shiro登入流程大剖析
關於shiro我會出一個專題進行講解,相信當家通過開濤部落格都不會陌生,今天著重講下登入流程
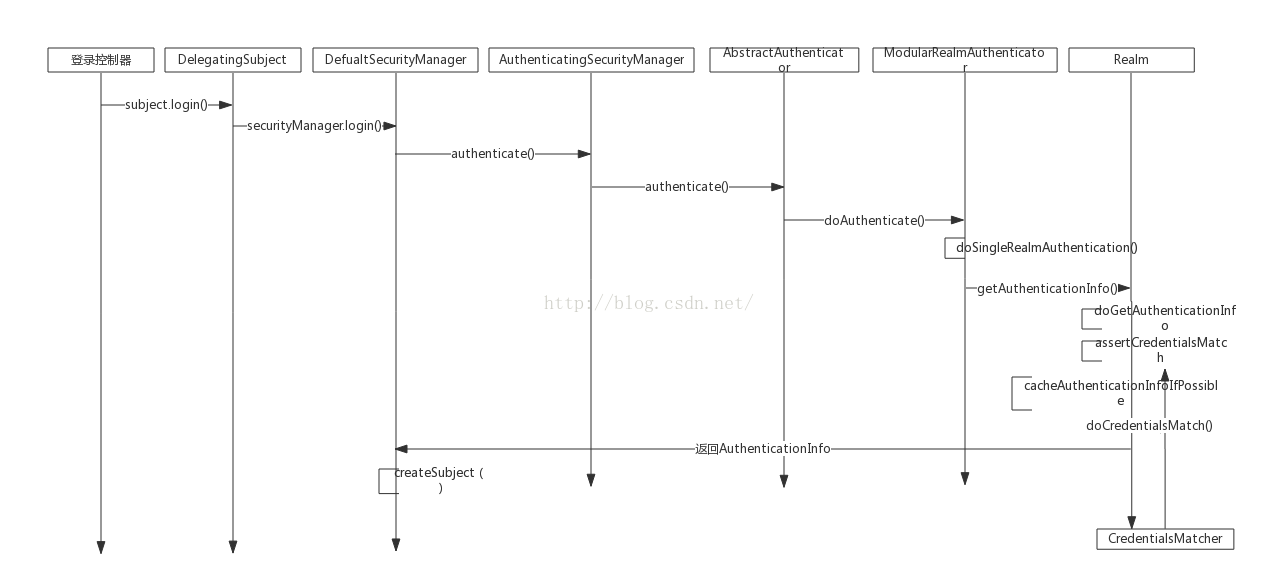
1.大致流程圖如下
第一步:使用者登入,根據使用者登入名密碼生產Token
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken(username, password);
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
subject.login(token);這裡呼叫了代理subject的login方法,程式碼如下:
可以看到第二行,實際是呼叫securityManager的login方法public void login(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { clearRunAsIdentitiesInternal(); Subject subject = securityManager.login(this, token); PrincipalCollection principals; String host = null; if (subject instanceof DelegatingSubject) { DelegatingSubject delegating = (DelegatingSubject) subject; //we have to do this in case there are assumed identities - we don't want to lose the 'real' principals: principals = delegating.principals; host = delegating.host; } else { principals = subject.getPrincipals(); } if (principals == null || principals.isEmpty()) { String msg = "Principals returned from securityManager.login( token ) returned a null or " + "empty value. This value must be non null and populated with one or more elements."; throw new IllegalStateException(msg); } this.principals = principals; this.authenticated = true; if (token instanceof HostAuthenticationToken) { host = ((HostAuthenticationToken) token).getHost(); } if (host != null) { this.host = host; } Session session = subject.getSession(false); if (session != null) { this.session = decorate(session); } else { this.session = null; } }
第二步:呼叫securityManager的login方法
public Subject login(Subject subject, AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { AuthenticationInfo info; try { info = authenticate(token); } catch (AuthenticationException ae) { try { onFailedLogin(token, ae, subject); } catch (Exception e) { if (log.isInfoEnabled()) { log.info("onFailedLogin method threw an " + "exception. Logging and propagating original AuthenticationException.", e); } } throw ae; //propagate } Subject loggedIn = createSubject(token, info, subject); onSuccessfulLogin(token, info, loggedIn); return loggedIn; }
第三步:呼叫securityManager的 authenticate方法 該方法在 其上級類 AuthenticatingSecurityManager中,程式碼如下:
public AuthenticationInfo authenticate(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
return this.authenticator.authenticate(token);
}實際呼叫了authenticator的authenticate方法,而AuthenticatingSecurityManager的無參建構函式中
public AuthenticatingSecurityManager() {
super();
this.authenticator = new ModularRealmAuthenticator();
}第四步:呼叫AbstractAuthenticator的authenticate方法
public final AuthenticationInfo authenticate(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
if (token == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Method argumet (authentication token) cannot be null.");
}
log.trace("Authentication attempt received for token [{}]", token);
AuthenticationInfo info;
try {
info = doAuthenticate(token);
if (info == null) {
String msg = "No account information found for authentication token [" + token + "] by this " +
"Authenticator instance. Please check that it is configured correctly.";
throw new AuthenticationException(msg);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
