Spark排程模式-FIFO和FAIR
Spark中的排程模式主要有兩種:FIFO和FAIR。預設情況下Spark的排程模式是FIFO(先進先出),誰先提交誰先執行,後面的任務需要等待前面的任務執行。而FAIR(公平排程)模式支援在排程池中為任務進行分組,不同的排程池權重不同,任務可以按照權重來決定執行順序。對這兩種排程模式的具體實現,接下來會根據spark-1.6.0的原始碼來進行詳細的分析。使用哪種排程器由引數spark.scheduler.mode來設定,可選的引數有FAIR和FIFO,預設是FIFO。
一、原始碼入口
在Scheduler模組中,當Stage劃分好,然後提交Task的過程中,會進入TaskSchedulerImpl#submitTasks方法。
schedulableBuilder.addTaskSetManager(manager, manager.taskSet.properties) //目前支援FIFO和FAIR兩種排程策略在上面程式碼中有一個schedulableBuilder物件,這個物件在TaskSchedulerImpl類中的定義及實現可以參考下面這段原始碼:
var schedulableBuilder: SchedulableBuilder = null
...
def initialize(backend: SchedulerBackend) {
this.backend = backend
// temporarily set rootPool name to empty 根據使用者配置的SchedulingMode決定是生成FIFOSchedulableBuilder還是生成FairSchedulableBuilder型別的schedulableBuilder物件。
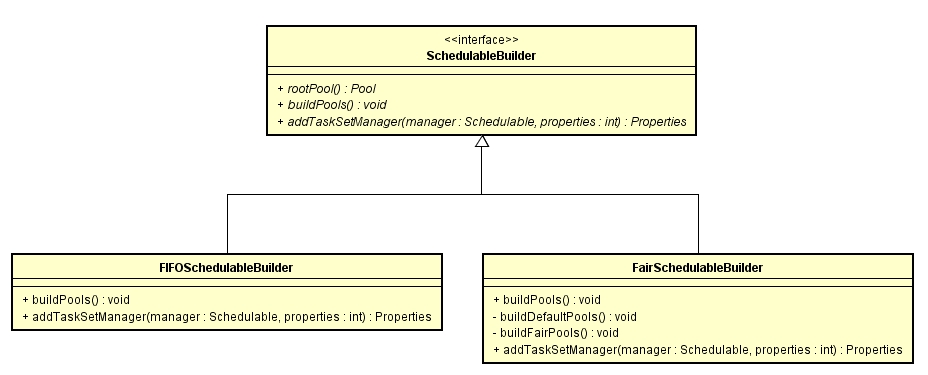
在生成schedulableBuilder後,呼叫其buildPools方法生成排程池。
排程模式由配置引數spark.scheduler.mode(預設值為FIFO)來確定。
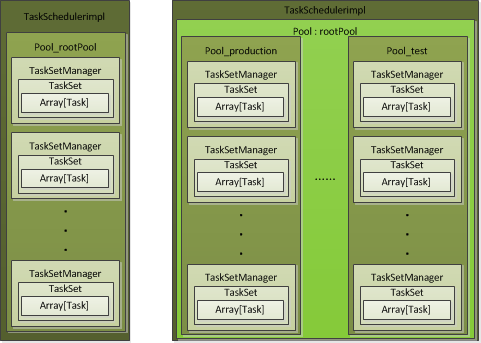
兩種模式的排程邏輯圖如下:
二、FIFOSchedulableBuilder
FIFO的rootPool包含一組TaskSetManager。從上面的類繼承圖中看出在FIFOSchedulableBuilder中有兩個方法:
1、buildPools
實現為空
override def buildPools() {
// nothing
}所以,對於FIFO模式,獲取到schedulableBuilder物件後,在呼叫buildPools方法後,不做任何操作。
2、addTaskSetManager
該方法將TaskSetManager裝載到rootPool中。直接呼叫的方法是Pool#addSchedulable()。
override def addTaskSetManager(manager: Schedulable, properties: Properties) {
rootPool.addSchedulable(manager)
}Pool#addSchedulable()方法:
val schedulableQueue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue[Schedulable]
...
