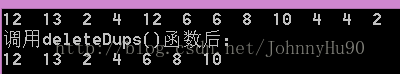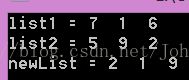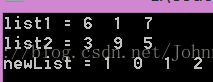面試考題之9.2:連結串列(C/C++版)
2.1 編寫程式碼,移除未排序連結串列中的重複結點。進階:如果不得使用臨時緩衝區,該怎麼解決?
解決方案:
方案1: 使用散列表
暫略
方案2:不借助額外緩衝區
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 |
#include <iostream> #include #include <cstdio> // getchar() #include <cstdlib> // free() #include "LinkedList.h" using namespace std; void printData(LinkedList aList) { cout << aList->data << " "; return; } /************************************************************************/ // 函式名稱:deleteDups // 函式目的:移除連結串列中重複的節點 // 函式引數:myList: 待操作的連結串列 // 函式返回:無 // 使用條件: /************************************************************************/ void deleteDups(LinkedList theList) { if (theList == NULL) return; LinkedList current = theList; while(current != NULL){ // 移除後續值相同的所有結點 LinkedList runner = current; while (runner->next != NULL){ if (runner->next->data == current->data){ LinkedList nextNode = runner->next; runner->next = runner->next->next; freeNode(nextNode); } else runner = runner->next; } current = current->next; } return; } int main() { int arr[] = { 12, 13, 2, 4, 12, 6, 6, 8, 10, 4, 4, 2 }; for (size_t i = 0; i < sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int); i++){ //insert( makeNode(arr[i]) ); insertBack( makeNode(arr[i]) ); } traverse(printData); cout << endl; LinkedList theList = getHead(); deleteDups(theList); cout << "呼叫deleteDups()函式後:" << endl; traverse(printData); cout << endl; destroy(); // 釋放連結串列 getchar(); return 0; } |
執行結果:
思考體會:
1、散列表怎樣解決該問題?
2.2 實現一個演算法,找出單向連結串列中倒數第K個結點。
解決方案:
方案1:遞迴
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 |
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> // getchar() #include "LinkedList.h" using namespace std; void printData(LinkedList aList) { cout << aList->data << " "; return; } /************************************************************************/ // 函式名稱:nthToLast // 函式目的:求倒數第K個結點 // 函式引數:aList: 待操作的連結串列, k:第K個結點、i:計數器 // 函式返回:無 // 使用條件: /************************************************************************/ LinkedList nthToLast(LinkedList aList, size_t k, size_t& i) { if (NULL == aList) { return NULL; } LinkedList theList = nthToLast(aList->next, k, i); i += 1; if (i == k){ return aList; } return theList; } int main() { int arr[] = { 12, 13, 2, 4, 12, 6, 6, 8, 10, 4, 4, 2 }; for (size_t i = 0; i < sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int); i++){ insertBack( makeNode(arr[i]) ); } traverse(printData); cout << endl; LinkedList theList = getHead(); size_t k1 = 1, k2 = 4, i1 = 0, i2 = 0; LinkedList alist1 = nthToLast(theList, k1, i1); LinkedList alist2 = nthToLast(theList, k2, i2); cout << "K1 = " << alist1->data << endl; cout << "K2 = " << alist2->data << endl; destroy(); // 釋放連結串列 getchar(); return 0; } |
其他方案:
執行結果:
思考體會:
2.3 實現一個演算法,刪除單向連結串列中間的某個結點,假定你只能訪問該結點。
示例
輸入:單向連結串列a->b->c->d->e中的結點c.
輸出:不返回任何資料,但該連結串列變為:a->b->d->e.