AuthenticationException ae = null;
if (t instanceof AuthenticationException) {
ae = (AuthenticationException) t;
}
if (ae == null) {
//Exception thrown was not an expected AuthenticationException. Therefore it is probably a little more
//severe or unexpected. So, wrap in an AuthenticationException, log to warn, and propagate:
String msg = "Authentication failed for token submission [" + token + "]. Possible unexpected " +
"error? (Typical or expected login exceptions should extend from AuthenticationException).";
ae = new AuthenticationException(msg, t);
}
try {
notifyFailure(token, ae);
} catch (Throwable t2) {
if (log.isWarnEnabled()) {
String msg = "Unable to send notification for failed authentication attempt - listener error?. " +
"Please check your AuthenticationListener implementation(s). Logging sending exception " +
"and propagating original AuthenticationException instead...";
log.warn(msg, t2);
}
}
throw ae;
}
log.debug("Authentication successful for token [{}]. Returned account [{}]", token, info);
notifySuccess(token, info);
return info;
}第五步:呼叫ModularRealmAuthenticator的doAuthenticate方法
protected AuthenticationInfo doAuthenticate(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
assertRealmsConfigured();
Collection<Realm> realms = getRealms();
if (realms.size() == 1) {
return doSingleRealmAuthentication(realms.iterator().next(), authenticationToken);
} else {
return doMultiRealmAuthentication(realms, authenticationToken);
}
}第二行獲取realms,但我們記得只配置過realm,realms是什麼時候賦值的呢,其實很簡單 spring對bean屬性的賦值是通過反射 實際呼叫的是set方法,即我們配置了一個property 為realm的屬性 對屬性注入的時候呼叫的setRealm方法
public void setRealm(Realm realm) {
if (realm == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Realm argument cannot be null");
}
Collection<Realm> realms = new ArrayList<Realm>(1);
realms.add(realm);
setRealms(realms);
}第六步:呼叫ModularRealmAuthenticator的doSingleRealmAuthentication方法
protected AuthenticationInfo doSingleRealmAuthentication(Realm realm, AuthenticationToken token) {
if (!realm.supports(token)) {
String msg = "Realm [" + realm + "] does not support authentication token [" +
token + "]. Please ensure that the appropriate Realm implementation is " +
"configured correctly or that the realm accepts AuthenticationTokens of this type.";
throw new UnsupportedTokenException(msg);
}
AuthenticationInfo info = realm.getAuthenticationInfo(token);
if (info == null) {
String msg = "Realm [" + realm + "] was unable to find account data for the " +
"submitted AuthenticationToken [" + token + "].";
throw new UnknownAccountException(msg);
}
return info;
}第七步:呼叫AuthenticatingRealm的getAuthenticationInfo方法
public final AuthenticationInfo getAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
AuthenticationInfo info = getCachedAuthenticationInfo(token);
if (info == null) {
//otherwise not cached, perform the lookup:
info = doGetAuthenticationInfo(token);
log.debug("Looked up AuthenticationInfo [{}] from doGetAuthenticationInfo", info);
if (token != null && info != null) {
cacheAuthenticationInfoIfPossible(token, info);
}
} else {