override def addSchedulable(schedulable: Schedulable) {
require(schedulable != null)
schedulableQueue.add(schedulable)
schedulableNameToSchedulable.put(schedulable.name, schedulable)
schedulable.parent = this
}將該TaskSetManager加入到排程佇列schedulableQueue中。
三、FairSchedulableBuilder
FAIR的rootPool中包含一組Pool,在Pool中包含了TaskSetManager。
1、buildPools
在該方法中,會讀取配置檔案,按照配置檔案中的配置引數呼叫buildFairSchedulerPool生成配置的排程池,以及呼叫buildDefaultPool生成預設排程池。
預設情況下FAIR模式的配置檔案是位於SPARK_HOME/conf/fairscheduler.xml檔案,也可以通過引數spark.scheduler.allocation.file設定使用者自定義配置檔案。
spark中提供的fairscheduler.xml模板如下所示:
<allocations>
<pool name="production">
<schedulingMode>FAIR</schedulingMode>
<weight>1</weight>
<minShare>2</minShare>
</pool>
<pool name="test">
<schedulingMode>FIFO</schedulingMode>
<weight>2</weight>
<minShare>3</minShare>
</pool>
</allocations>引數含義:
(1)name: 該排程池的名稱,可根據該引數使用指定pool,入sc.setLocalProperty("spark.scheduler.pool", "test")
(2)weight: 該排程池的權重,各排程池根據該引數分配系統資源。每個排程池得到的資源數為weight / sum(weight),weight為2的分配到的資源為weight為1的兩倍。
(3)minShare: 該排程池需要的最小資源數(CPU核數)。fair排程器首先會嘗試為每個排程池分配最少minShare資源,然後剩餘資源才會按照weight大小繼續分配。
(4)schedulingMode: 該排程池內的排程模式。
2、buildFairSchedulerPool
從上面的配置檔案可以看到,每一個排程池有一個name屬性指定名字,然後在該pool中可以設定其schedulingMode(可為空,預設為FIFO), weight(可為空,預設值是1), 以及minShare(可為空,預設值是0)引數。然後使用這些引數生成一個Pool物件,把該pool物件放入rootPool中。入下所示:
val pool = new Pool(poolName, schedulingMode, minShare, weight)
rootPool.addSchedulable(pool)3、buildDefaultPool
如果如果配置檔案中沒有設定一個name為default的pool,系統才會自動生成一個使用預設引數生成的pool物件。各項引數的預設值在buildFairSchedulerPool中有提到。
4、addTaskSetManager
這一段邏輯中是把配置檔案中的pool,或者default pool放入rootPool中,然後把TaskSetManager存入rootPool對應的子pool。
override def addTaskSetManager(manager: Schedulable, properties: Properties) {
var poolName = DEFAULT_POOL_NAME
var parentPool = rootPool.getSchedulableByName(poolName)
if (properties != null) {
poolName = properties.getProperty(FAIR_SCHEDULER_PROPERTIES, DEFAULT_POOL_NAME)
parentPool = rootPool.getSchedulableByName(poolName)
if (parentPool == null) {
// we will create a new pool that user has configured in app
// instead of being defined in xml file
parentPool = new Pool(poolName, DEFAULT_SCHEDULING_MODE,
DEFAULT_MINIMUM_SHARE, DEFAULT_WEIGHT)
rootPool.addSchedulable(parentPool)
logInfo("Created pool %s, schedulingMode: %s, minShare: %d, weight: %d".format(
poolName, DEFAULT_SCHEDULING_MODE, DEFAULT_MINIMUM_SHARE, DEFAULT_WEIGHT))
}
}
parentPool.addSchedulable(manager)
logInfo("Added task set " + manager.name + " tasks to pool " + poolName)
}5、FAIR排程池使用方法
如果不加設定,jobs會提交到default排程池中。由於排程池的使用是Thread級別的,只能通過具體的SparkContext來設定local屬性(即無法在配置檔案中通過引數
spark.scheduler.pool來設定,因為配置檔案中的引數會被載入到SparkConf物件中)。所以需要使用指定排程池的話,需要在具體程式碼中通過SparkContext物件sc來按照如下方法進行設定:
