Java解析rdf和xml檔案以及處理excel
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-07
一.Java解析rdf檔案
1.下載jena庫
- 首先,從這裡下載 jena 包 apache-jana-2.7.*.tar.gz(我用的是2.7)。解壓。
- 開啟 Eclipse,新建一個Java Project。
- 右鍵點選專案->properties->Java Build Path -> libraries。將解壓後 lib 目錄下的 jar 檔案新增到build path 中。
- OK。現在可以在專案裡使用 jena 了。
2.jean中的資料結構
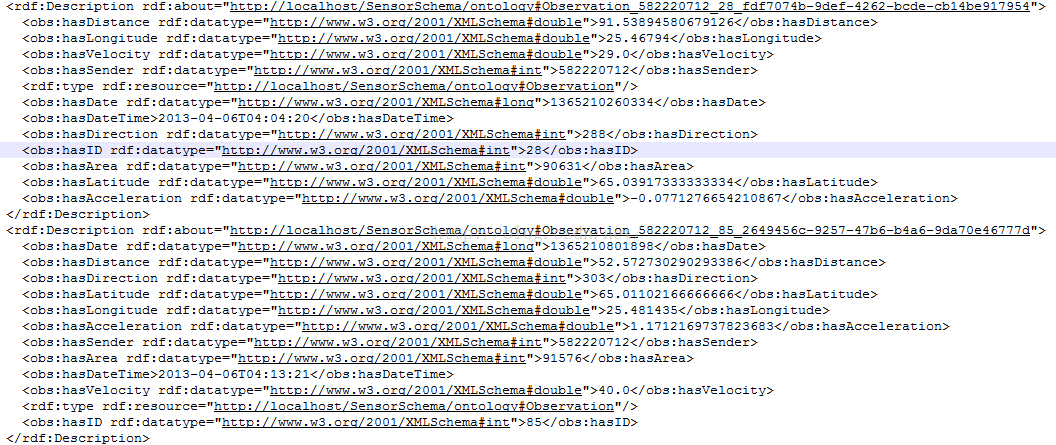
在 Jena 中,資源用 Resource 類來表示,其屬性用 Property 類來表示。而整體模型用Model 類來表示。一個 Model 物件可以包含多個資源。每一個資源又包括主語subject、謂語predicate、客體object來表示(下面是一個記錄車輛移動資料的rdf檔案)。
其中整個rdf檔案可以看做是一個model,每個rdf標籤可以看做是一個subject,每個rdf標籤下的obs:hasxxx可以看做是predictate,每個<obs>xxx</obs>中間的xxx看做是object。整個解析類似xml。
3.使用jean
//獲取modelpublic static Model readRDF(String fileName) { Model model = ModelFactory.createDefaultModel(); InputStream in = FileManager.get().open(fileName); if (in == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("File: " + fileName + " not found"); } // 讀取RDF/XML 檔案 return model.read(in, com.hp.hpl.jena.vocabulary.RDF.getURI(), "RDF/XML-ABBREV"); // model.write(System.out); }
/** * 獲取經緯度以及傳送者ID * @param model 資料 * @param list 儲存結果 */ public static void getWantedItems(Model model, Map<String, List<Map<String, String>>> senderMap, HashSet<String> nameSet) { ResIterator subjects = model.listSubjects(); while (subjects.hasNext()) { Resource subject = subjects.next(); //Property property = model.createProperty(); //System.out.println(subject.getLocalName()); StmtIterator properties = subject.listProperties(); Map<String, String> item = new HashMap<String, String>(); String sender = null; while (properties.hasNext()) { Statement stmt = properties.nextStatement(); Property predicate = stmt.getPredicate(); RDFNode object = stmt.getObject(); String val = null; String name = predicate.getLocalName().trim(); //System.out.println(name); val = object.toString().split("\\^\\^")[0]; if (name.equals("hasLongitude")) { item.put("longitude", val); } else if (name.equals("hasLatitude")) { item.put("latitude", val); } else if (name.equals("hasSender")) { sender = val.trim(); item.put("sender", val); nameSet.add(sender); } //System.out.println(); } if (senderMap.get(sender)!=null) { senderMap.get(sender).add(item); }else { System.out.println("新車id:"+sender+"建立list成功"); List<Map<String, String>> list = new ArrayList<Map<String,String>>(); list.add(item); senderMap.put(sender, list); } properties.close(); } subjects.close(); //System.out.println(list); }
二.Java解析xml
1.DOM方式
DOM模式解析XML,是把整個XML文件當成一個物件來處理,會先把整個文件讀入到記憶體裡。是基於樹的結構,通常需要載入整文件和構造DOM樹,然後才能開始工作。
優缺點:解析簡單,但不適合大檔案
2.SAX方式
基於事件驅動的方式,適合大檔案,非一次性將檔案讀入記憶體,主要是要寫自己的handler。/**
* 讀取xml檔案,使用SAXParser解析
*
* @param uri
* @param NodeName
* @return
*/
public static List<Map<String, String>> ReadXML(String uri, String NodeName) {
try {
// 建立一個解析XML的工廠物件
SAXParserFactory parserFactory = SAXParserFactory.newInstance();
// 建立一個解析XML的物件
SAXParser parser = parserFactory.newSAXParser();
// 建立一個解析助手類
Myhandler myhandler = new Myhandler("Observation");
parser.parse(uri, myhandler);
return myhandler.getList();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
}
return null;
}
/**
* 將list容器裡的內容寫入到新的xml檔案
*
* @param vanet
*/
public static void createXML(List<Map<String, String>> vanet) {
try {
// 建立工廠
SAXTransformerFactory factory = (SAXTransformerFactory) SAXTransformerFactory
.newInstance();
TransformerHandler handler = factory.newTransformerHandler();
Transformer info = handler.getTransformer();
// 是否自動新增額外的空白
info.setOutputProperty(OutputKeys.INDENT, "yes");
// 設定字元編碼
info.setOutputProperty(OutputKeys.ENCODING, "utf-8");
info.setOutputProperty(OutputKeys.VERSION, "1.0");
info.setOutputProperty(OutputKeys.STANDALONE, "no");
// 儲存建立的saxvanet.xml
StreamResult result = new StreamResult(new FileOutputStream(
"f:\\xml\\map2.gpx"));
handler.setResult(result);
// 開始xml
handler.startDocument();
AttributesImpl impl = new AttributesImpl();
impl.clear();
addAttr(impl);
handler.startElement("", "", "gpx", impl);
for (int i = 0; i < vanet.size(); i++) {
