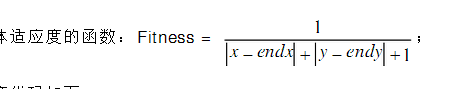遺傳演算法在走迷宮遊戲中的應用
前言
遺傳(GA)演算法是一個非常有意思的演算法,因為他利用了生物進化理論的知識進行問題的求解。演算法的核心就是把擁有更好環境適應度的基因遺傳給下一代,這就是其中的關鍵的選擇操作,遺傳演算法整體的階段分為選擇,交叉和變異操作,選擇操作和變異操作在其中又是比較重要的步驟。本篇文章不會講述GA演算法的具體細節,之前我曾經寫過一篇專門的文章介紹過此演算法,連結:http://blog.csdn.net/androidlushangderen/article/details/44041499,裡面介紹了一些基本的概念和演算法的原理過程,如果你對GA演算法掌握的還不錯的話,那麼對於理解後面遺傳演算法在走迷宮的應用來說應該不是難事。
演算法在迷宮遊戲中的應用
先說說走迷宮遊戲要解決的問題是什麼, 走迷宮遊戲說白了就是給定起點,終點,中間設定一堆的障礙,然後要求可達的路徑,注意這裡指的是可達路徑,並沒有說一定是最優路徑,因為最優路徑一定是用步數最少的,這一點還是很不同的。而另一方面,遺傳演算法也是用來搜尋問題最優解的,所以剛剛好可以轉移到這個問題上。用一個遺傳演算法去解決生活中的實際問題最關鍵的就是如何用遺傳演算法中的概念表示出來,比如遺傳演算法中核心的幾個概念,基因編碼,基因長度的設定,適應度函式的定義,3個概念每個都很重要。好的,目的要求已經慢慢的明確了,下面一個個問題的解決。
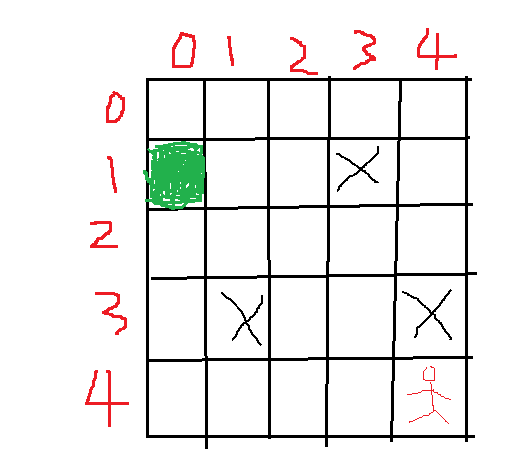
為了能讓大家更好的理解,下面舉出一個例子,如圖所示:
圖是自己做的,比較簡略,以左邊點的形式表示,從圖中可以看出,起點位置(4, 4),出口左邊為綠色區域位置(1,0),X符號表示的障礙區域,不允許經過,問題就轉為搜尋出從起點到終點位置的最短路徑,因為本身例子構造的不是很複雜,我們按照對角線的方式出發,總共的步數=4-1 + 4-0=7步,只要中間不拐彎,每一步都是靠近目標點方向的移動就是最佳的方式。下面看看如何轉化成遺傳演算法中的概念表示。
個體基因長度
首先是基於長度,因為最後篩選出的是一個個體,就是滿足條件的個體,他的基因編碼就是問題的最優解,所以就能聯想把角色的每一步移動操作看出是一個基因編碼,總共7步就需要7個基因值表示,所以基因的長度在本例子中就是7。
基因表示
已經將角色的每一次的移動步驟轉化為基因的表示,每次的移動總共有4種可能,上下左右,基因編碼是標準的二進位制形式,所以可以取值為00代表向上,01向下,10向左,11向右,也就是說,每個基因組用2個編碼表示,所以總共的編碼數字就是2*7=14個,兩兩一對。
適應度函式
適應度函式的設定應該是在遺傳演算法中最重要了吧,以為他的設定好壞直接決定著遺傳質量的好壞,基因組表示的移動的操作步驟,給定起點位置,通過基因組的編碼組資料,我們可以計算出最終的抵達座標,這裡可以很容易的得出結論,如果最後的抵達座標越接近出口座標,就越是我們想要的結果,也就是適應值越高,所以我們可以用下面的公式作為適應度函式:
(x, y)為計算出的適應值的函式值在0到1之間波動,1為最大值,就是抵達的座標恰好是出口位置的時候,當然適應度函式的表示不是唯一的。
演算法的程式碼實現
演算法地圖資料的輸入mapData.txt:
0 0 0 0 0
2 0 0 -1 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 -1 0 0 -1
0 0 0 0 1
就是上面圖示的那個例子.
