Java常用類庫--Arrays、比較器(comparable、Comparator)
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-05
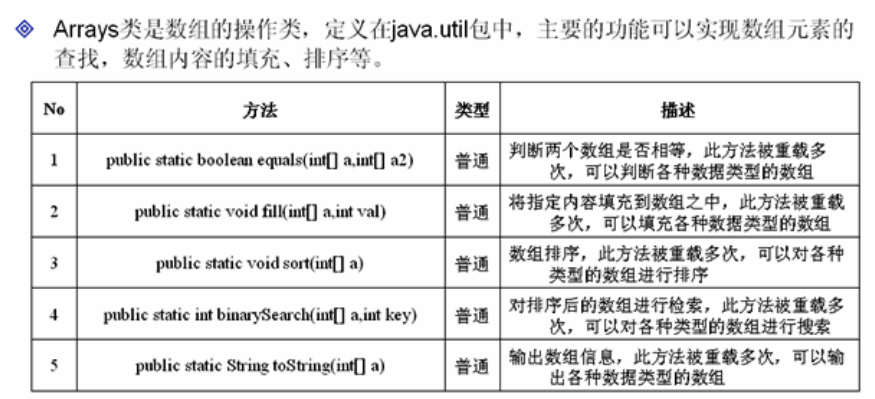
1、Arrays類
Arrays表示陣列的操作類,直接定義在java.util包中
import java.util.* ; public class ArraysDemo{ public static void main(String arg[]){ int temp[] = {3,4,5,7,9,1,2,6,8} ; // 宣告一個整型陣列 Arrays.sort(temp) ; // 進行排序的操作 System.out.print("排序後的陣列:") ; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(temp)) ; // 以字串輸出陣列 // 如果要想使用二分法查詢的話,則必須是排序之後的陣列 int point = Arrays.binarySearch(temp,3) ; // 檢索位置 System.out.println("元素‘3’的位置在:" + point) ; Arrays.fill(temp,3) ;// 填充陣列 System.out.print("陣列填充:") ; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(temp)) ; } };
2、Comparable介面的作用


class Student implements Comparable<Student> { // 指定型別為Student private String name ; private int age ; private float score ; public Student(String name,int age,float score){ this.name = name ; this.age = age ; this.score = score ; } public String toString(){ return name + "\t\t" + this.age + "\t\t" + this.score ; } public int compareTo(Student stu){ // 覆寫compareTo()方法,實現排序規則的應用 if(this.score>stu.score){ return -1 ; }else if(this.score<stu.score){ return 1 ; }else{ if(this.age>stu.age){ return 1 ; }else if(this.age<stu.age){ return -1 ; }else{ return 0 ; } } } }; public class ComparableDemo01{ public static void main(String args[]){ Student stu[] = {new Student("張三",20,90.0f), new Student("李四",22,90.0f),new Student("王五",20,99.0f), new Student("趙六",20,70.0f),new Student("孫七",22,100.0f)} ; java.util.Arrays.sort(stu) ; // 進行排序操作 for(int i=0;i<stu.length;i++){ // 迴圈輸出陣列中的內容 System.out.println(stu[i]) ; } } };