解決方案:
解法:將後繼結點的資料複製到當前結點,然後刪除這個後繼結點。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 |
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> // getchar() #include "LinkedList.h" using namespace std; void printData(LinkedList aList) { cout << aList->data << " "; return; } /************************************************************************/ // 函式名稱:deletNode2 // 函式目的:刪除單鏈表中的某個結點 // 函式引數:pNode:連結串列結點 // 函式返回:true:刪除成功 // 使用條件:pNode為非尾結點 /************************************************************************/ bool deletNode2(LinkedList pNode) { if (pNode == NULL || pNode->next == NULL) return false; LinkedList nextNode = pNode->next; pNode->data = nextNode->data; pNode->next = nextNode->next; freeNode(nextNode); return true; } int main() { int arr[] = { 12, 13, 2, 4, 12, 6, 6, 8, 10, 4, 4, 2 }; for (size_t i = 0; i < sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int); i++){ insertBack( makeNode(arr[i]) ); } traverse(printData); cout << endl; LinkedList theList = getHead(); LinkedList pNode = search(8); deletNode2(pNode); traverse(printData); destroy(); // 釋放連結串列 getchar(); return 0; } |
執行結果:
思考體會:
1、只要考查特殊情況。
2、在C++中刪除後繼結點時要手動刪除。
2.4 編寫程式碼,以給定值x為基準將連結串列分割為兩部分,所有小於x的結點排在大於或等於x的結點之前。
解決方案:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 |
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> // getchar() #include "LinkedList.h" using namespace std; void printData(LinkedList aNode) { cout << aNode->data << " "; return; } /************************************************************************/ // 函式名稱:partition // 函式目的:以定值X分割pList // 函式引數:pList:待操作連結串列首結點 // 函式返回: // 使用條件: /************************************************************************/ LinkedList partition(LinkedList pList, int x) { LinkedList beforeStart = NULL; LinkedList beforeEnd = NULL; LinkedList afterStart = NULL; LinkedList afterEnd = NULL; if (pList == NULL) return NULL; // 分割連結串列 LinkedList current = pList; // 指向第一個元素 while (current != NULL){ // current結點要插入before或after表 LinkedList nextNode = current->next; current->next = NULL; if (current->data < x){ // 將結點插入before連結串列 if (beforeStart == NULL){ beforeStart = current; beforeEnd = beforeStart; }else { beforeEnd->next = current; beforeEnd = current; } }else { // 將結點插入before連結串列 if (afterStart == NULL){ afterStart = current; afterEnd = afterStart; }else { afterEnd->next = current; afterEnd = current; } } current = nextNode; } // end while() if (beforeStart == NULL) { return afterStart; } // 合併before和after連結串列 beforeEnd->next = afterStart; return beforeStart; } int main() { int arr[] = { 12, 13, 2, 4, 12, 6, 6, 8, 10, 4, 4, 2 }; for (size_t i = 0; i < sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int); i++){ insertBack( makeNode(arr[i]) ); } traverse(printData); cout << endl; LinkedList theList = getHead(); theList = partition(theList, 8); sethead(theList); traverse(printData); cout << endl; destroy(); // 釋放連結串列 getchar(); return 0; } |
執行結果:
思考體會:
1、沒有重新分配記憶體存放新的連結串列,靠移動指標來完成題設要求。
2、注意處理時一些細節。
2.5 給定兩個連結串列表示的整數,每個結點包含一個數位。這些數位是反向存放的,也就是個位排在連結串列首部。編寫函式對這兩個整數求和,並用連結串列形式返回結果。
示例:
輸入:(7->1->6) + (5->9->2), 即:617 + 295.
輸出:2->1->9,即:912.
進階:假設這些數位是正向存放的,請在做一遍。
示例:(6->1->7) + (2->9->5), 即:617 + 295.