演算法的主要實現類GATool.java:
package GA_Maze;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.text.MessageFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* 遺傳演算法在走迷宮遊戲的應用-遺傳演算法工具類
*
* @author lyq
*
*/
public class GATool {
// 迷宮出入口標記
public static final int MAZE_ENTRANCE_POS = 1;
public static final int MAZE_EXIT_POS = 2;
// 方向對應的編碼陣列
public static final int[][] MAZE_DIRECTION_CODE = new int[][] { { 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1 }, { 1, 0 }, { 1, 1 }, };
// 座標點方向改變
public static final int[][] MAZE_DIRECTION_CHANGE = new int[][] {
{ -1, 0 }, { 1, 0 }, { 0, -1 }, { 0, 1 }, };
// 方向的文字描述
public static final String[] MAZE_DIRECTION_LABEL = new String[] { "上",
"下", "左", "右" };
// 地圖資料檔案地址
private String filePath;
// 走迷宮的最短步數
private int stepNum;
// 初始個體的數量
private int initSetsNum;
// 迷宮入口位置
private int[] startPos;
// 迷宮出口位置
private int[] endPos;
// 迷宮地圖資料
private int[][] mazeData;
// 初始個體集
private ArrayList<int[]> initSets;
// 隨機數產生器
private Random random;
public GATool(String filePath, int initSetsNum) {
this.filePath = filePath;
this.initSetsNum = initSetsNum;
readDataFile();
}
/**
* 從檔案中讀取資料
*/
public void readDataFile() {
File file = new File(filePath);
ArrayList<String[]> dataArray = new ArrayList<String[]>();
try {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String str;
String[] tempArray;
while ((str = in.readLine()) != null) {
tempArray = str.split(" ");
dataArray.add(tempArray);
}
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.getStackTrace();
}
int rowNum = dataArray.size();
mazeData = new int[rowNum][rowNum];
for (int i = 0; i < rowNum; i++) {
String[] data = dataArray.get(i);
for (int j = 0; j < data.length; j++) {
mazeData[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(data[j]);
// 賦值入口和出口位置
if (mazeData[i][j] == MAZE_ENTRANCE_POS) {
startPos = new int[2];
startPos[0] = i;
startPos[1] = j;
} else if (mazeData[i][j] == MAZE_EXIT_POS) {
endPos = new int[2];
endPos[0] = i;
endPos[1] = j;
}
}
}
// 計算走出迷宮的最短步數
stepNum = Math.abs(startPos[0] - endPos[0])
+ Math.abs(startPos[1] - endPos[1]);
}
/**
* 產生初始資料集
*/
private void produceInitSet() {
// 方向編碼
int directionCode = 0;
random = new Random();
initSets = new ArrayList<>();
// 每個步驟的操作需要用2位數字表示
int[] codeNum;
for (int i = 0; i < initSetsNum; i++) {
codeNum = new int[stepNum * 2];
for (int j = 0; j < stepNum; j++) {
directionCode = random.nextInt(4);
codeNum[2 * j] = MAZE_DIRECTION_CODE[directionCode][0];
