粘包與分包問題的出現及解決
1、粘包出現的原因:服務端與客戶端沒有約定好要使用的資料結構。Socket Client實際是將資料包傳送到一個快取buffer中,通過buffer刷到資料鏈路層。因服務端接收資料包時,不能斷定資料包1何時結束,就有可能出現數據包2的部分資料結合資料包1傳送出去,導致伺服器讀取資料包1時包含了資料包2的資料。這種現象稱為粘包。
2、案例展示:(1)、服務端程式碼如下,具體註釋說明
package com.server; import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; import io.netty.channel.Channel; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder; import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder; /** * Netty5服務端 * @author zhengzx * */ public class ServerSocket { public static void main(String[] args) { //建立服務類 ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); //boss和worker NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup(); NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { //設定執行緒池 serverBootstrap.group(boss,worker); //設定socket工廠,Channel 是對 Java 底層 Socket 連線的抽象 serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class); //設定管道工廠 serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { //設定後臺轉換器(二進位制轉換字串) ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder()); ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder()); ch.pipeline().addLast(new ServerSocketHandler()); } }); //設定TCP引數 serverBootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 2048);//連線緩衝池大小 serverBootstrap.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);//維持連線的活躍,清除死連線 serverBootstrap.childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true);//關閉超時連線 ChannelFuture future = serverBootstrap.bind(10010);//繫結埠 System.out.println("服務端啟動"); //等待服務端關閉 future.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //釋放資源 boss.shutdownGracefully(); worker.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
(2)、ServerSocketHandler處理類展示:
package com.server; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler; public class ServerSocketHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String>{ @Override protected void messageReceived(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) throws Exception { System.out.println(msg); } }
(3)、客戶端傳送請求程式碼展示:
package com.client; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.Socket; import java.net.UnknownHostException; public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException, IOException { //建立連線 Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 10010); //迴圈傳送請求 for(int i=0;i<1000;i++){ socket.getOutputStream().write("hello".getBytes()); } //關閉連線 socket.close(); } }
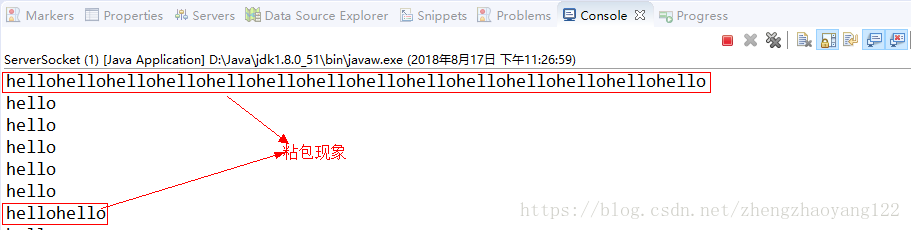
(4)、列印結果。(正常情況應為一行一個hello列印)
3、分包:資料包資料被分開一部分發送出去,服務端一次讀取資料時可能讀取到完整資料包的一部分,剩餘部分被第二次讀取。具體情況如下圖展示:
4、解決辦法1:定義一個穩定的結構。
(1)、包頭+length+資料包:客戶端程式碼展示:包頭——>用來防止socket攻擊,length——>用來獲取資料包的長度。
package com.server;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import org.omg.CORBA.PRIVATE_MEMBER;
import org.omg.CORBA.PUBLIC_MEMBER;
/**
* @category 通過長度+資料包的方式解決粘包分包問題
* @author zhengzx
*
*/
public class Client {
//定義包頭
public static int BAO = 24323455;
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException, IOException {
//建立連線
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 10010);
//客戶端傳送的訊息
String msg = "hello";
//獲取訊息的位元組碼
byte[] bytes = msg.getBytes();
//初始化buffer的長度:4+4表示包頭長度+存放資料長度的整數的長度
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(8+bytes.length);
//將長度和資料存入buffer中
buffer.putInt(BAO);
buffer.putInt(bytes.length);
buffer.put(bytes);
//獲取緩衝區中的資料
byte[] array = buffer.array();
//迴圈傳送請求
for(int i=0;i<1000;i++){
socket.getOutputStream().write(array);
}
//關閉連線
socket.close();
}
}
(2)、服務端:需要注意的是,添加了MyDecoder類,此類具體下面介紹
package com.server;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import org.jboss.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.ChannelPipelineFactory;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.Channels;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannelFactory;