/*
* <wpt lat="25.55" lon="99.1666666666667">
* <ele>123</ele>
* <name>礦1</name>
* <desc>test</desc>
* <sym>unistrong:104</sym>
* </wpt>
*/
Map<String, String> map = vanet.get(i);
Vehicle vh = setVehicle(map);
// 生成<wpt lat="xx" lon="xx">
impl.clear(); // 清空屬性
impl.addAttribute("", "", "lat", "", vh.getLatitude());
impl.addAttribute("", "", "lon", "", vh.getLongitude());
handler.startElement("", "", "wpt", impl);
// 生成<name>xx</name>元素
impl.clear();
handler.startElement("", "", "name", impl);
String name = vh.getSender();
//System.out.println("name:"+name);
handler.characters(name.toCharArray(), 0, name.length()); // 為name元素新增文字
handler.endElement("", "", "name");
impl.clear();
handler.endElement("", "", "wpt");
}
// 生成</class>
handler.endElement("", "", "gpx");
handler.endDocument();
System.out.println("complete.................................................");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void addAttr(AttributesImpl impl) {
impl.addAttribute("", "", "xmlns", "",
"http://www.topografix.com/GPX/1/1");
impl.addAttribute("", "", "creator", "", "MapSource 6.5");
impl.addAttribute("", "", "version", "", "1.1");
impl.addAttribute("", "", "xmlns:xsi", "",
"http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance");
impl.addAttribute("", "", "xsi:schemaLocation", "",
"http://www.topografix.com/GPX/1/1 http://www.topografix.com/GPX/1/1/gpx.xsd");
System.out.println("新增屬性成功");
}public class Myhandler extends DefaultHandler {
//
private HashSet<String> set = null;
// 儲存正在解析的元素的資料
private Map<String, String> map = null;
// 儲存所有解析的元素的資料
private List<Map<String, String>> list = null;
// 正在解析的元素的名字
String currentTag = null;
// 正在解析的元素的元素值
String currentValue = null;
// 開始解析的元素
String nodeName = null;
public Myhandler(String nodeName) {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
this.nodeName = nodeName;
}
public HashSet<String> getSet() {
return set;
}
public List<Map<String, String>> getList() {
return list;
}
/*
* <Observation ID="18"> <Time>2013-04-18T08:00:00+00:00</Time>
* <Area>90268</Area> <Coordinates X="2521.4661" Y="6507.9541" />
* <Velocity>60</Velocity> <Direction>169</Direction>
* <ManualInfo>0</ManualInfo> <Sender>134569370</Sender> </Observation>
*/
// 開始解析文件,即開始解析XML根元素時呼叫該方法
@Override
public void startDocument() throws SAXException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("--startDocument()--");
// 初始化Map
//list = new ArrayList<Map<String, String>>();
set = new HashSet<String>();
}
// 開始解析每個元素時都會呼叫該方法
@Override
public void startElement(String uri, String localName, String qName,
Attributes attributes) throws SAXException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// 判斷正在解析的元素是不是開始解析的元素
currentTag = null;
//System.out.println("--startElement()--" + qName);
if (qName.equals(nodeName)) {
//map = new HashMap<String, String>();
return;
}
/*if (qName.equals("Time") || qName.equals("Area")
|| qName.equals("Velocity") || qName.equals("Direction")||qName.equals("ManualInfo")) {
return;
}*/
if (qName.equals("Sender")) {
//System.out.println("sender");
// 判斷正在解析的元素是否有屬性值,如果有則將其全部取出並儲存到map物件中,如:<person id="00001"></person>
/*if (attributes != null && map != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < attributes.getLength(); i++) {
//map.put(attributes.getQName(i), attributes.getValue(i));
//set.add(e)
}
}*/
currentTag = qName; // 正在解析的元素
}else {
return ;
}
}
// 解析到每個元素的內容時會呼叫此方法
@Override
public void characters(char[] ch, int start, int length)
throws SAXException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//System.out.println("--characters()--");&& map != null
if (currentTag != null) {
currentValue = new String(ch, start, length);
// 如果內容不為空和空格,也不是換行符則將該元素名和值和存入map中
if (currentValue != null && !currentValue.trim().equals("")
&& !currentValue.trim().equals("\n")) {
//map.put(currentTag, currentValue);
set.add(currentValue);
System.out.println(currentTag + ": " + currentValue);
}