codeNum[2 * j + 1] = MAZE_DIRECTION_CODE[directionCode][1];
}
initSets.add(codeNum);
}
}
/**
* 選擇操作,把適值較高的個體優先遺傳到下一代
*
* @param initCodes
* 初始個體編碼
* @return
*/
private ArrayList<int[]> selectOperate(ArrayList<int[]> initCodes) {
double randomNum = 0;
double sumFitness = 0;
ArrayList<int[]> resultCodes = new ArrayList<>();
double[] adaptiveValue = new double[initSetsNum];
for (int i = 0; i < initSetsNum; i++) {
adaptiveValue[i] = calFitness(initCodes.get(i));
sumFitness += adaptiveValue[i];
}
// 轉成概率的形式,做歸一化操作
for (int i = 0; i < initSetsNum; i++) {
adaptiveValue[i] = adaptiveValue[i] / sumFitness;
}
for (int i = 0; i < initSetsNum; i++) {
randomNum = random.nextInt(100) + 1;
randomNum = randomNum / 100;
//因為1.0是無法判斷到的,,總和會無限接近1.0取為0.99做判斷
if(randomNum == 1){
randomNum = randomNum - 0.01;
}
sumFitness = 0;
// 確定區間
for (int j = 0; j < initSetsNum; j++) {
if (randomNum > sumFitness
&& randomNum <= sumFitness + adaptiveValue[j]) {
// 採用拷貝的方式避免引用重複
resultCodes.add(initCodes.get(j).clone());
break;
} else {
sumFitness += adaptiveValue[j];
}
}
}
return resultCodes;
}
/**
* 交叉運算
*
* @param selectedCodes
* 上步驟的選擇後的編碼
* @return
*/
private ArrayList<int[]> crossOperate(ArrayList<int[]> selectedCodes) {
int randomNum = 0;
// 交叉點
int crossPoint = 0;
ArrayList<int[]> resultCodes = new ArrayList<>();
// 隨機編碼佇列,進行隨機交叉配對
ArrayList<int[]> randomCodeSeqs = new ArrayList<>();
// 進行隨機排序
while (selectedCodes.size() > 0) {
randomNum = random.nextInt(selectedCodes.size());
randomCodeSeqs.add(selectedCodes.get(randomNum));
selectedCodes.remove(randomNum);
}
int temp = 0;
int[] array1;
int[] array2;
// 進行兩兩交叉運算
for (int i = 1; i < randomCodeSeqs.size(); i++) {
if (i % 2 == 1) {
array1 = randomCodeSeqs.get(i - 1);
array2 = randomCodeSeqs.get(i);
crossPoint = random.nextInt(stepNum - 1) + 1;
// 進行交叉點位置後的編碼調換
for (int j = 0; j < 2 * stepNum; j++) {
if (j >= 2 * crossPoint) {
temp = array1[j];
array1[j] = array2[j];
array2[j] = temp;
}
}
// 加入到交叉運算結果中
resultCodes.add(array1);
resultCodes.add(array2);
}
}
return resultCodes;
}
/**
* 變異操作
*
* @param crossCodes
* 交叉運算後的結果
* @return
*/
private ArrayList<int[]> variationOperate(ArrayList<int[]> crossCodes) {
// 變異點
int variationPoint = 0;
ArrayList<int[]> resultCodes = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] array : crossCodes) {
variationPoint = random.nextInt(stepNum);
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i += 2) {
// 變異點進行變異
if (i % 2 == 0 && i / 2 == variationPoint) {
