react-native之ART繪圖詳解
背景
在移動應用的開發過程中,繪製基本的二維圖形或動畫是必不可少的。然而,考慮到Android和iOS均有一套各自的API方案,因此採用一種更普遍接受的技術方案,更有利於程式碼的雙平臺相容。
art是一個旨在多瀏覽器相容的Node style CommonJS模組。在它的基礎上,Facebook又開發了react-art ,封裝art,使之可以被react.js所使用,即實現了前端的svg庫。然而,考慮到react.js的JSX語法,已經支援將等等svg標籤直接插入到dom中(當然此時使用的就不是react-art庫了)此外還有HTML canvas的存在,因此,在前端上,react-art並非不可替代。
然而,在移動端,考慮到跨平臺的需求,加之web端的技術積累,react-art成為了現成的繪製圖形的解決方案。react-native分別在0.10.0和0.18.0上添加了iOS和Android平臺上對react-art的支援。
示例程式碼
React.js和React-Native的區別,只在於下文所述的ART獲取上,然後該例子就可以同時應用在Web端和移動端上了。react-art自帶的官方例子:Vector-Widget
Vector-Widget額外實現了旋轉,以及滑鼠點選事件的旋轉加速響應。Web端可以看到點選加速,但是在移動端無效,原因是React Native並未對Group中onMouseDown和onMouseUp屬性作處理。本文著重於靜態svg的實現,暫時無視動畫部分效果即可。
ART
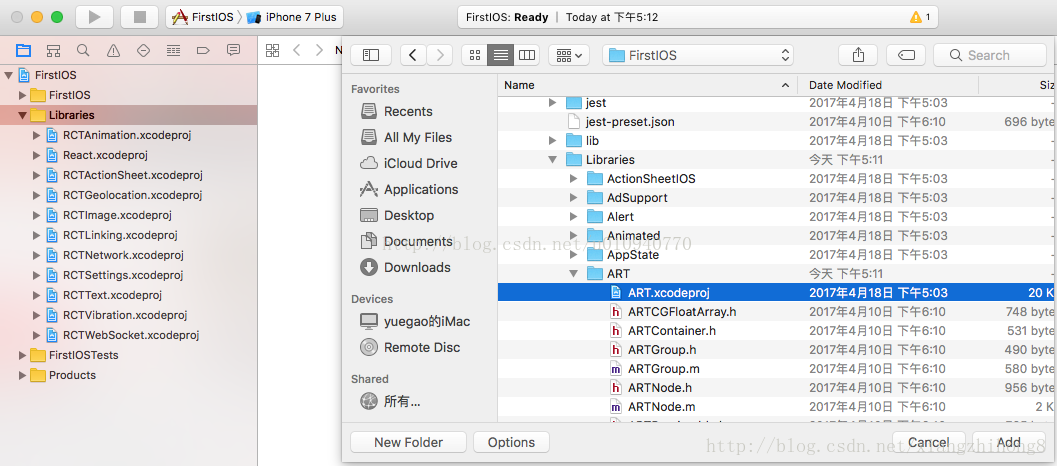
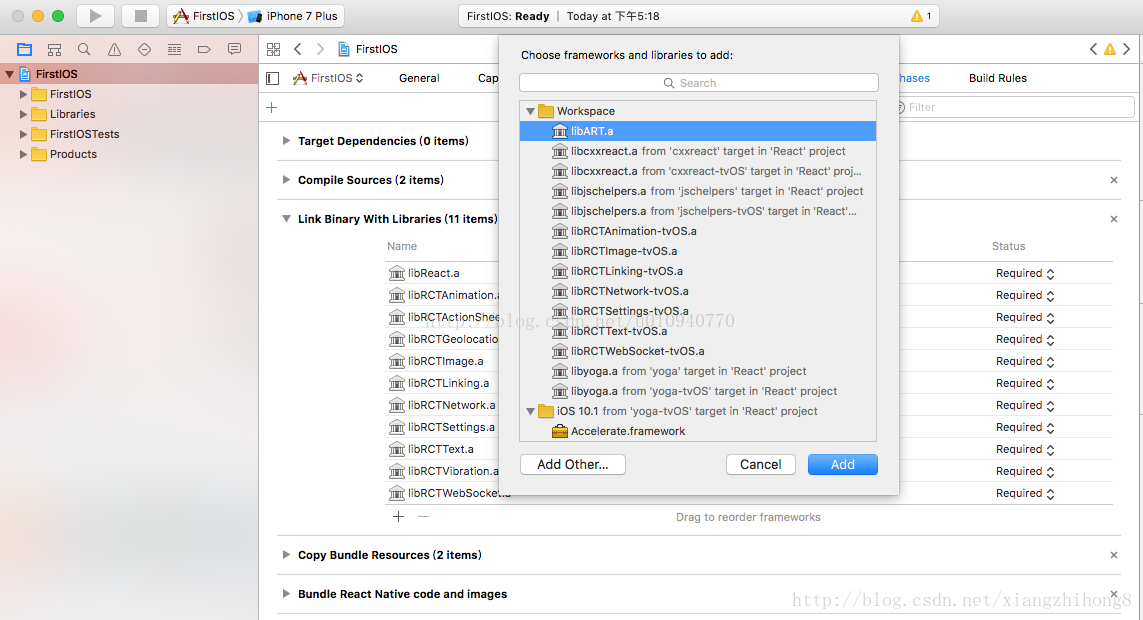
在React Native中ART是個非常重要的庫,它讓非常酷炫的繪圖及動畫變成了可能。需要注意的是,在React Native引入ART過程中,Android預設就包含ART庫,IOS需要單獨新增依賴庫。
ios新增依賴庫
1、使用xcode中開啟React-native中的iOS專案,選中‘Libraries’目錄 ——> 右鍵選擇‘Add Files to 專案名稱’ ——> 'node_modules/react-native/Libraries/ART/ART.xcodeproj' 新增;
2、選中專案根目錄 ——> 點選’Build Phases‘ ——> 點選‘Link Binary With Libraries’ ——> 點選左下方‘+’ ——> 選中‘libART.a’新增。
基礎元件
ART暴露的元件共有7個,本文介紹常用的四個元件:Surface、Group、Shape、Text。
- Surface - 一個矩形可渲染的區域,是其他元素的容器
- Group - 可容納多個形狀、文字和其他的分組
- Shape - 形狀定義,可填充
- Text - 文字形狀定義
