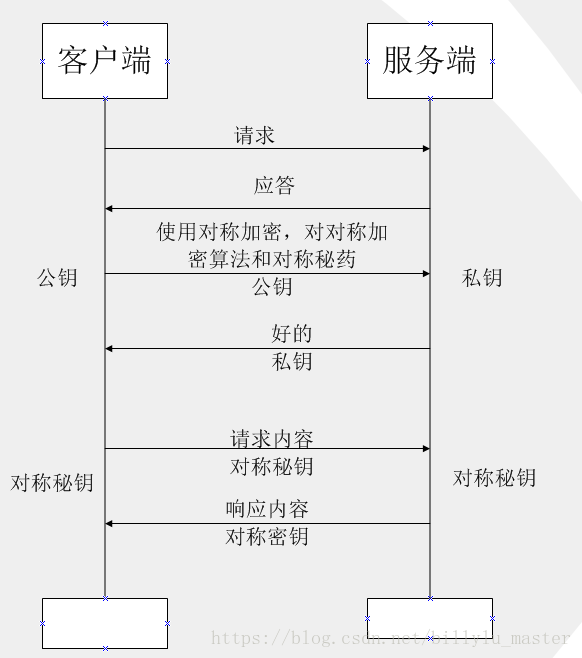
對稱加密演算法和非對稱加密演算法的完美結合
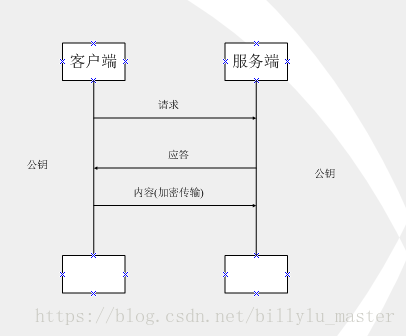
如上圖所示,此種方式屬於對稱加密,雙方擁有相同的金鑰,資訊得到安全傳輸,但此種方式的缺點是:
(1)不同的客戶端、伺服器數量龐大,所以雙方都需要維護大量的金鑰,維護成本很高
(2)因每個客戶端、伺服器的安全級別不同,金鑰極易洩露
這裡舉例一個使用DES演算法來實現對稱加密的例子:
public class DESUtils {
public byte[] initKey(){
try {
KeyGenerator keyGenerator = KeyGenerator.getInstance("DES");
keyGenerator.init(56);
SecretKey secretKey = keyGenerator.generateKey();
return secretKey.getEncoded();
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* @Method: encrypt
* @Description: 加密演算法
* @param data 被加密位元組陣列
* @param key 隨機對稱金鑰
* @return
* 返回型別:byte[]
*/
public byte[] encrypt(byte[] data,byte[] key){
SecretKey secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(key, "DES");
Cipher cipher;
try {
cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES");
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey);
return cipher.doFinal(data);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* @Method: decode
* @Description: TODO
* @param 被解密的位元組陣列
* @param key 隨機對稱金鑰(和加密金鑰務必保持一致)
* @return
* 返回型別:byte[]
*/
public byte[] decode(byte[] data,byte[] key){
SecretKey secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(key, "DES");
Cipher cipher;
try {
cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES");
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKey);
return cipher.doFinal(data);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
測試程式碼為:
public static void testDes(){
DESUtils desUtils = new DESUtils();
byte[] key = desUtils.initKey(); //
String originData = "123456";
System.out.println("原始資料:"+originData);
try {
// 將原始資料轉化為字串
byte[] arrayOrigin = originData.getBytes("utf-8");
// 對原始資料進行加密
byte[] encryption = desUtils.encrypt(arrayOrigin, key);
// 通過BASE64Encoder轉化處理
String encryptionStr = new BASE64Encoder().encode(encryption);
System.out.println("經過加密之後的字串:"+encryptionStr);
try {
// 使用BASE64Decoder進行轉化處理
byte[] decoceOrigin = new BASE64Decoder().decodeBuffer(encryptionStr);
// 使用DES進行解密操作
byte[] decode = desUtils.decode(decoceOrigin, key);
// 把位元組陣列轉化為字串
String decodeStr = new String(decode,"utf-8");
System.out.println("對加密字串進行解密:"+decodeStr);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
執行結果如下:
原始資料:123456
經過加密之後的字串:jaKOVkHJtOQ=
對加密字串進行解密:123456
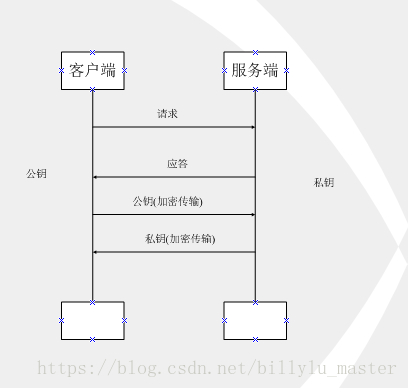
如上圖所示,客戶端用公鑰對請求內容加密,伺服器使用私鑰對內容解密,反之亦然,但上述過程也存在缺點:
公鑰是公開的(也就是黑客也會有公鑰),所以第 ④ 步私鑰加密的資訊,如果被黑客截獲,其可以使用公鑰進行解密,獲取其中的內容。
實現非對稱加密演算法例子:
public class AsymmetricEncryption {
public static final String KEY_ALGORITHM = "RSA";
/** 貌似預設是RSA/NONE/PKCS1Padding,未驗證 */
public static final String CIPHER_ALGORITHM = "RSA/ECB/PKCS1Padding";
public static final String PUBLIC_KEY = "publicKey";
public static final String PRIVATE_KEY = "privateKey";
/** RSA金鑰長度必須是64的倍數,在512~65536之間。預設是1024 */
public static final int KEY_SIZE = 2048;
public static final String PLAIN_TEXT = "hello world!";
/**
* @Method: generateKeyBytes
* @Description: 首先產生一個公鑰和私鑰對,使用HashMap儲存起來
* @return 返回型別:Map<String,byte[]>
*/
public static Map<String, byte[]> generateKeyBytes() {
try {
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator
.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM);
keyPairGenerator.initialize(KEY_SIZE);
KeyPair keyPair = keyPairGenerator.generateKeyPair();