array[i] = (array[i] == 0 ? 1 : 0);
array[i + 1] = (array[i + 1] == 0 ? 1 : 0);
break;
}
}
resultCodes.add(array);
}
return resultCodes;
}
/**
* 根據編碼計算適值
*
* @param code
* 當前的編碼
* @return
*/
public double calFitness(int[] code) {
double fintness = 0;
// 由編碼計算所得的終點橫座標
int endX = 0;
// 由編碼計算所得的終點縱座標
int endY = 0;
// 基於片段所代表的行走方向
int direction = 0;
// 臨時座標點橫座標
int tempX = 0;
// 臨時座標點縱座標
int tempY = 0;
endX = startPos[0];
endY = startPos[1];
for (int i = 0; i < stepNum; i++) {
direction = binaryArrayToNum(new int[] { code[2 * i],
code[2 * i + 1] });
// 根據方向改變陣列做座標點的改變
tempX = endX + MAZE_DIRECTION_CHANGE[direction][0];
tempY = endY + MAZE_DIRECTION_CHANGE[direction][1];
// 判斷座標點是否越界
if (tempX >= 0 && tempX < mazeData.length && tempY >= 0
&& tempY < mazeData[0].length) {
// 判斷座標點是否走到阻礙塊
if (mazeData[tempX][tempY] != -1) {
endX = tempX;
endY = tempY;
}
}
}
// 根據適值函式進行適值的計算
fintness = 1.0 / (Math.abs(endX - endPos[0])
+ Math.abs(endY - endPos[1]) + 1);
return fintness;
}
/**
* 根據當前編碼判斷是否已經找到出口位置
*
* @param code
* 經過若干次遺傳的編碼
* @return
*/
private boolean ifArriveEndPos(int[] code) {
boolean isArrived = false;
// 由編碼計算所得的終點橫座標
int endX = 0;
// 由編碼計算所得的終點縱座標
int endY = 0;
// 基於片段所代表的行走方向
int direction = 0;
// 臨時座標點橫座標
int tempX = 0;
// 臨時座標點縱座標
int tempY = 0;
endX = startPos[0];
endY = startPos[1];
for (int i = 0; i < stepNum; i++) {
direction = binaryArrayToNum(new int[] { code[2 * i],
code[2 * i + 1] });
// 根據方向改變陣列做座標點的改變
tempX = endX + MAZE_DIRECTION_CHANGE[direction][0];
tempY = endY + MAZE_DIRECTION_CHANGE[direction][1];
// 判斷座標點是否越界
if (tempX >= 0 && tempX < mazeData.length && tempY >= 0
&& tempY < mazeData[0].length) {
// 判斷座標點是否走到阻礙塊
if (mazeData[tempX][tempY] != -1) {
endX = tempX;
endY = tempY;
}
}
}
if (endX == endPos[0] && endY == endPos[1]) {
isArrived = true;
}
return isArrived;
}
/**
* 二進位制陣列轉化為數字
*
* @param binaryArray
* 待轉化二進位制陣列
*/
private int binaryArrayToNum(int[] binaryArray) {
int result = 0;
for (int i = binaryArray.length - 1, k = 0; i >= 0; i--, k++) {
if (binaryArray[i] == 1) {
result += Math.pow(2, k);
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* 進行遺傳演算法走出迷宮
*/
public void goOutMaze() {
// 迭代遺傳次數
int loopCount = 0;
boolean canExit = false;
// 結果路徑
int[] resultCode = null;
ArrayList<int[]> initCodes;
ArrayList<int[]> selectedCodes;
ArrayList<int[]> crossedCodes;
ArrayList<int[]> variationCodes;
// 產生初始資料集
produceInitSet();
initCodes = initSets;
while (true) {