屬性
Surface
- width : 渲染區域的寬
- height : 定義渲染區域的高
Shape
- d : 定義繪製路徑
- stroke : 描邊顏色
- strokeWidth : 描邊寬度
- strokeDash : 定義虛線
- fill : 填充顏色
Text
- funt : 字型樣式,定義字型、大小、是否加粗 如: bold 35px Heiti SC
Path
- moveTo(x,y) : 移動到座標(x,y)
- lineTo(x,y) : 連線到(x,y)
- arc() : 繪製弧線
- close() : 封閉空間
程式碼示例
繪製直線
import React from 'react'
import {
View,
ART
} from 'react-native'
export default class Line extends React.Component{
render(){
const path = ART.Path();
path.moveTo(1,1); //將起始點移動到(1,1) 預設(0,0)
path.lineTo(300,1); //連線到目標點(300,1)
return(
<View style={this.props.style}>
<ART.Surface width={300} height={2}>
<ART.Shape d={path} stroke="#000000" strokeWidth={1} />
</ART.Surface>
</View>
)
}
}
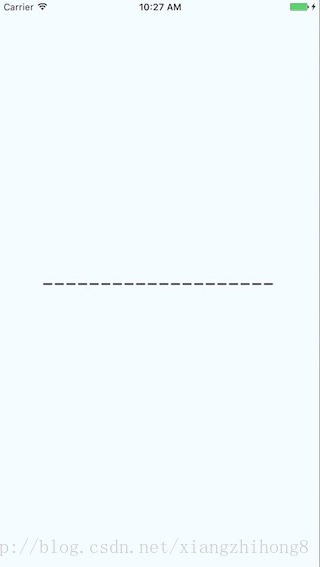
繪製虛線
瞭解strokeDash的引數,
[10,5] : 表示繪10畫素實線在繪5畫素空白,如此迴圈
[10,5,20,5] : 表示繪10畫素實線在繪製5畫素空白在繪20畫素實線及5畫素空白
import React from 'react'
import {
View,
ART
} from 'react-native'
const {Surface, Shape, Path} = ART;
export default class DashLine extends React.Component{
render(){
const path = Path()
.moveTo(1,1)
.lineTo(300,1);
return(
<View style={this.props.style}>
<Surface width={300} height={2}>
<Shape d={path} stroke="#000000" strokeWidth={2} strokeDash={[10,5]}/>
</Surface>
</View>
)
}
}
繪製矩形
首先通過lineTo繪製三條邊,在使用close連結第四條邊。fill做顏色填充.