RSAPublicKey publicKey = (RSAPublicKey) keyPair.getPublic();
RSAPrivateKey privateKey = (RSAPrivateKey) keyPair.getPrivate();
Map<String, byte[]> keyMap = new HashMap<String, byte[]>();
keyMap.put(PUBLIC_KEY, publicKey.getEncoded());
keyMap.put(PRIVATE_KEY, privateKey.getEncoded());
return keyMap;
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 還原公鑰,X509EncodedKeySpec 用於構建公鑰的規範
*
* @param keyBytes
* @return
*/
public static PublicKey restorePublicKey(byte[] keyBytes) {
X509EncodedKeySpec x509EncodedKeySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(keyBytes);
try {
KeyFactory factory = KeyFactory.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM);
PublicKey publicKey = factory.generatePublic(x509EncodedKeySpec);
return publicKey;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 還原私鑰,PKCS8EncodedKeySpec 用於構建私鑰的規範
*
* @param keyBytes
* @return
*/
public static PrivateKey restorePrivateKey(byte[] keyBytes) {
PKCS8EncodedKeySpec pkcs8EncodedKeySpec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(
keyBytes);
try {
KeyFactory factory = KeyFactory.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM);
PrivateKey privateKey = factory
.generatePrivate(pkcs8EncodedKeySpec);
return privateKey;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 加密,三步走。
*
* @param key
* @param plainText
* @return
*/
public static byte[] RSAEncode(PublicKey key, byte[] plainText) {
try {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(CIPHER_ALGORITHM);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key);
return cipher.doFinal(plainText);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public static String RSADecode(PrivateKey key, byte[] encodedText) {
try {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(CIPHER_ALGORITHM);
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, key);
return new String(cipher.doFinal(encodedText));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
測試程式碼如下:
public static void tesRSA(){
Map<String, byte[]> keyMap = AsymmetricEncryption.generateKeyBytes();
// 加密
PublicKey publicKey = AsymmetricEncryption.restorePublicKey(keyMap.get(AsymmetricEncryption.PUBLIC_KEY));
byte[] encodedText = AsymmetricEncryption.RSAEncode(publicKey, AsymmetricEncryption.PLAIN_TEXT.getBytes());
String rsaString = new BASE64Encoder().encode(encodedText);
System.out.println("RSA encoded: " + rsaString);
PrivateKey privateKey = AsymmetricEncryption.restorePrivateKey(keyMap.get(AsymmetricEncryption.PRIVATE_KEY));
System.out.println("RSA decoded: "+ AsymmetricEncryption.RSADecode(privateKey, encodedText));
}
執行結果如下所示:
RSA encoded: e7wIyV32VtiJhiraQGIYxD2TKtC4O6dRJx0lgVuEUsjCTSjqNFmEVNlYmFzd3ohIiW67XyIfEzWD
W9YFpFnDekRFLgeerh7c5gXMLVsVkf7k7XuTbiGmQOlOBUmL8VWpWVWTk8Rgn7Y+G7/dz9+DOEnH
csMnssKC/MBM80Ad5Za+QHqgb6BdZNHjZYzWpDIztBEUf/yHWfkGhmJahxo6Ff6y8er/shiP+qL3
hMJlw70TTGoGlrAWQqxUMYGPrv4IELi/iNSednXxo5bNNatJYke7FhKnuy8GEOWNH/K8Q52vl24L
cururJGLEJR6Hn/oaGxnXQbs2Fzo3vUziDj1cQ==
RSA decoded: hello world!
第三 非對稱和對稱完美結合
非對稱加密既然也有缺陷,那我們就將對稱加密,非對稱加密兩者結合起來,取其精華、去其糟粕,發揮兩者的各自的優勢:
如上圖所示
(1)第 ③ 步時,客戶端說:(咱們後續回話採用對稱加密吧,這是對稱加密的演算法和對稱金鑰)這段話用公鑰進行加密,然後傳給伺服器
(2)伺服器收到資訊後,用私鑰解密,提取出對稱加密演算法和對稱金鑰後,伺服器說:(好的)對稱金鑰加密
(3)後續兩者之間資訊的傳輸就可以使用對稱加密的方式了
這是個非常非常經典的資料傳輸過程,也是Https傳輸協議裡面最經典的部分。也是把對稱加密和非對稱加密的作用發揮到了很好的地方。在https傳輸的過程中,如果單獨只用對稱加密,或者單獨使用非對稱加密都會出現問題。