[hankerank]Day 15: Linked List
Objective
Today we're working with Linked Lists. Check out the Tutorial tab for learning materials and an instructional video!
A Node class is provided for you in the editor. A Node object has an integer data field, , and a Node instance pointer, , pointing to another node (i.e.: the next node in a list).
A Node insert function is also declared in your editor. It has two parameters: a pointer, , pointing to the first node of a linked list, and an integer value that must be added to the end of the list as a new Node object.
Task
Complete the insert function in your editor so that it creates a new Node
Note: If the argument passed to the insert function is null, then the initial list is empty.
Input Format
The insert
The constructor for Node has parameter: an integer value for the field.
You do not need to read anything from stdin.
Output Format
Your insert function should return a reference to the node of the linked list.
Sample Input
The following input is handled for you by the locked code in the editor:
The first line contains T, the number of test cases.
The subsequent lines of test cases each contain an integer to be inserted at the list's tail.
4
2
3
4
1
Sample Output
The locked code in your editor prints the ordered data values for each element in your list as a single line of space-separated integers:
2 3 4 1
Explanation
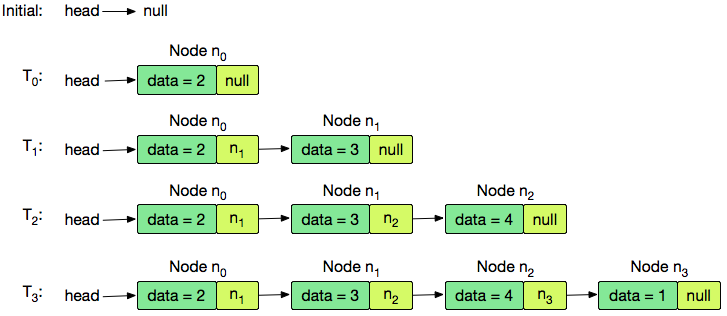
, so the locked code in the editor will be inserting nodes.
The list is initially empty, so is null; accounting for this, our code returns a new node containing the data value as the of our list. We then create and insert nodes , , and at the tail of our list. The resulting list returned by the last call to is , so the printed output is 2 3 4 1.
Current Buffer (saved locally, editable)
class Node:
def __init__(self,data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class Solution:
def display(self,head):
current = head
while current:
print(current.data,end=' ')
current = current.next
def insert(self,head,data):
#Complete this method
node=Node(data)
if head==None:
head=node
else:
pre=head
while pre.next:
pre=pre.next
pre.next=node
return head
mylist= Solution()
T=int(input())
head=None
for i in range(T):
data=int(input())
head=mylist.insert(head,data)
mylist.display(head); 注意:
- 在定義連結串列時,沒有繼承節點的父類。
- head不是表示頭指標,可以看成是正在重新整理中連結串列。
- 如果在生成class Linklist 中使用了初始化函式__init__(parameters)必須在定義中寫明括號中的變數名稱class Linklist(parameters)。