import React from 'react'
import {
View,
ART
} from 'react-native'
const {Surface, Shape, Path} = ART;
export default class Rect extends React.Component{
render(){
const path = new Path()
.moveTo(1,1)
.lineTo(1,99)
.lineTo(99,99)
.lineTo(99,1)
.close();
return(
<View style={this.props.style}>
<Surface width={100} height={100}>
<Shape d={path} stroke="#000000" fill="#892265" strokeWidth={1} />
</Surface>
</View>
)
}
}
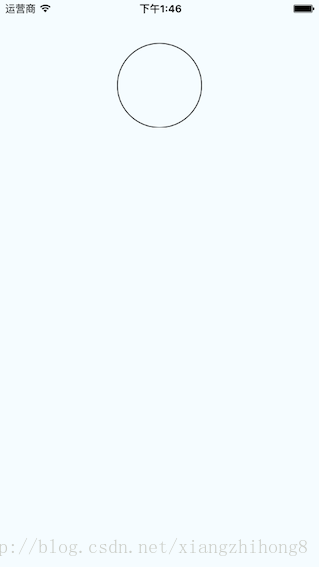
繪圓
瞭解arc(x,y,radius)的使用, 終點座標距離起點座標的相對距離。
import React from 'react'
import {
View,
ART
} from 'react-native'
const {Surface, Shape, Path} = ART;
export default class Circle extends React.Component{
render(){
const path = new Path()
.moveTo(50,1)
.arc(0,99,25)
.arc(0,-99,25)
.close();
return(
<View style={this.props.style}>
<Surface width={100} height={100}>
<Shape d={path} stroke="#000000" strokeWidth={1}/>
</Surface>
</View>
)
}
}
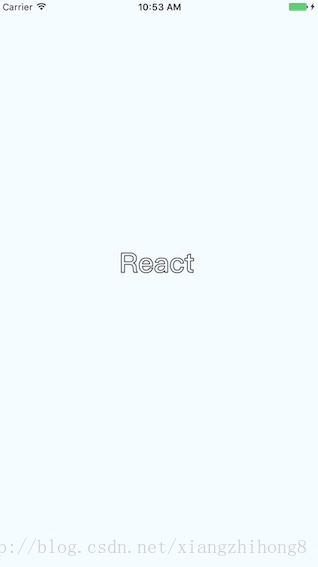
繪製文字
瞭解funt屬性的使用,規則是“粗細 字號 字型”
注意: 字型應該是支援path屬性的,應該是實現bug並沒有不生效。 Android通過修改原始碼是可以解決的,IOS沒看原始碼。
import React, {Component} from 'react';
import {
AppRegistry,
StyleSheet,
ART,
View
} from 'react-native';
const {Surface, Text, Path} = ART;
export default class ArtTextView extends Component {
render() {
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Surface width={100} height={100}>
<Text strokeWidth={1} stroke="#000" font="bold 35px Heiti SC" path={new Path().moveTo(40,40).lineTo(99,10)} >React</Text>
</Surface>
</View>
);
}
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'center',
backgroundColor: '#F5FCFF',
},
});
繪製扇形
在這裡需要使用arc做路徑繪製。
Wedge.js
import React, { Component, PropTypes } from 'react';
import { ART } from 'react-native';
const { Shape, Path } = ART;
/**
* Wedge is a React component for drawing circles, wedges and arcs. Like other
* ReactART components, it must be used in a <Surface>.
