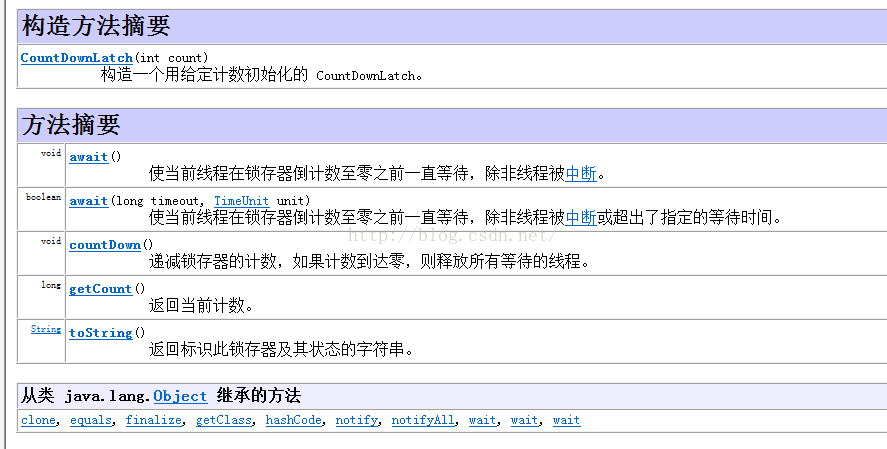
【JAVA】java中CountDownLatch的用法,例項講解
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-05
CountDownLatch主要用於多執行緒環境中,當所有的執行緒都countDown了,就會釋放所有的等待的執行緒,await在到0之前一直等待。
直接看一段程式碼:
package thread.thread; import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque; import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; /** * ClassName:CountDownLatchTest <br/> * Function: TODO ADD FUNCTION. <br/> * Reason: TODO ADD REASON. <br/> * Date: 2015年7月30日 下午2:04:07 <br/> * * @author chiwei * @version * @since JDK 1.6 * @see */ public class CountDownLatchTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadPoolExecutor poolExe = new ThreadPoolExecutor(100, 1000, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<Runnable>(100)); // 考試開始鈴聲響起,考試開始 final CountDownLatch examBegin = new CountDownLatch(1); // 單個考生,考試結束交卷 final CountDownLatch student = new CountDownLatch(10); // 一個考場10位考生 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Runnable runnable = new Runnable() { public void run() { try { System.out.println("考生" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "在等待考試開始的鈴聲響起"); examBegin.await(); System.out.println("考生聽到鈴聲" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "開始答題"); Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random() * 100));//答題過程,真正的業務邏輯處理部分 System.out.println("考生" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "交卷"); student.countDown(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }; poolExe.execute(runnable); // 運動員開始任務 } try { // 答題時間 Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random() * 10000)); System.out.println("考場" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "開始鈴聲即將響起"); examBegin.countDown(); // 命令計數器置為0 System.out.println("考場" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "考試開始鈴聲響起"); student.await(); // 所有考生交卷 System.out.println("考場" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "考試結束"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } poolExe.shutdown(); } }
如以上程式碼所示,有兩個CountDownLatch類,一個控制考場,整個考試的開始和結束,一個控制所有考生是否都交卷了。
examBegin只有在countDown後,10個考生才有可能開始答題,因為答題前有examBegin.await(),會阻塞住;同理,在考試結束前,student.await()會阻塞住,因為只有當所有的學生都交卷了(countDown),await才會通過。
多執行緒使用場景下,你的CountDownLatch的count值要等於執行緒數。考生pool-1-thread-3在等待考試開始的鈴聲響起 考生pool-1-thread-2在等待考試開始的鈴聲響起 考生pool-1-thread-7在等待考試開始的鈴聲響起 考生pool-1-thread-10在等待考試開始的鈴聲響起 考生pool-1-thread-8在等待考試開始的鈴聲響起 考生pool-1-thread-1在等待考試開始的鈴聲響起 考生pool-1-thread-6在等待考試開始的鈴聲響起 考生pool-1-thread-9在等待考試開始的鈴聲響起 考生pool-1-thread-4在等待考試開始的鈴聲響起 考生pool-1-thread-5在等待考試開始的鈴聲響起 考場main開始鈴聲即將響起 考場main考試開始鈴聲響起 考生聽到鈴聲pool-1-thread-3開始答題 考生聽到鈴聲pool-1-thread-10開始答題 考生聽到鈴聲pool-1-thread-7開始答題 考生聽到鈴聲pool-1-thread-2開始答題 考生聽到鈴聲pool-1-thread-8開始答題 考生聽到鈴聲pool-1-thread-6開始答題 考生聽到鈴聲pool-1-thread-9開始答題 考生聽到鈴聲pool-1-thread-1開始答題 考生聽到鈴聲pool-1-thread-4開始答題 考生聽到鈴聲pool-1-thread-5開始答題 考生pool-1-thread-4交卷 考生pool-1-thread-8交卷 考生pool-1-thread-9交卷 考生pool-1-thread-1交卷 考生pool-1-thread-10交卷 考生pool-1-thread-3交卷 考生pool-1-thread-2交卷 考生pool-1-thread-6交卷 考生pool-1-thread-5交卷 考生pool-1-thread-7交卷 考場main考試結束
等待count個執行緒全部執行完了,整個任務才算執行結束了。