雙線性插值matlab版
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-09
雙線性插值(bilinear interpolation)是一種常見的插值運算方法,常見的運用是影象處理當中。與之齊名的還有最鄰近插值(nearest interpolation)和雙三次插值(bicubic interpolation)。相比之下雙線性插值要比最鄰近插值效果好,但是比雙三次插值效果差,計算量也處於兩者之間,算是比較折中的一種方法,應用也比較廣泛。


然後在 y 方向進行線性插值,得到


如果選擇一個座標系統使得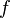 的四個已知點座標分別為
(0, 0)、(0, 1)、(1, 0) 和 (1, 1),那麼插值公式就可以化簡為
的四個已知點座標分別為
(0, 0)、(0, 1)、(1, 0) 和 (1, 1),那麼插值公式就可以化簡為

圖上可以看出來雙線性插值是有兩個變數的插值函式的線性插值擴充套件,其核心思想是在兩個方向分別進行一次線性插值。
假如我們想得到未知函式 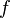 在點
在點  的值,假設我們已知函式
的值,假設我們已知函式 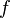 在
在  ,
,  ,
,  ,
及
,
及  四個點的值。
四個點的值。
首先在 x 方向進行線性插值,得到


然後在 y 方向進行線性插值,得到

這樣就得到所要的結果  ,
,


如果選擇一個座標系統使得
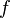 的四個已知點座標分別為
(0, 0)、(0, 1)、(1, 0) 和 (1, 1),那麼插值公式就可以化簡為
的四個已知點座標分別為
(0, 0)、(0, 1)、(1, 0) 和 (1, 1),那麼插值公式就可以化簡為

以下是matlab程式碼用來實現雙線性插值
% 針對單幅影象簡單放大縮小而進行的雙線性插值演算法(不包含選轉等變化) f = imread('cameraman.tif'); [nrows, ncols] = size(f); K = str2double( inputdlg('please input scale factor (between 0.2-5.0)',... 'INPUT scale factor', 1, {'0.5'} )); if( K<0.2||K>5.0 ) errordlg('scale factor beyond permitted range (0.2-5.0), 'ERROR'); error('please input scale factor (must between 0.2-0.5)'); end figure, imshow(f); % output image width and height, both scaled by factor K width = floor(K * nrows); height = floor(K * ncols); J = uint8(zeros(height, width)); widthScale = ncols / width; heightScale = nrows / height; % pad the image to handle the edge effect I = padarray(f, [1 1], 'replicate', 'post'); % bilinear interpolation for x = 1:height for y = 1:width xx = x * widthScale; yy = y * heightScale; if(xx/double(uint16(xx))==1.0) || (yy/double(uint16(yy))==1.0) J(x,y) = I(uint16(xx), uint16(yy)); else a = double(fix(xx)); b = double(fix(yy)); if(a == 0) a = 1; elseif a>=nrows-1 a = nrows - 1; end if(b == 0) b = 1; elseif b>=ncols-1 b = ncols - 1; end x11 = double(I(a,b)); x12 = double(I(a,b+1)); x21 = double(I(a+1,b)); x22 = double(I(a+1,b+1)); J(x,y) = uint8((b+1-yy) * ((xx-a) * x21 + (a+1-xx) * x11) + ... (yy-b) * ((xx-a) * x22 + (a+1-xx) * x12); end end end figure, imshow(J);
注:以上圖片和公式均來自維基百科