sc.setLocalProperty("spark.scheduler.pool", "test")
設定該引數後,在該thread中提交的所有job都會提交到test Pool中。
如果接下來不再需要使用到該test排程池,
sc.setLocalProperty("spark.scheduler.pool", null)
四、FIFO和FAIR的排程順序
這裡必須提到的一個類是上面提到的Pool,在這個類中實現了不同調度模式的排程演算法。
var taskSetSchedulingAlgorithm: SchedulingAlgorithm = {
schedulingMode match {
case SchedulingMode.FAIR =>
new FairSchedulingAlgorithm()
case SchedulingMode.FIFO =>
new FIFOSchedulingAlgorithm()
}
}FIFO模式的演算法類是FIFOSchedulingAlgorithm,FAIR模式的演算法實現類是FairSchedulingAlgorithm。
接下來的兩節中comparator方法傳入引數Schedulable型別是一個trait,具體實現主要有兩個:1,Pool;2,TaskSetManager。與最前面那個排程模式的邏輯圖相對應。
1、FIFO模式的排程演算法FIFOSchedulingAlgorithm
在這個類裡面,主要邏輯是一個comparator方法。
override def comparator(s1: Schedulable, s2: Schedulable): Boolean = {
val priority1 = s1.priority //實際上是Job ID
val priority2 = s2.priority
var res = math.signum(priority1 - priority2)
if (res == 0) { //如果Job ID相同,就比較Stage ID
val stageId1 = s1.stageId
val stageId2 = s2.stageId
res = math.signum(stageId1 - stageId2)
}
if (res < 0) {
true
} else {
false
}
}如果有兩個排程任務s1和s2,首先獲得兩個任務的priority,在FIFO中該優先順序實際上是Job ID。首先比較兩個任務的Job ID,如果priority1比priority2小,那麼返回true,表示s1的優先順序比s2的高。我們知道Job ID是順序生成的,先生成的Job ID比較小,所以先提交的job肯定比後提交的job先執行。但是如果是同一個job的不同任務,接下來就比較各自的Stage ID,類似於比較Job ID,Stage ID小的優先順序高。
2、FAIR模式的排程演算法FairSchedulingAlgorithm
這個類中的comparator方法原始碼如下:
override def comparator(s1: Schedulable, s2: Schedulable): Boolean = {
val minShare1 = s1.minShare //在這裡share理解成份額,即每個排程池要求的最少cpu核數
val minShare2 = s2.minShare
val runningTasks1 = s1.runningTasks // 該Pool或者TaskSetManager中正在執行的任務數
val runningTasks2 = s2.runningTasks
val s1Needy = runningTasks1 < minShare1 // 如果正在執行任務數比該排程池最小cpu核數要小
val s2Needy = runningTasks2 < minShare2
val minShareRatio1 = runningTasks1.toDouble / math.max(minShare1, 1.0).toDouble
val minShareRatio2 = runningTasks2.toDouble / math.max(minShare2, 1.0).toDouble
val taskToWeightRatio1 = runningTasks1.toDouble / s1.weight.toDouble
val taskToWeightRatio2 = runningTasks2.toDouble / s2.weight.toDouble
var compare: Int = 0
if (s1Needy && !s2Needy) {
return true
} else if (!s1Needy && s2Needy) {
return false
} else if (s1Needy && s2Needy) {
compare = minShareRatio1.compareTo(minShareRatio2)
} else {
compare = taskToWeightRatio1.compareTo(taskToWeightRatio2)
}
if (compare < 0) {
true
} else if (compare > 0) {
false
} else {
s1.name < s2.name
}
} minShare對應fairscheduler.xml配置檔案中的minShare屬性。
(1)如果s1所在Pool或者TaskSetManager中執行狀態的task數量比minShare小,s2所在Pool或者TaskSetManager中執行狀態的task數量比minShare大,那麼s1會優先排程。反之,s2優先排程。
(2)如果s1和s2所在Pool或者TaskSetManager中執行狀態的task數量都比各自minShare小,那麼minShareRatio小的優先被排程。
minShareRatio是執行狀態task數與minShare的比值,即相對來說minShare使用較少的先被排程。
(3)如果minShareRatio相同,那麼最後比較各自Pool的名字。