3、分析比較器的排序原理
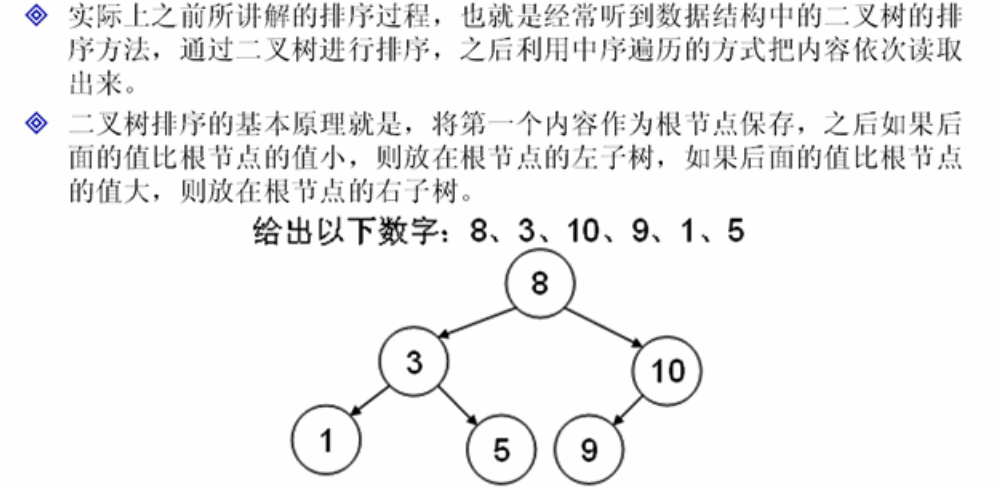
下面自己手工實現一個二叉樹的比較演算法。
為了操作方便,此處使用Integer類完成。
public class ComparableDemo02{
public static void main(String args[]){
Comparable com = null ; // 宣告一個Comparable介面物件
com = 30 ; // 通過Integer為Comparable例項化
System.out.println("內容為:" + com) ; // 呼叫的是toString()方法
}
};class BinaryTree{ class Node{ // 宣告一個節點類 private Comparable data ; // 儲存具體的內容 private Node left ; // 儲存左子樹 private Node right ; // 儲存右子樹 public Node(Comparable data){ this.data = data ; } public void addNode(Node newNode){ // 確定是放在左子樹還是右子樹 if(newNode.data.compareTo(this.data)<0){ // 內容小,放在左子樹 if(this.left==null){ this.left = newNode ; // 直接將新的節點設定成左子樹 }else{ this.left.addNode(newNode) ; // 繼續向下判斷 } } if(newNode.data.compareTo(this.data)>=0){ // 放在右子樹 if(this.right==null){ this.right = newNode ; // 沒有右子樹則將此節點設定成右子樹 }else{ this.right.addNode(newNode) ; // 繼續向下判斷 } } } public void printNode(){ // 輸出的時候採用中序遍歷 if(this.left!=null){ this.left.printNode() ; // 輸出左子樹 } System.out.print(this.data + "\t") ; if(this.right!=null){ this.right.printNode() ; } } }; private Node root ; // 根元素 public void add(Comparable data){ // 加入元素 Node newNode = new Node(data) ; // 定義新的節點 if(root==null){ // 沒有根節點 root = newNode ; // 第一個元素作為根節點 }else{ root.addNode(newNode) ; // 確定是放在左子樹還是放在右子樹 } } public void print(){ this.root.printNode() ; // 通過根節點輸出 } }; public class ComparableDemo03{ public static void main(String args[]){ BinaryTree bt = new BinaryTree() ; bt.add(8) ; bt.add(3) ; bt.add(3) ; bt.add(10) ; bt.add(9) ; bt.add(1) ; bt.add(5) ; bt.add(5) ; System.out.println("排序之後的結果:") ; bt.print() ; } };
4、Comparator比較器

import java.util.* ;
class Student{ // 指定型別為Student
private String name ;
private int age ;
public Student(String name,int age){
this.name = name ;
this.age = age ;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj){ // 覆寫equals方法
if(this==obj){
return true ;
}
if(!(obj instanceof Student)){
return false ;
}
Student stu = (Student) obj ;
if(stu.name.equals(this.name)&&stu.age==this.age){
return true ;
}else{
return false ;
}
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name ;
}
public void setAge(int age){
this.age = age ;
}
public String getName(){
return this.name ;
}
public int getAge(){
return this.age ;
}
public String toString(){
return name + "\t\t" + this.age ;
}
};
class StudentComparator implements Comparator<Student>{ // 實現比較器
// 因為Object類中本身已經有了equals()方法
public int compare(Student s1,Student s2){
if(s1.equals(s2)){
return 0 ;
}else if(s1.getAge()<s2.getAge()){ // 按年齡比較
return 1 ;
}else{
return -1 ;
}
}
};
public class ComparatorDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
Student stu[] = {new Student("張三",20),
new Student("李四",22),new Student("王五",20),
new Student("趙六",20),new Student("孫七",22)} ;
java.util.Arrays.sort(stu,new StudentComparator()) ; // 進行排序操作
for(int i=0;i<stu.length;i++){ // 迴圈輸出陣列中的內容
System.out.println(stu[i]) ;
}
}
};