import org.jboss.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
import org.jboss.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder;
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//服務類
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
//boss執行緒監聽埠,worker執行緒負責資料讀寫
ExecutorService boss = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
ExecutorService worker = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
//設定niosocket工廠
bootstrap.setFactory(new NioServerSocketChannelFactory(boss, worker));
//設定管道的工廠
bootstrap.setPipelineFactory(new ChannelPipelineFactory() {
@Override
public ChannelPipeline getPipeline() throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = Channels.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new MyDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("handler1", new HelloHandler());
return pipeline;
}
});
bootstrap.bind(new InetSocketAddress(10101));
System.out.println("start!!!");
}
}
(3)、MyDecode類,需要繼承FrameDecoder類。此類中用ChannelBuffer快取沒有讀取的資料包,等接收到第二次傳送的資料包時,會將此資料包與快取的資料包進行拼接處理。
當return一個String時,FarmedDecoder通過判斷返回型別,呼叫相應的sendUpStream(event)向下傳遞資料。原始碼展示:
public static void fireMessageReceived(
ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object message, SocketAddress remoteAddress) {
ctx.sendUpstream(new UpstreamMessageEvent(
ctx.getChannel(), message, remoteAddress));
}當返回null時,會進行break,不處理資料包中的資料,原始碼展示:
while (cumulation.readable()) {
int oldReaderIndex = cumulation.readerIndex();
Object frame = decode(context, channel, cumulation);
if (frame == null) {
if (oldReaderIndex == cumulation.readerIndex()) {
// Seems like more data is required.
// Let us wait for the next notification.
break;
} else {
// Previous data has been discarded.
// Probably it is reading on.
continue;
}
}我們自己寫的MyDecoder類,程式碼展示:(包含socket攻擊的校驗)
package com.server;
import org.jboss.netty.buffer.ChannelBuffer;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.Channel;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import org.jboss.netty.handler.codec.frame.FrameDecoder;
public class MyDecoder extends FrameDecoder{
@Override
protected Object decode(ChannelHandlerContext arg0, Channel arg1, ChannelBuffer buffer) throws Exception {
//buffer.readableBytes獲取緩衝區中的資料 需要 大於基本長度
if(buffer.readableBytes() > 4) {
//防止socket攻擊,當緩衝區資料大於2048時,清除資料。
if(buffer.readableBytes() > 2048) {
buffer.skipBytes(buffer.readableBytes());
}
//迴圈獲取包頭,確定資料包的開始位置
while(true) {
buffer.markReaderIndex();
if(buffer.readInt() == Client.BAO) {
break;
}
//只讀取一個位元組
buffer.resetReaderIndex();
buffer.readByte();
if(buffer.readableBytes() < 4) {
return null;
}
}
//做標記
buffer.markReaderIndex();
//獲取資料包的傳送過來時的長度
int readInt = buffer.readInt();
//判斷buffer中剩餘的資料包長度是否大於單個數據包的長度(readInt)
if(buffer.readableBytes() < readInt) {
//返回到上次做標記的地方,因為此次資料讀取的不是一個完整的資料包。
buffer.resetReaderIndex();
//快取當前資料,等待剩下資料包到來
return null;
}
//定義一個數據包的長度
byte[] bt = new byte[readInt];
//讀取資料
buffer.readBytes(bt);
//往下傳遞物件
return new String(bt);
}
//快取當前資料包,等待第二次資料的到來
return null;
}
}
(4)、服務端,處理請求的handler。
package com.server;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.MessageEvent;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.SimpleChannelHandler;
public class HelloHandler extends SimpleChannelHandler {
private int count = 1;
@Override
public void messageReceived(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MessageEvent e) throws Exception {
System.out.println(e.getMessage() + " " +count);
count++;
}
}
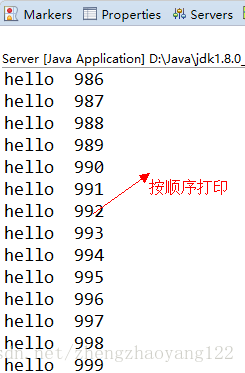
(5)、結果展示(按順序列印):
5、解決辦法2:在訊息的尾部加一些特殊字元,那麼在讀取資料的時候,只要讀到這個特殊字元,就認為已經可以擷取一個完整的資料包了,這種情況在一定的業務情況下實用。