輸出:9->1->2, 即:912。
解決方案:
方案1:數位反向存放
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 |
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> // getchar() #include "LinkedList.h" using namespace std; void printData(LinkedList aNode) { cout << aNode->data << " "; return; } /************************************************************************/ // 函式名稱:addLists // 函式目的:兩個連結串列相加 // 函式引數:list1、ist2 // 函式返回:相加之後的連結串列 // 使用條件: 數位反向存放 /************************************************************************/ LinkedList addLists(LinkedList list1, LinkedList list2) { LinkedList lt1 = list1, lt2 = list2, newList = NULL; int addData = 0; // 相加和 int carryI = 0; // 進位值 while ( lt1 != NULL || lt2 != NULL ){ if (lt1 != NULL && lt2 != NULL){ addData = lt1->data + lt2->data; lt1 = lt1->next; lt2 = lt2->next; }else if (lt1 == NULL && lt2 != NULL){ addData = lt2->data; lt2 = lt2->next; }else { addData = lt1->data; lt1 = lt1->next; } int totalData = addData + carryI; newList = insertBack( newList, makeNode(totalData % 10) ); //newList = insert( newList, makeNode(totalData % 10) ); carryI = totalData / 10; } if (carryI > 0){ newList = insertBack( newList, makeNode(carryI) ); //newList = insert( newList, makeNode(carryI) ); } return newList; } int main() { int arr1[] = {6, 1, 7}; int arr2[] = {2, 9, 5}; LinkedList list1 = NULL, list2 = NULL, newList = NULL; for (size_t i = 0; i < sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(int); i++){ //list1 = insertBack( list1, makeNode(arr1[i]) ); list1 = insert( list1, makeNode(arr1[i]) ); } for (size_t i = 0; i < sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(int); i++){ //list2 = insertBack( list2, makeNode(arr2[i]) ); list2 = insert( list2, makeNode(arr2[i]) ); } newList = addLists(list1, list2); cout << "list1 = "; traverse(list1, printData); cout << endl; cout << "list2 = "; traverse(list2, printData); cout << endl; cout << "newList = "; traverse(newList, printData); cout << endl; getchar(); return 0; } |
執行結果:
方案2:數位正向存放
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 |
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> // getchar() #include "LinkedList.h" using namespace std; void printData(LinkedList aNode) { cout << aNode->data << " "; return; } /************************************************************************/ // 函式名稱:addLists // 函式目的:兩個連結串列相加 // 函式引數:list1、ist2 // 函式返回:相加之後的連結串列 // 使用條件: 數位反向存放 /************************************************************************/ LinkedList addLists(LinkedList list1, LinkedList list2) { LinkedList lt1 = list1, lt2 = list2, newList = NULL; int addData = 0; // 相加和 int carryI = 0; // 進位值 while ( lt1 != NULL || lt2 != NULL ){ if (lt1 != NULL && lt2 != NULL){ addData = lt1->data + lt2->data; lt1 = lt1->next; lt2 = lt2->next; }else if (lt1 == NULL && lt2 != NULL){ addData = lt2->data; lt2 = lt2->next; }else { addData = lt1->data; lt1 = lt1->next; } int totalData = addData + carryI; newList = insertBack( newList, makeNode(totalData % 10) ); carryI = totalData / 10; } if (carryI > 0){ newList = insertBack( newList, makeNode(carryI) ); } return newList; } int main() { int arr1[] = {6, 1, 7}; int arr2[] = {3, 9, 5}; LinkedList list1 = NULL, list2 = NULL, newList = NULL; for (size_t i = 0; i < sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(int); i++){ list1 = insertBack( list1, makeNode(arr1[i]) ); } for (size_t i = 0; i < sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(int); i++){ list2 = insertBack( list2, makeNode(arr2[i]) ); } list1 = reverse(list1); list2 = reverse(list2); newList = addLists(list1, list2); // 轉換回原來的順序 list1 = reverse(list1); list2 = reverse(list2); newList = reverse(newList); cout << "list1 = "; traverse(list1, printData); cout << endl; cout << "list2 = "; traverse(list2, printData); cout << endl; cout << "newList = "; traverse(newList, printData); cout << endl; getchar(); return 0; } |
執行結果:
思考體會:
1、正向存放題設解決這裡用一個函式reverse來反轉連結串列,在通過原來的addList計算,再把得到結果反轉回去。
2、其他更高效簡潔方法?
3、遞迴求解?
