可見。
到此,該view的結構如圖:
好了,繼續看init()
headerLayout.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener()
{
@Override
public void onClick(View v)
{
if (!isAnimationRunning)
{
if (contentLayout.getVisibility() == VISIBLE)
collapse(contentLayout);
else
expand(contentLayout);
isAnimationRunning = true;
new Handler().postDelayed(new Runnable()
{
@Override
public void run()
{
isAnimationRunning = false;
}
}, duration);
}
}
});
typedArray.recycle();這段程式碼,為headerLayout設定點選事件,點選的時候,如果contentLayout可見,就執行collapse,否則執行expand,並且duration之後執行handler.
到此,init()方法結束。我們開看collapse()方法和expand方法
collapse()方法:
private void collapse(final View v)
{
final int initialHeight = v.getMeasuredHeight();
animation = new Animation()
{
@Override
protected void applyTransformation(float interpolatedTime, Transformation t) {
//在繪製動畫的過程中會反覆的呼叫applyTransformation函式,
// 每次呼叫引數interpolatedTime值都會變化,該引數從0漸 變為1,當該引數為1時表明動畫結束
if(interpolatedTime == 1) //動畫結束
{
v.setVisibility(View.GONE);
isOpened = false;
}
else{
v.getLayoutParams().height = initialHeight - (int)(initialHeight * interpolatedTime);
v.requestLayout();
}
}
@Override
public boolean willChangeBounds() {
return true;
}
};
animation.setDuration(duration);
v.startAnimation(animation);
}程式碼就是執行了一個動畫,使contentLayout的LayoutParams的height不斷變小,最後動畫結束的時候,contentLayout設定為不可見。
expand()方法
private void expand(final View v)
{
v.measure(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
final int targetHeight = v.getMeasuredHeight();
v.getLayoutParams().height = 0;
v.setVisibility(VISIBLE);
animation = new Animation()
{
@Override
protected void applyTransformation(float interpolatedTime, Transformation t)
{
if (interpolatedTime == 1)
isOpened = true;
v.getLayoutParams().height = (interpolatedTime == 1) ? LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT : (int) (targetHeight * interpolatedTime);
v.requestLayout();
}
@Override
public boolean willChangeBounds() {
return true;
}
};
animation.setDuration(duration);
v.startAnimation(animation);
}與collapse相反,expand執行了一段動畫,在動畫執行前使contentLayout可見,動畫執行過程中不斷增加contentLayout的LayoutParams的height。
值得注意的是,在collpase和expand函式中,我們一直用isOpen來標誌contentLayout是否已經完全看見。
好了,以上就是ExpandableLayout的原始碼解析。
ExpandableLayoutItem
與ExpandableLayout相似,我們來看ExpandableLayoutItem.
與ExpandableLayout的大部分程式碼都一樣,主要的不同在於init()函式的最後有setOnClickListenr改為setOnTouchListener
headerLayout.setOnTouchListener(new OnTouchListener()
{
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event)
{
if (isOpened() && event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP)
{
hide();
closeByUser = true;
}
return isOpened() && event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN;
}
});
ExpandableLayoutListView
public class ExpandableLayoutListView extends ListView
{
private Integer position = -1;
public ExpandableLayoutListView(Context context)
{
super(context);
setOnScrollListener(new OnExpandableLayoutScrollListener());
}
public ExpandableLayoutListView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs)
{
super(context, attrs);
setOnScrollListener(new OnExpandableLayoutScrollListener());
}
public ExpandableLayoutListView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle)
{
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
setOnScrollListener(new OnExpandableLayoutScrollListener());
}
@Override
public boolean performItemClick(View view, int position, long id)
{
this.position = position;
for (int index = 0; index < getChildCount(); ++index)
{
if (index != (position - getFirstVisiblePosition()))
{
ExpandableLayoutItem currentExpandableLayout = (ExpandableLayoutItem) getChildAt(index).findViewWithTag(ExpandableLayoutItem.class.getName());
currentExpandableLayout.hide();
}
}