*/
export default class Wedge extends Component<void, any, any> {
static propTypes = {
outerRadius: PropTypes.number.isRequired,
startAngle: PropTypes.number.isRequired,
endAngle: PropTypes.number.isRequired,
originX: PropTypes.number.isRequired,
originY: PropTypes.number.isRequired,
innerRadius: PropTypes.number,
};
constructor(props : any) {
super(props);
(this:any).circleRadians = Math.PI * 2;
(this:any).radiansPerDegree = Math.PI / 180;
(this:any)._degreesToRadians = this._degreesToRadians.bind(this);
}
/**
* _degreesToRadians(degrees)
*
* Helper function to convert degrees to radians
*
* @param {number} degrees
* @return {number}
*/
_degreesToRadians(degrees : number) : number {
if (degrees !== 0 && degrees % 360 === 0) { // 360, 720, etc.
return (this:any).circleRadians;
}
return degrees * (this:any).radiansPerDegree % (this:any).circleRadians;
}
/**
* _createCirclePath(or, ir)
*
* Creates the ReactART Path for a complete circle.
*
* @param {number} or The outer radius of the circle
* @param {number} ir The inner radius, greater than zero for a ring
* @return {object}
*/
_createCirclePath(or : number, ir : number) : Path {
const path = new Path();
path.move(0, or)
.arc(or * 2, 0, or)
.arc(-or * 2, 0, or);
if (ir) {
path.move(or - ir, 0)
.counterArc(ir * 2, 0, ir)
.counterArc(-ir * 2, 0, ir);
}
path.close();
return path;
}
/**
* _createArcPath(sa, ea, ca, or, ir)
*
* Creates the ReactART Path for an arc or wedge.
*
* @param {number} startAngle The starting degrees relative to 12 o'clock
* @param {number} endAngle The ending degrees relative to 12 o'clock
* @param {number} or The outer radius in pixels
* @param {number} ir The inner radius in pixels, greater than zero for an arc
* @return {object}
*/
_createArcPath(originX : number, originY : number, startAngle : number, endAngle : number, or : number, ir : number) : Path {
const path = new Path();
// angles in radians
const sa = this._degreesToRadians(startAngle);
const ea = this._degreesToRadians(endAngle);
// central arc angle in radians
const ca = sa > ea ? (this:any).circleRadians - sa + ea : ea - sa;
// cached sine and cosine values
const ss = Math.sin(sa);
const es = Math.sin(ea);
const sc = Math.cos(sa);
const ec = Math.cos(ea);
// cached differences
const ds = es - ss;
const dc = ec - sc;
const dr = ir - or;
// if the angle is over pi radians (180 degrees)
// we will need to let the drawing method know.
const large = ca > Math.PI;
// TODO (sema) Please improve theses comments to make the math
// more understandable.
//
// Formula for a point on a circle at a specific angle with a center
// at (0, 0):
// x = radius * Math.sin(radians)
// y = radius * Math.cos(radians)
//
// For our starting point, we offset the formula using the outer
// radius because our origin is at (top, left).
// In typical web layout fashion, we are drawing in quadrant IV
// (a.k.a. Southeast) where x is positive and y is negative.
