資料結構以孩子兄弟鏈儲存的樹的高度
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-08
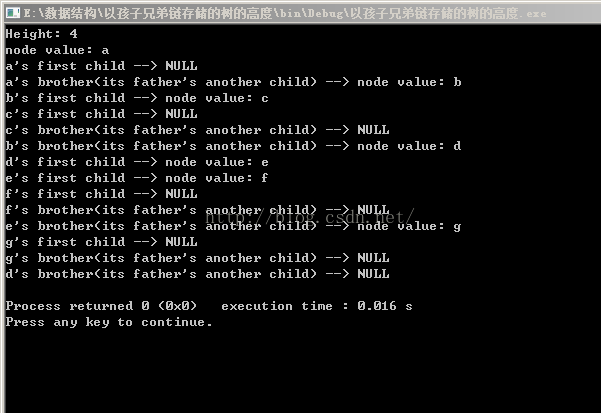
執行結果:
程式碼:
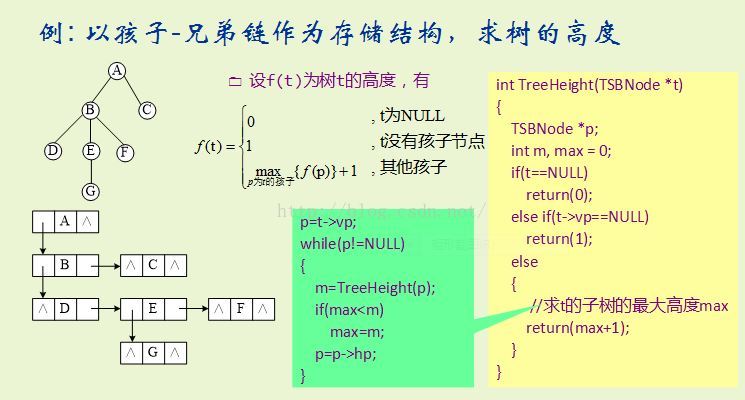
#include <stdio.h> #include <malloc.h> typedef char ElemType; typedef struct tnode { ElemType data; //節點的值 struct tnode *hp; //指向兄弟 struct tnode *vp; //指向孩子節點 } TSBNode; int TreeHeight(TSBNode *t); void TreeCreate(TSBNode *&t); void TreeDisp(TSBNode *t); int TreeHeight(TSBNode *t) { TSBNode *p; int m, max = 0; if(t==NULL) return(0); else if(t->vp==NULL) return(1); else { //求t的子樹的最大高度max p=t->vp; while(p!=NULL) { m=TreeHeight(p); if(max<m) max=m; p=p->hp; } return(max+1); } } int main() { TSBNode *tree; TreeCreate(tree); printf("Height: %d\n", TreeHeight(tree)); TreeDisp(tree); return 0; } void TreeCreate(TSBNode *&t) { //本例僅建造說明中特定的樹,以支援演示 TSBNode *a, *b, *c, *d, *e, *f, *g; a = (TSBNode *)malloc(sizeof(TSBNode)); b = (TSBNode *)malloc(sizeof(TSBNode)); c = (TSBNode *)malloc(sizeof(TSBNode)); d = (TSBNode *)malloc(sizeof(TSBNode)); e = (TSBNode *)malloc(sizeof(TSBNode)); f = (TSBNode *)malloc(sizeof(TSBNode)); g = (TSBNode *)malloc(sizeof(TSBNode)); a->data = 'a'; b->data = 'b'; c->data = 'c'; d->data = 'd'; e->data = 'e'; f->data = 'f'; g->data = 'g'; a->vp = b; a->hp = NULL; b->vp = d; b->hp = c; c->vp = NULL; c->hp = NULL; d->vp = NULL; d->hp = e; e->vp = g; e->hp = f; f->vp = NULL; f->hp = NULL; g->vp = NULL; g->hp = NULL; t=a; //a作為根 return; } void TreeDisp(TSBNode *t) { if(t!=NULL) { printf("node value: %c\n", t->data); printf("%c\'s first child --> ", t->data); TreeDisp(t->hp); printf("%c\'s brother(its father\'s another child) --> ", t->data); TreeDisp(t->vp); } else { printf("NULL\n"); } }