ExpandableLayoutItem expandableLayout = (ExpandableLayoutItem) getChildAt(position - getFirstVisiblePosition()).findViewWithTag(ExpandableLayoutItem.class.getName());
if (expandableLayout.isOpened())
expandableLayout.hide();
else
expandableLayout.show();
return super.performItemClick(view, position, id);
}
@Override
public void setOnScrollListener(OnScrollListener l)
{
if (!(l instanceof OnExpandableLayoutScrollListener))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("OnScrollListner must be an OnExpandableLayoutScrollListener");
super.setOnScrollListener(l);
}
public class OnExpandableLayoutScrollListener implements OnScrollListener
{
private int scrollState = 0;
@Override
public void onScrollStateChanged(AbsListView view, int scrollState)
{
this.scrollState = scrollState;
}
@Override
public void onScroll(AbsListView view, int firstVisibleItem, int visibleItemCount, int totalItemCount)
{
if (scrollState != SCROLL_STATE_IDLE)
{
for (int index = 0; index < getChildCount(); ++index)
{
ExpandableLayoutItem currentExpandableLayout = (ExpandableLayoutItem) getChildAt(index).findViewWithTag(ExpandableLayoutItem.class.getName());
if (currentExpandableLayout.isOpened() && index != (position - getFirstVisiblePosition()))
{
currentExpandableLayout.hideNow();
}
else if (!currentExpandableLayout.getCloseByUser() && !currentExpandableLayout.isOpened() && index == (position - getFirstVisiblePosition()))
{
currentExpandableLayout.showNow();
}
}
}
}
}
}ExpandableLayoutListView程式碼主要的部分就是onScrollListener和performItemClick.我們一個一個來看。
performItemClick
for (int index = 0; index < getChildCount(); ++index)
{
if (index != (position - getFirstVisiblePosition()))
{
ExpandableLayoutItem currentExpandableLayout = (ExpandableLayoutItem) getChildAt(index).findViewWithTag(ExpandableLayoutItem.class.getName());
currentExpandableLayout.hide();
}
}這段程式碼,迴圈遍歷所有的item,使所有的item的contentLayout收起。
ExpandableLayoutItem expandableLayout = (ExpandableLayoutItem) getChildAt(position - getFirstVisiblePosition()).findViewWithTag(ExpandableLayoutItem.class.getName());
if (expandableLayout.isOpened())
expandableLayout.hide();
else
expandableLayout.show();這段程式碼,得到點選的item view,如果是開啟的,就關閉,如果是關閉的,就開啟。
onScrollListener
public class OnExpandableLayoutScrollListener implements OnScrollListener
{
private int scrollState = 0;
@Override
public void onScrollStateChanged(AbsListView view, int scrollState)
{
this.scrollState = scrollState;
}
@Override
public void onScroll(AbsListView view, int firstVisibleItem, int visibleItemCount, int totalItemCount)
{
if (scrollState != SCROLL_STATE_IDLE)
{
for (int index = 0; index < getChildCount(); ++index)
{
ExpandableLayoutItem currentExpandableLayout = (ExpandableLayoutItem) getChildAt(index).findViewWithTag(ExpandableLayoutItem.class.getName());
if (currentExpandableLayout.isOpened() && index != (position - getFirstVisiblePosition()))
{
currentExpandableLayout.hideNow();
}
else if (!currentExpandableLayout.getCloseByUser() && !currentExpandableLayout.isOpened() && index == (position - getFirstVisiblePosition()))
{
currentExpandableLayout.showNow();
}
}
}
}
}我們看onScroll方法內的操作。
if (scrollState != SCROLL_STATE_IDLE)如果在滾動狀態,進行操作。
for (int index = 0; index < getChildCount(); ++index)
{
ExpandableLayoutItem currentExpandableLayout = (ExpandableLayoutItem) getChildAt(index).findViewWithTag(ExpandableLayoutItem.class.getName());
if (currentExpandableLayout.isOpened() && index != (position - getFirstVisiblePosition()))
{
currentExpandableLayout.hideNow();
}
else if (!currentExpandableLayout.getCloseByUser() && !currentExpandableLayout.isOpened() && index == (position - getFirstVisiblePosition()))
{
currentExpandableLayout.showNow();
}
}遍歷所有的item.
如果item view是開啟的,但是不在螢幕內,就關閉了。
如果在螢幕內的item view不是由使用者關閉的,就顯示開啟狀態。