安卓服務service全解,生命週期,前臺服務、後臺服務,啟動登出、繫結解綁,註冊
全棧工程師開發手冊 (作者:欒鵬)
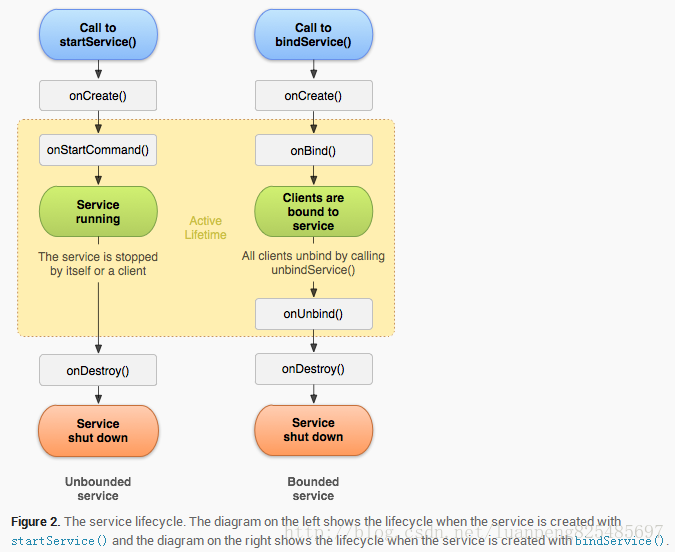
定義服務(服務的生命週期)
呼叫context.startService()時依次執行 ->onCreate()- >onStartCommand()->Service running
呼叫context.stopService()時依次執行 ->onDestroy()
呼叫context.bindService()時依次執行->onCreate()->onBind()->Service running
呼叫context.onUnbind()時依次執行 -> onDestroy()
當繫結service和所有客戶端解除繫結之後,Android系統將會銷燬它,(除非它同時被onStartCommand()方法開啟)。
因此,如果你的service是一個純粹的繫結service,那麼你不需要管理它的生命週期。
然而,如果你選擇實現onStartCommand()回撥方法,那麼你必須顯式地停止service,因為service此時被看做是開啟的。
這種情況下,service會一直執行到它自己呼叫 stopSelf()或另一個元件呼叫stopService(),不論它是否和客戶端繫結。
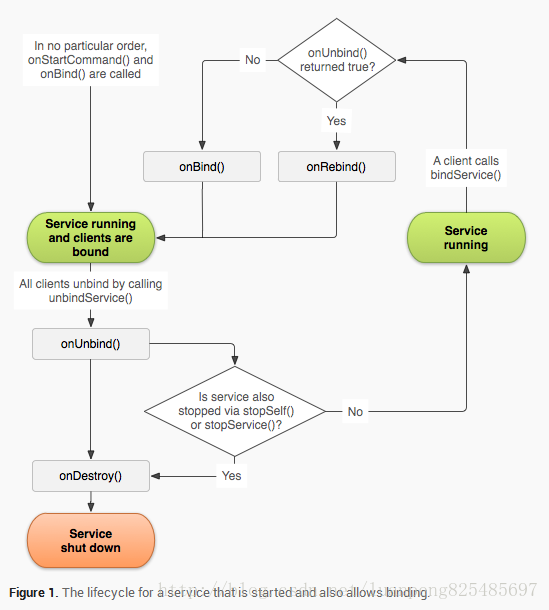
另外,如果你的service被開啟並且接受繫結,那麼當系統呼叫你的 onUnbind()方法時,如果你想要在下次客戶端繫結的時候接受一個onRebind()的呼叫(而不是呼叫 onBind()),你可以選擇在 onUnbind()中返回true。
onRebind()的返回值為void,但是客戶端仍然在它的 onServiceConnected()回撥方法中得到 IBinder 物件。
下圖展示了這種service(被開啟,還允許繫結)的生命週期:
程式碼示例:
程式碼中設計服務的生命週期,服務設定為前臺服務和後臺服務。
package com.lp.app.service;
import com.lp.app.Activity1;
import com.lp.app.R;
import android.app.Notification;
import android.app.PendingIntent;
import 在manifest檔案中註冊服務
這裡我們hi演示顯式啟動服務和隱式啟動服務。所有這裡處理設定服務的名稱,還設定了觸發條件
<!-- service註冊服務,其中permission表示要想外部應用程式使用這個服務,必須要包含的自定義許可權(只是個名稱) -->
<service
android:name="com.lp.app.service.Service1"
android:permission="com.lp.my_service1_permission">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.lp.action.service1"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/>
</intent-filter>
</service> 顯式的啟動和終止服務
Intent serviceIntent=null;
//顯示啟動一個服務
private void explicitStart() {
serviceIntent = new Intent(this, Service1.class);
startService(serviceIntent);
}
//顯式終止一個服務
private void explicitStop() {
if(serviceIntent!=null)
stopService(serviceIntent);
}隱式的啟動和終止服務
隱式啟動,相當於把自定義服務註冊為系統服務,再以啟動系統服務的方式啟動自定義服務。
這種方式的和顯式的啟動和停止服務不同,而是通過intent觸發指定名稱的事件。而這個事件又觸發了註冊在manifest檔案中的service,所以需要在manifest檔案中註冊服務時,設定觸發源
//隱式的啟動一個Service。相當於把自定義服務註冊為系統服務,再以啟動系統服務的方式啟動自定義服務
private void implicitStart() {
Intent intent = new Intent(Service1.action_name); //在註冊服務是設定了intent-filter,所以啟動這個,可以啟動對應的服務
intent.putExtra(Service1.key1, "value1");
intent.putExtra(Service1.key2, "value2");
startService(intent);
}
//隱式終止一個服務
private void implicitStop() {
Intent intent = new Intent(Service1.action_name);
stopService(intent);
}繫結和解除繫結
//為Service繫結建立一個service連線
//service的引用
private Service1 serviceRef;
//處理service和 activity之間的連線
private ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
//當建立連線時呼叫此函式
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName className, IBinder service) {
serviceRef = ((Service1.MyBinder)service).getService();
Log.v("服務繫結客戶端", "服務繫結建立連線");
}
//當service意外斷開時執行
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName className) {
serviceRef = null;
Log.v("服務繫結客戶端", "服務繫結斷開連線");
}
};
Intent bindIntent=null;
//繫結一個service和activity
private void bindToService() {
bindIntent = new Intent(this, Service1.class);
bindService(bindIntent, mConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
//BIND_AUTO_CREATE表示收到繫結請求的時候,如果服務尚未建立,則即刻建立,在系統記憶體不足需要先摧毀優先順序元件來釋放記憶體,且只有駐留該服務的程序成為被摧毀物件時,服務才被摧毀
//BIND_DEBUG_UNBIND通常用於除錯場景中判斷繫結的服務是否正確,但容易引起記憶體洩漏,因此非除錯目的的時候不建議使用
//BIND_NOT_FOREGROUND表示系統將阻止駐留該服務的程序具有前臺優先順序,僅在後臺執行,該標誌位位於Froyo中引入
}
//解除一個繫結
private void unbindToService() {
if (bindIntent!=null) {
unbindService(mConnection);
}
}