log.debug("Using cached authentication info [{}] to perform credentials matching.", info);
}
if (info != null) {
assertCredentialsMatch(token, info);
} else {
log.debug("No AuthenticationInfo found for submitted AuthenticationToken [{}]. Returning null.", token);
}
return info;
}
而我們的cacheManager哪來的呢,我們發現在setRealm方法中呼叫了setRealms
public void setRealms(Collection<Realm> realms) {
if (realms == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Realms collection argument cannot be null.");
}
if (realms.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Realms collection argument cannot be empty.");
}
this.realms = realms;
afterRealmsSet();
}
protected void afterRealmsSet() {
applyCacheManagerToRealms();
applyEventBusToRealms();
}protected void applyCacheManagerToRealms() {
CacheManager cacheManager = getCacheManager();
Collection<Realm> realms = getRealms();
if (cacheManager != null && realms != null && !realms.isEmpty()) {
for (Realm realm : realms) {
if (realm instanceof CacheManagerAware) {
((CacheManagerAware) realm).setCacheManager(cacheManager);
}
}
}
}(有點囉嗦,哈哈,自己當時就是這麼想的)
在上面getAuthenticationInfo方法中,我們剛才說過第一行是從快取中取AuthenticationInfo,如果為空
第八步:呼叫realm的doGetAuthenticationInfo方法
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String userName = (String) token.getPrincipal();
//通過token獲取使用者資訊,這裡我們一般從資料庫中查詢
SimpleAuthenticationInfo authenticationInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user, password, getName());
return authenticationInfo;
}返回AuthenticationInfo,接著下面程式碼
if (token != null && info != null) {
cacheAuthenticationInfoIfPossible(token, info);
}關於從快取中查詢AuthenticationInfo以及快取AuthenticationInfo資訊的方法 這裡就不作分析了,可以看做對一個map的操作吧當然到這裡還沒完,同樣在上面方法中,
if (info != null) {
assertCredentialsMatch(token, info);
} else {
log.debug("No AuthenticationInfo found for submitted AuthenticationToken [{}]. Returning null.", token);
}第九步:呼叫assertCredentialsMatch方法
protected void assertCredentialsMatch(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) throws AuthenticationException {
CredentialsMatcher cm = getCredentialsMatcher();
if (cm != null) {
if (!cm.doCredentialsMatch(token, info)) {
//not successful - throw an exception to indicate this:
String msg = "Submitted credentials for token [" + token + "] did not match the expected credentials.";
throw new IncorrectCredentialsException(msg);
}
} else {
throw new AuthenticationException("A CredentialsMatcher must be configured in order to verify " +
"credentials during authentication. If you do not wish for credentials to be examined, you " +
"can configure an " + AllowAllCredentialsMatcher.class.getName() + " instance.");
}
}第十步:呼叫CredentialsMatcher的doCredentialsMatch方法,當然CredentialsMatcher我們可以自定義了
第十一步:上面步驟都通過以後回到DefualtSecurityManager的login方法中
Subject loggedIn = createSubject(token, info, subject);protected Subject createSubject(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info, Subject existing) {
SubjectContext context = createSubjectContext();
context.setAuthenticated(true);
context.setAuthenticationToken(token);
context.setAuthenticationInfo(info);
if (existing != null) {
context.setSubject(existing);
}
return createSubject(context);
}