走迷宮問題(深度優先遍歷 + 廣度優先遍歷)
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-08
迷宮是許多小方格構成的矩形,在每個小方格中有的是牆(用1表示),有的是路(用0表示)。走迷宮就是從一個小方格沿上、下、左、右四個方向到鄰近的方格,當然不能穿牆。設迷宮的入口是在左上角(1,1),出口是在右下角(8,8)。根據給定的迷宮,找出一條從入口到出口的路徑。
解法一(深度優先遍歷,列印所有可行的路徑):
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int maze[8][8] = {{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},{0,1,1,1,1,0,1,0},{0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0},{0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0},
{0,1,0,1,1,0,1,0},{0,1,0,0,0,0,1,1},{0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0},{0,1,1,1,1,1,1,0}};
//下、右、上、左
const int fx[4] = {1,0,-1,0};
const int fy[4] = {0,1,0,-1};
//maze[i 執行結果:
解法二(廣度優先遍歷):
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int maze[8][8] = {{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},{0,1,1,1,1,0,1,0},{0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0},{0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0},
{0,1,0,1,1,0,1,0},{0,1,0,0,0,0,1,1},{0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0},{0,1,1,1,1,1,1,0}};
//下、右、上、左
const int fx[4] = {1,0,-1,0};
const int fy[4] = {0,1,0,-1};
struct sq{
int x;
int y;
int pre;
};
//標記路徑,正確的點值賦為3
void markPath(const vector<sq> &q, int index)
{
sq tmp = q[index];
maze[tmp.x][tmp.y] = 3;
if ( 0 == tmp.x && 0 == tmp.y )
{
return ;
}
else
{
markPath(q, tmp.pre);
}
}
//列印路徑
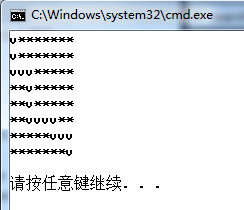
void printPath()
{
for (int i=0;i<8;++i)
{
for (int j=0;j<8;++j)
{
if (3 == maze[i][j])
{
cout<<"v";
}
else
{
cout<<"*";
}
}
cout<<endl;
}
cout<<endl;
}
//檢查點(i,j)是否滿足
bool check(int i, int j)
{
if (i >= 0 && i<8 && j>=0 && j<8 && 0 == maze[i][j])
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
void search()
{
//模仿佇列,之所以不用真正的佇列,因為後面需要通過下標對佇列進行隨機訪問
vector<sq> q;
int qh = 0;
sq fnode;
fnode.pre = -1;
fnode.x = 0;
fnode.y = 0;
//標記已訪問
maze[fnode.x][fnode.y] = -1;
q.push_back(fnode);
int qe = 1;
sq tmp;
while (qh != qe)
{
//出隊
tmp = q[qh];
++qh;
int newx, newy;
for (int k=0;k<4;++k)
{
newx = tmp.x + fx[k];
newy = tmp.y + fy[k];
if (check(newx, newy))
{
sq n_node;
n_node.pre = qh - 1;
n_node.x = newx;
n_node.y = newy;
//入隊
q.push_back(n_node);
++qe;
//找到出口,列印
if (7 == newx && 7 == newy)
{
markPath(q, qe-1);
printPath();
return;
}
}
}
//maze[tmp.x][tmp.y] = -1;
}
}
int main()
{
maze[0][0] = 3;
search();
return 0;
}執行結果: