Android 仿360懸浮球與加速球
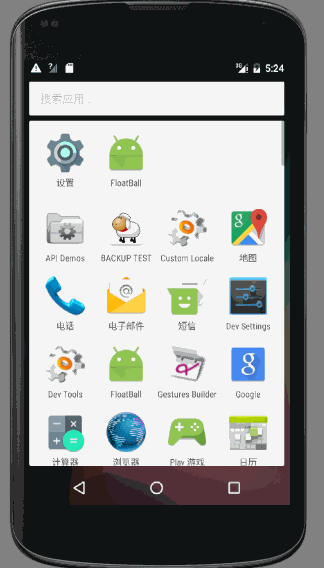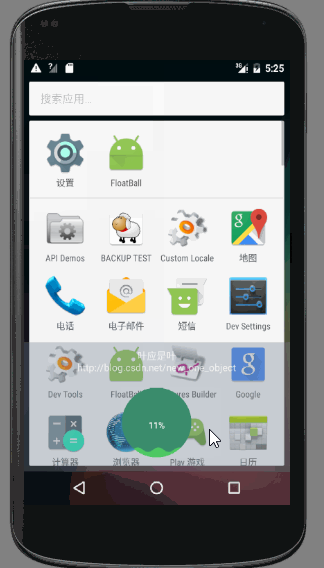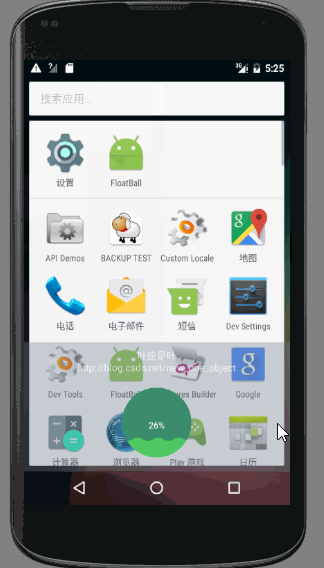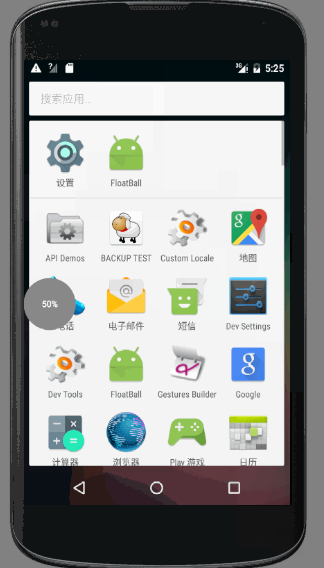
先來看一張動態圖
昨天跟著視訊學瞭如何自定義View並做成仿360懸浮球與加速球的樣式
可以看出來,做成的效果有:
- 點選按鈕後退出Activity,呈現一個圓形的懸浮球,可以隨意拖動並會自動依靠到螢幕一側,且拖動時會變成一張圖片
- 當點選懸浮球時,懸浮球隱藏,底部出現一個加速球,雙擊加速球時,呈現水量逐漸增高且波動幅度較小的效果,單擊時波浪上下波動且幅度漸小
- 點選螢幕不包含底部加速球的部位,加速球會隱藏,懸浮球重新出現
要做出這麼一個效果,需要兩個自定義View與一個自定義ViewGroup
首先,需要先設計懸浮球View——FloatBall
簡單起見,為FloatBall指定一個預設寬度和高度——150畫素
然後在onDraw(Canvas canvas)
/**
* Created by ZY on 2016/8/10.
* 懸浮球
*/
public class FloatBall extends View {
public int width = 150;
public int height = 150;
//預設顯示的文字
private String text = "50%";
//是否在拖動
private boolean isDrag;
private Paint ballPaint;
private 因為FloatBall是不存在於Activity中而在螢幕單獨顯示的,所以需要用WindowManager來新增View並顯示
新建一個類,命名為ViewManager,用來總的管理View的顯示與刪除
私有化建構函式並採用單例模式
private static ViewManager manager;
//私有化建構函式
private ViewManager(Context context) {
this.context = context;
init();
}
//獲取ViewManager例項
public static ViewManager getInstance(Context context) {
if (manager == null) {
manager = new ViewManager(context);
}
return manager;
}ViewManager包含有顯示與隱藏懸浮球與加速球的函式
//顯示浮動小球
public void showFloatBall() {
if (floatBallParams == null) {
floatBallParams = new LayoutParams();
floatBallParams.width = floatBall.width;
floatBallParams.height = floatBall.height - getStatusHeight();
floatBallParams.gravity = Gravity.TOP | Gravity.LEFT;
floatBallParams.type = LayoutParams.TYPE_TOAST;
floatBallParams.flags = LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE | LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_TOUCH_MODAL;
floatBallParams.format = PixelFormat.RGBA_8888;
}
windowManager.addView(floatBall, floatBallParams);
}
//顯示底部選單
private void showFloatMenu() {
if (floatMenuParams == null) {
floatMenuParams = new LayoutParams();
floatMenuParams.width = getScreenWidth();
floatMenuParams.height = getScreenHeight() - getStatusHeight();
floatMenuParams.gravity = Gravity.BOTTOM;
floatMenuParams.type = LayoutParams.TYPE_TOAST;
floatMenuParams.flags = LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE | LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_TOUCH_MODAL;
floatMenuParams.format = PixelFormat.RGBA_8888;
}
windowManager.addView(floatMenu, floatMenuParams);
}
//隱藏底部選單
public void hideFloatMenu() {
if (floatMenu != null) {
windowManager.removeView(floatMenu);
}
}將懸浮球置於Service中開啟,這樣懸浮球就不那麼容易被系統去除了
在onCreate()方法中呼叫showFloatBall()
public class StartFloatBallService extends Service {
public StartFloatBallService() {
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// TODO: Return the communication channel to the service.
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not yet implemented");
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
ViewManager manager = ViewManager.getInstance(this);
manager.showFloatBall();
super.onCreate();
}
}此時,只要為MainActivity新增一個按鈕,並設定當點選按鈕後開啟Service,此時即可看到螢幕顯示了一個懸浮球
public void startService(View view) {
Intent intent = new Intent(this, StartFloatBallService.class);
startService(intent);
finish();
}不過此時懸浮球還不支援拖動與點選,還需要為其新增OnTouchListener與OnClickListener
View.OnTouchListener touchListener = new View.OnTouchListener() {
float startX;
float startY;
float tempX;
float tempY;
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
startX = event.getRawX();
startY = event.getRawY();
tempX = event.getRawX();
tempY = event.getRawY();
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
float x = event.getRawX() - startX;
float y = event.getRawY() - startY;
//計算偏移量,重新整理檢視
floatBallParams.x += x;
floatBallParams.y += y;
floatBall.setDragState(true);
windowManager.updateViewLayout(floatBall, floatBallParams);
startX = event.getRawX();
startY = event.getRawY();
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
//判斷鬆手時View的橫座標是靠近螢幕哪一側,將View移動到依靠螢幕
float endX = event.getRawX();
float endY = event.getRawY();
if (endX < getScreenWidth() / 2) {
endX = 0;
} else {
endX = getScreenWidth() - floatBall.width;
}
floatBallParams.x = (int) endX;
floatBall.setDragState(false);
windowManager.updateViewLayout(floatBall, floatBallParams);
//如果初始落點與鬆手落點的座標差值超過6個畫素,則攔截該點選事件
//否則繼續傳遞,將事件交給OnClickListener函式處理
if (Math.abs(endX - tempX) > 6 && Math.abs(endY - tempY) > 6) {
return true;
}
break;
}
return false;
}
};
OnClickListener clickListener = new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
windowManager.removeView(floatBall);
showFloatMenu();
floatMenu.startAnimation();
}
};
floatBall.setOnTouchListener(touchListener);
floatBall.setOnClickListener(clickListener);加速球ProgressBall的設計較為複雜,需要用到貝塞爾曲線來呈現波浪效果,且單擊雙擊的效果也需要分開呈現
同樣是讓ProgressBall繼承於View
進度值的意義在於限制水面最終上升到的高度,即根據目標進度值與最大進度值的比例來決定水面高度
波浪總的起伏次數Count用於在單擊加速球時,水面上下波動的次數
//view的寬度
private int width = 200;
//view的高度
private int height = 200;
//最大進度值
private final int maxProgress = 100;
//當前進度值
private int currentProgress = 0;
//目標進度值
private final int targetProgress = 70;
//是否為單擊
private boolean isSingleTop;
//設定波浪總的起伏次數
private final int Count = 20;
//當前起伏次數
private int currentCount;
//初始振幅大小
private final int startAmplitude = 15;
//波浪週期性出現的次數
private final int cycleCount = width / (startAmplitude * 4) + 1;初始化畫筆與監聽函式
private void init() {
//初始化小球畫筆
ballPaint = new Paint();
ballPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
ballPaint.setColor(Color.argb(0xff, 0x3a, 0x8c, 0x6c));
//初始化(波浪)進度條畫筆
progressPaint = new Paint();
progressPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
progressPaint.setColor(Color.argb(0xff, 0x4e, 0xc9, 0x63));
progressPaint.setXfermode(new PorterDuffXfermode(PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN));
//初始化文字畫筆
textPaint = new Paint();
textPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
textPaint.setColor(Color.WHITE);
textPaint.setTextSize(25);
handler = new Handler();
path = new Path();
bitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(width, height, Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
bitmapCanvas = new Canvas(bitmap);
//手勢監聽
//重點在於將單擊和雙擊操作分隔開
SimpleOnGestureListener listener = new SimpleOnGestureListener() {
//雙擊
@Override
public boolean onDoubleTap(MotionEvent e) {
//當前波浪起伏次數為零,說明“單擊效果”沒有影響到現在
if (currentCount == 0) {
//當前進度為零或者已達到目標進度值,說明“雙擊效果”沒有影響到現在,此時可以允許進行雙擊操作
if (currentProgress == 0 || currentProgress == targetProgress) {
currentProgress = 0;
isSingleTop = false;
startDoubleTapAnimation();
}
}
return super.onDoubleTap(e);
}
//單擊
@Override
public boolean onSingleTapConfirmed(MotionEvent e) {
//當前進度值等於目標進度值,且當前波動次數為零,則允許進行單擊操作
if (currentProgress == targetProgress && currentCount == 0) {
isSingleTop = true;
startSingleTapAnimation();
}
return super.onSingleTapConfirmed(e);
}
};
gestureDetector = new GestureDetector(context, listener);
setOnTouchListener(new OnTouchListener() {
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
return gestureDetector.onTouchEvent(event);
}
});
//接受點選操作
setClickable(true);
}單擊或雙擊後的漸變效果是利用Handler的postDelayed(Runnable r, long delayMillis)方法來實現的,可以設定一個延時時間去執行Runnable ,然後在Runnable 中再次呼叫自身
class DoubleTapRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
if (currentProgress < targetProgress) {
invalidate();
handler.postDelayed(doubleTapRunnable, 50);
currentProgress++;
} else {
handler.removeCallbacks(doubleTapRunnable);
}
}
}
//開啟雙擊動作動畫
public void startDoubleTapAnimation() {
handler.postDelayed(doubleTapRunnable, 50);
}
class SingleTapRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
if (currentCount < Count) {
invalidate();
currentCount++;
handler.postDelayed(singleTapRunnable, 100);
} else {
handler.removeCallbacks(singleTapRunnable);