2.6 給定一個有環連結串列,實現一個演算法返回環路的開頭結點。有環連結串列定義:
在連結串列中某個結點的next元素指向在它前面出現過的結點,則表明該連結串列存在環路。
示例:
輸入:A->B->C->D->E->C(C結點出現兩次)。
輸出:C
解決方案:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 |
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> // getchar() #include "LinkedList.h" using namespace std; /************************************************************************/ // 函式名稱:findBegining // 函式目的:找到有環連結串列的開頭結點 // 函式引數:head:有環連結串列 // 函式返回:環開頭結點 // 使用條件: /************************************************************************/ Node* findBegining(LinkedList head) { LinkedList slow = head; LinkedList fast = head; /* 找出碰撞處,將處於連結串列中LOOP_SIZE-k步的位置 */ while (fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){ slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; if (slow == fast) { // 碰撞 break; } } /* 錯誤檢查,沒有碰撞處,也即沒有環路*/ if (fast == NULL || fast->next == NULL){ return NULL; } /* 將slow指向首部,fast指向碰撞處,兩者 * 距離環路起始處k步,若兩者以相同的速度移動, * 則必定會在環路處碰撞在一起 */ slow = head; while (slow != fast){ slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next; } /* 至此兩者均指向環路起始處 */ return fast; } int main() { int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}; for (size_t i = 0; i < sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int); i++){ insertBack( makeNode(arr[i]) ); } // 插入後形成環路 Node* pNode = search(5); insertBack( pNode ); LinkedList head = getHead(); Node* nodeBegin = findBegining( head ); cout << "迴環開頭結點是:" << ((nodeBegin != NULL) ? nodeBegin : NULL ) << endl; cout << "迴環開頭結點值是:" << ((nodeBegin != NULL) ? nodeBegin->data : 0 ) << endl; getchar(); return 0; } |
執行結果:
思考體會:
1、解答該題找到條件成立的點,得到規律。
2、經典面試題:檢測連結串列是否有環路,的變體。
2.7 編寫一個函式,檢查連結串列是否為迴文。
解決方案:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 |
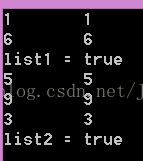
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> // getchar() #include "LinkedList.h" using namespace std; /************************************************************************/ // 函式名稱:isPalindromes (遞迴實現) // 函式目的:判斷一個連結串列是否是迴文 // 函式引數:head: 連結串列 // 函式返回:true: 是迴文 // 使用條件: /************************************************************************/ bool isPalindrome(LinkedList head, size_t length, Node** nextNode) { bool success = false; if ( NULL == head || length == 0){ return false; } else if (length == 2){ // 偶數 *nextNode = head->next; } else if (length == 3 ) { // 連結串列有奇數個元素,跳過中間元素 *nextNode = head->next->next; } else { success = isPalindrome(head->next, length - 2, nextNode); if (!success) return false; } if ( nextNode == NULL || (*nextNode) == NULL) { return false; } // test cout << head->data << "\t" << (*nextNode)->data << endl; if (head->data != (*nextNode)->data) { return false; } *nextNode = (*nextNode)->next; // 後移一位 return true; } int main() { int arr1[] = {6, 1, 7, 1, 6}; int arr2[] = {3, 9, 5, 5, 9, 3}; LinkedList list1 = NULL, list2 = NULL; for (size_t i = 0; i < sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(int); i++){ list1 = insertBack( list1, makeNode(arr1[i]) ); } for (size_t i = 0; i < sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(int); i++){ list2 = insertBack( list2, makeNode(arr2[i]) ); } Node** theNode = &list1; cout << "list1 = " << (isPalindrome(list1, size(list1), theNode) ? "true" : "false") << endl; cout << "list2 = " << (isPalindrome(list2, size(list2), theNode) ? "true" : "false") << endl; getchar(); return 0; } |
執行結果:
思考體會:
1、理解遞迴的的的巧妙運用.
2、仔細體會指標的指標的應用.