GDB除錯fork+exec建立的子程序的方法
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-06
多程序是Linux程式設計中一個很重要的內容,典型的例子就是守護程序(daemon)。有關守護程序的定義和程式設計規範,請參考:
最常見的多程序的形式如下:
pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) { // fork failed
printf("fork error\n");
exit(1);
} else if (pid > 0) { // parent process
// command
} else { // child process
// command
}使用:set follow-fork-mode child,即可追蹤子程序。而set follow-fork-mode parent可除錯父程序。
還有一種多程序程式的形式為:
pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) { // fork failed
printf("fork error\n");
exit(1);
} else if (pid > 0) { // parent process
// command
} else { // child process
execv("a.out", NULL);
}當前有兩個程式碼test.c和child.c,其中test.c中的子程序通過execv呼叫child.c。
test.c
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
int ret = 0;
ret = fork();
if (ret == 0) {
execv("a.out", NULL); //a.out是child.c編譯成的可執行檔案
}
return 0;
}child.c #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> int main() { my_print(); return 0; } int my_print() { printf("hello world\n"); return 0; }
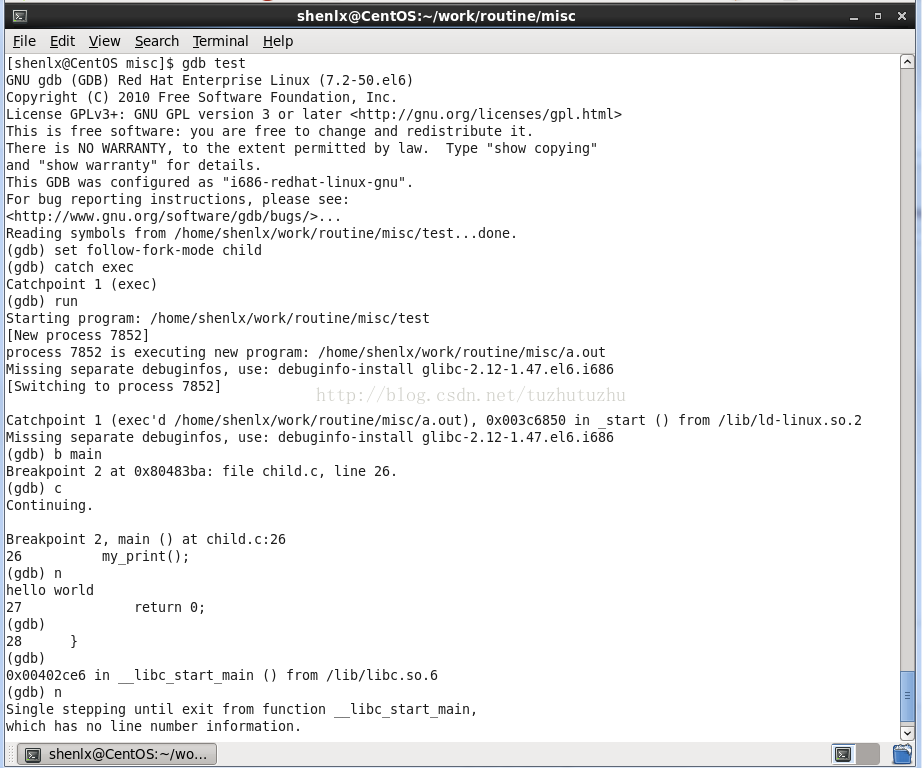
使用gdb除錯的詳細過程如下所示:
上面的例子中,最重要的操作時catch exec這個事件。捕獲到exec這個事件之後再往子程序的程式中打一個斷點,然後執行continue操作。可以看到,此時程式就會進入到exec呼叫的子程序中了。
網上介紹gdb除錯fork+exec建立的子程序的方法有不少,實際使用之後覺得,還是這種方法操作起來較為簡潔明瞭。大家如果有什麼更好的方法,請一定告訴我。
後記:
本文主要介紹的是使用gdb除錯fork+exec建立的子程序的方法。雖然方法是知道了,但是在實際的工作中,這種方法的實用性並不是十分的高。因為上述方法有很大的侷限性:這種方法只能用在父程序中僅有一個exec的程式中。
當程式中存在多個fork+exec,使用上述的方法只能進入到第一個子程序中!!因此,想要除錯其他的子程序就不行了。然而,對於任意一個子程序都可以自由的進行除錯,才是我的真正目標。我也會繼續調查gdb對於fork+exec建立的多個子程序的除錯方法,一旦有進展將會及時和大家分享。