// 當前的元素已解析過,將其置空用於下一個元素的解析
currentTag = null;
currentValue = null;
}
}
// 每個元素結束的時候都會呼叫該方法
@Override
public void endElement(String uri, String localName, String qName)
throws SAXException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//System.out.println("--endElement()--" + qName);
// 判斷是否為一個節點結束的元素標籤
/*if (qName.equals(nodeName)) {
list.add(map);
map = null;
}*/
}
// 結束解析文件,即解析根元素結束標籤時呼叫該方法
@Override
public void endDocument() throws SAXException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("--endDocument()--");
super.endDocument();
}
}使用jxl庫,其使用還是比較簡單的(程式碼可能不能直接用, 裡面有些entity類需要自己建,有些list也需要自己處理)。
public class WriteToExcelUtils {
private static final int MAXROWS = 60000;
private static int INDEX = 0;
public static void writeExcel(String fileName,
List<Map<String, String>> list, String excel) {
String excelName = excel;
String sheetName = list.get(0).get("dateTime");
//System.out.println("表名:"+sheetName);
int startLine = 0;
int rows = list.size();
Workbook wb = null;
WritableWorkbook wwb = null;
boolean flag = false;
try {
File is = new File(fileName+"\\"+excelName+".xls");
if (!is.exists()) {
System.out.println("新的excel:"+excelName+".xls");
wwb = Workbook.createWorkbook(is);
flag = true;
} else {
wb = Workbook.getWorkbook(is);
Sheet sheet = wb.getSheet(sheetName);
if (sheet!=null) {
// 獲取行
int length = sheet.getRows();
startLine = length;
}else {
//System.out.println(sheetName+"不存在");
flag = true;
}
// 首先要使用Workbook類的工廠方法建立一個可寫入的工作薄(Workbook)物件
// wwb = Workbook.createWorkbook(new File(fileName));
wwb = Workbook.createWorkbook(is, wb);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (wwb != null) {
// 建立一個可寫入的工作表
// Workbook的createSheet方法有兩個引數,第一個是工作表的名稱,第二個是工作表在工作薄中的位置
// System.out.println(index);
WritableSheet ws = null;
if (flag) {
System.out.println("建立新的sheet: "+sheetName);
ws = wwb.createSheet(sheetName, 0);
} else{
//System.out.println(sheetName);
ws = wwb.getSheet(0);
}
// 下面開始新增單元格
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
Vehicle vh = SaxService.setVehicle(list.get(i));
String dte = vh.getDate();
String longitude = vh.getLongitude();
String latitude = vh.getLatitude();
List<String> items = new ArrayList<String>();
items.add(dte);
items.add(longitude);
items.add(latitude);
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
write2Cell(ws, j, i + startLine, items.get(j));
}
}
//index += rows;
try {
// 從記憶體中寫入檔案中
wwb.write();
// 關閉資源,釋放記憶體
wwb.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (WriteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void write2Cell(WritableSheet ws, int c, int r, String item) {
// System.out.println(index+r);
// 這裡需要注意的是,在Excel中,第一個引數表示列,第二個表示行
Label labelC = new Label(c, r, item);
try {
// 將生成的單元格新增到工作表中
ws.addCell(labelC);
} catch (RowsExceededException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (WriteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}<pre name="code" class="java"> /**
* 讀Excel
*
* @param pathname
*/
public static LinkedList<HashMap<String, String>> readExcel(String pathname) {
LinkedList<HashMap<String, String>> list = new LinkedList<HashMap<String, String>>();
File file = new File(pathname);
String uri = "f:\\xml\\map\\edge.xml";
Workbook wb = null;
try {
wb = Workbook.getWorkbook(file);
Sheet sheet = wb.getSheet(0);
int rows = sheet.getRows();
// ThreadPoolExecutorTest threadPool = new
// ThreadPoolExecutorTest(queue);
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
// System.out.println("第"+(i+1)+"條資料正在執行");
Cell[] cols = sheet.getRow(i);
String sender = cols[0].getContents();
String nodeID = cols[1].getContents();
String wayID = cols[2].getContents();
String depart = cols[3].getContents();
String edgeID = SaxService.getWayIdFromNodeXML(uri, nodeID, wayID);
map.put("sender", sender);
map.put("nodeID", nodeID);
map.put("wayID", wayID);
map.put("edgeID", edgeID);
map.put("depart", depart);
list.add(map);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return list;
}