//
// The arguments for path.arc and path.counterArc used below are:
// (endX, endY, radiusX, radiusY, largeAngle)
path.move(or + or * ss, or - or * sc) // move to starting point
.arc(or * ds, or * -dc, or, or, large) // outer arc
.line(dr * es, dr * -ec); // width of arc or wedge
if (ir) {
path.counterArc(ir * -ds, ir * dc, ir, ir, large); // inner arc
}
return path;
}
render() : any {
// angles are provided in degrees
const startAngle = this.props.startAngle;
const endAngle = this.props.endAngle;
// if (startAngle - endAngle === 0) {
// return null;
// }
// radii are provided in pixels
const innerRadius = this.props.innerRadius || 0;
const outerRadius = this.props.outerRadius;
const { originX, originY } = this.props;
// sorted radii
const ir = Math.min(innerRadius, outerRadius);
const or = Math.max(innerRadius, outerRadius);
let path;
if (endAngle >= startAngle + 360) {
path = this._createCirclePath(or, ir);
} else {
path = this._createArcPath(originX, originY, startAngle, endAngle, or, ir);
}
return <Shape {...this.props} d={path} />;
}
}
示例程式碼:
import React from 'react'
import {
View,
ART
} from 'react-native'
const {Surface} = ART;
import Wedge from './Wedge'
export default class Fan extends React.Component{
render(){
return(
<View style={this.props.style}>
<Surface width={100} height={100}>
<Wedge
outerRadius={50}
startAngle={0}
endAngle={60}
originX={50}
originY={50}
fill="blue"/>
</Surface>
</View>
)
}
}
綜合示例
相關程式碼:
/**
* Sample React Native App
* https://github.com/facebook/react-native
* @flow
*/
import React, {
Component
}from 'react';
import {
ART as Art,
StyleSheet,
View,
Dimensions,
TouchableWithoutFeedback,
Animated
} from 'react-native';
var HEART_SVG = "M130.4-0.8c25.4 0 46 20.6 46 46.1 0 13.1-5.5 24.9-14.2 33.3L88 153.6 12.5 77.3c-7.9-8.3-12.8-19.6-12.8-31.9 0-25.5 20.6-46.1 46-46.2 19.1 0 35.5 11.7 42.4 28.4C94.9 11 111.3-0.8 130.4-0.8"
var HEART_COLOR = 'rgb(226,38,77,1)';
var GRAY_HEART_COLOR = "rgb(204,204,204,1)";
var FILL_COLORS = [
'rgba(221,70,136,1)',
'rgba(212,106,191,1)',
'rgba(204,142,245,1)',
'rgba(204,142,245,1)',
'rgba(204,142,245,1)',
'rgba(0,0,0,0)'
];
var PARTICLE_COLORS = [
'rgb(158, 202, 250)',
'rgb(161, 235, 206)',
'rgb(208, 148, 246)',
'rgb(244, 141, 166)',
'rgb(234, 171, 104)',
'rgb(170, 163, 186)'
]
getXYParticle = (total, i, radius) => {
var angle = ( (2 * Math.PI) / total ) * i;
var x = Math.round((radius * 2) * Math.cos(angle - (Math.PI / 2)));
var y = Math.round((radius * 2) * Math.sin(angle - (Math.PI / 2)));
return {
x: x,
y: y,
}
}
getRandomInt = (min, max) => {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min)) + min;
}
shuffleArray = (array) => {
for (var i = array.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
var j = Math.floor(Math.random() * (i + 1));
var temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
return array;
}
var {
Surface,
Group,
Shape,
Path
} = Art;
//使用Animated.createAnimatedComponent對其他元件建立對話
//建立一個灰色的新型圖片
var AnimatedShape = Animated.createAnimatedComponent(Shape);
var {
width: deviceWidth,
height: deviceHeight
} = Dimensions.get('window');
export default class ArtAnimView extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
animation: new Animated.Value(0)
};
}
explode = () => {
Animated.timing(this.state.animation, {
duration: 1500,
toValue: 28
}).start(() => {
this.state.animation.setValue(0);
this.forceUpdate();
});
}
getSmallExplosions = (radius, offset) => {
return [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6].map((v, i, t) => {
var scaleOut = this.state.animation.interpolate({
inputRange: [0, 5.99, 6, 13.99, 14, 21],
outputRange: [0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
extrapolate: 'clamp'
});
var moveUp = this.state.animation.interpolate({
inputRange: [0, 5.99, 14],
outputRange: [0, 0, -15],
extrapolate: 'clamp'
});
var moveDown = this.state.animation.interpolate({
inputRange: [0, 5.99, 14],
outputRange: [0, 0, 15],
extrapolate: 'clamp'
});
var color_top_particle = this.state.animation.interpolate({
inputRange: [6, 8, 10, 12, 17, 21],
outputRange: shuffleArray(PARTICLE_COLORS)
})
var color_bottom_particle = this.state.animation.interpolate({
inputRange: [6, 8, 10, 12, 17, 21],
outputRange: shuffleArray(PARTICLE_COLORS)
})
var position = getXYParticle(7, i, radius)
return (
<Group
x={position.x + offset.x }
y={position.y + offset.y}
rotation={getRandomInt(0,