currentCount = 0;
}
}
}
//開啟單擊動作動畫
public void startSingleTapAnimation() {
handler.postDelayed(singleTapRunnable, 100);
}onDraw(Canvas canvas)的重點在於根據比例值來計算水面高度
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
//繪製圓形
bitmapCanvas.drawCircle(width / 2, height / 2, width / 2, ballPaint);
path.reset();
//高度隨當前進度值的變化而變化
float y = (1 - (float) currentProgress / maxProgress) * height;
//屬性PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN代表了progressPaint只顯示與下層層疊的部分,
//所以以下四點雖然連起來是個矩形,可呈現出來的依然是圓形
//右上角
path.moveTo(width, y);
//右下角
path.lineTo(width, height);
//左下角
path.lineTo(0, height);
//左上角
path.lineTo(0, y);
//繪製頂部波浪
if (!isSingleTop) {
//是雙擊
//根據當前進度大小調整振幅大小,有逐漸減小的趨勢
float tempAmplitude = (1 - (float) currentProgress / targetProgress) * startAmplitude;
for (int i = 0; i < cycleCount; i++) {
path.rQuadTo(startAmplitude, tempAmplitude, 2 * startAmplitude, 0);
path.rQuadTo(startAmplitude, -tempAmplitude, 2 * startAmplitude, 0);
}
} else {
//是單擊
//根據當前次數調整振幅大小,有逐漸減小的趨勢
float tempAmplitude = (1 - (float) currentCount / Count) * startAmplitude;
//因為想要形成波浪上下起伏的效果,所以根據currentCount的奇偶性來變化貝塞爾曲線轉折點位置
if (currentCount % 2 == 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < cycleCount; i++) {
path.rQuadTo(startAmplitude, tempAmplitude, 2 * startAmplitude, 0);
path.rQuadTo(startAmplitude, -tempAmplitude, 2 * startAmplitude, 0);
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < cycleCount; i++) {
path.rQuadTo(startAmplitude, -tempAmplitude, 2 * startAmplitude, 0);
path.rQuadTo(startAmplitude, tempAmplitude, 2 * startAmplitude, 0);
}
}
}
path.close();
bitmapCanvas.drawPath(path, progressPaint);
String text = (int) (((float) currentProgress / maxProgress) * 100) + "%";
float textWidth = textPaint.measureText(text);
Paint.FontMetrics metrics = textPaint.getFontMetrics();
float baseLine = height / 2 - (metrics.ascent + metrics.descent);
bitmapCanvas.drawText(text, width / 2 - textWidth / 2, baseLine, textPaint);
canvas.drawBitmap(bitmap, 0, 0, null);
}因為要呈現ProgressBall時不僅僅是其本身,或者還需要背景色或者文字之類的內容,所以可以將其置於ViewGroup中來顯示
佈局檔案
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/layout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:background="#556f7f8f"
android:clickable="true"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="葉應是葉\nhttp://blog.csdn.net/new_one_object" />
<com.czy.floatball.View.ProgressBall
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="20dp" />
</LinearLayout>
</RelativeLayout>FloatMenu就作為容納ProgressBall的容器,併為其賦予從下往上滑動顯示的動畫效果
/**
* Created by ZY on 2016/8/10.
* 底部選單欄
*/
public class FloatMenu extends LinearLayout {
private LinearLayout layout;
private TranslateAnimation animation;
public FloatMenu(final Context context) {
super(context);
View root = View.inflate(context, R.layout.float_menu, null);
layout = (LinearLayout) root.findViewById(R.id.layout);
animation = new TranslateAnimation(Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0,
Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0,
Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 1.0f,
Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0);
animation.setDuration(500);
animation.setFillAfter(true);
layout.setAnimation(animation);
root.setOnTouchListener(new OnTouchListener() {
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
ViewManager manager = ViewManager.getInstance(context);
manager.showFloatBall();
manager.hideFloatMenu();
return false;
}
});
addView(root);
}
public void startAnimation() {
animation.start();
}
}