for (int[] array : initCodes) {
// 遺傳迭代的終止條件為是否找到出口位置
if (ifArriveEndPos(array)) {
resultCode = array;
canExit = true;
break;
}
}
if (canExit) {
break;
}
selectedCodes = selectOperate(initCodes);
crossedCodes = crossOperate(selectedCodes);
variationCodes = variationOperate(crossedCodes);
initCodes = variationCodes;
loopCount++;
//如果遺傳次數超過100次,則退出
if(loopCount >= 100){
break;
}
}
System.out.println("總共遺傳進化了" + loopCount + "次");
printFindedRoute(resultCode);
}
/**
* 輸出找到的路徑
*
* @param code
*/
private void printFindedRoute(int[] code) {
if(code == null){
System.out.println("在有限的遺傳進化次數內,沒有找到最優路徑");
return;
}
int tempX = startPos[0];
int tempY = startPos[1];
int direction = 0;
System.out.println(MessageFormat.format(
"起始點位置({0},{1}), 出口點位置({2}, {3})", tempX, tempY, endPos[0],
endPos[1]));
System.out.print("搜尋到的結果編碼:");
for(int value: code){
System.out.print("" + value);
}
System.out.println();
for (int i = 0, k = 1; i < code.length; i += 2, k++) {
direction = binaryArrayToNum(new int[] { code[i], code[i + 1] });
tempX += MAZE_DIRECTION_CHANGE[direction][0];
tempY += MAZE_DIRECTION_CHANGE[direction][1];
System.out.println(MessageFormat.format(
"第{0}步,編碼為{1}{2},向{3}移動,移動後到達({4},{5})", k, code[i], code[i+1],
MAZE_DIRECTION_LABEL[direction], tempX, tempY));
}
}
}
package GA_Maze;
/**
* 遺傳演算法在走迷宮遊戲的應用
* @author lyq
*
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//迷宮地圖檔案資料地址
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\lyq\\Desktop\\icon\\mapData.txt";
//初始個體數量
int initSetsNum = 4;
GATool tool = new GATool(filePath, initSetsNum);
tool.goOutMaze();
}
}演算法的輸出:
我測了很多次的資料,因為有可能會一時半會搜尋不出來,我設定了最大遺傳次數100次。
總共遺傳進化了2次
起始點位置(4,4), 出口點位置(1, 0)
搜尋到的結果編碼:10100000100010
第1步,編碼為10,向左移動,移動後到達(4,3)
第2步,編碼為10,向左移動,移動後到達(4,2)
第3步,編碼為00,向上移動,移動後到達(3,2)
第4步,編碼為00,向上移動,移動後到達(2,2)
第5步,編碼為10,向左移動,移動後到達(2,1)
第6步,編碼為00,向上移動,移動後到達(1,1)
第7步,編碼為10,向左移動,移動後到達(1,0)
總共遺傳進化了8次
起始點位置(4,4), 出口點位置(1, 0)
搜尋到的結果編碼:10001000101000
第1步,編碼為10,向左移動,移動後到達(4,3)
第2步,編碼為00,向上移動,移動後到達(3,3)
第3步,編碼為10,向左移動,移動後到達(3,2)
第4步,編碼為00,向上移動,移動後到達(2,2)
第5步,編碼為10,向左移動,移動後到達(2,1)
第6步,編碼為10,向左移動,移動後到達(2,0)
第7步,編碼為00,向上移動,移動後到達(1,0)
總共遺傳進化了100次
在有限的遺傳進化次數內,沒有找到最優路徑
演算法小結
遺傳演算法在走迷宮中的應用總體而言還是非常有意思的如果你去認真的體會的話,至少讓我更加深入的理解了GA演算法,如果博友向要親自實現這演算法,我給幾點建議,第一是迷宮難度的和初始個體數量的設定,為什麼要注意這2點呢,一個是這關係到遺傳迭代的次數,在一段時間內有的時候遺傳演算法是找不出來的,如果找不出來,PC機的CPU會持續高速的計算,所以不要讓遺傳進行無限制的進行,最好做點次數限制,也可能是我的本本配置太爛了。。在演算法的除錯中修復了一個之前沒發現的bug,就是選擇階段的時候對於隨機數的判斷少考慮了一種情形,當隨機數取到1.0的時候,其實是不能判斷到的,因為概念和只會無限接近1,就不知道被劃分到哪個區域中了。