Unity3d 中的 A*尋路
在本章中,我們將在Unity3D環境中使用C#實現A*演算法.儘管有很多其他演算法,像Dijkstra演算法,但A*演算法以其簡單性和有效性而廣泛的應用於遊戲和互動式應用中.我們之前在第一章AI介紹中短暫的涉及到了該演算法.不過現在我們從實現的角度來再次複習該演算法.
A*演算法複習
在我們進入下一部分實現A*之前,我們再次複習一下A*演算法.首先,我們將需要用可遍歷的資料結構來表示地圖.儘管可能有很多結構可實現,在這個例子中我們將使用2D格子陣列.我們稍後將實現GridManager類來處理這個地圖資訊.我們的類GridManager將記錄一系列的Node物件,這些Node物件才是2D格子的主題.所以我們需要實現Node類來處理一些東西,比如節點型別,他是是一個可通行的節點還是障礙物,穿過節點的代價和到達目標節點的代價等等.
我們將用兩個變數來儲存已經處理過的節點和我們要處理的節點.我們分別稱他們為關閉列表和開放列表.我們將在PriorityQueue類裡面實現該列表型別.我們現在看看它:
- 首先,從開始節點開始,將開始節點放入開放列表中.
- 只要開放列表中有節點,我們將進行一下過程.
- 從開放列表中選擇第一個節點並將其作為當前節點(我們將在程式碼結束時提到它,這假定我們已經對開放列表排好序且第一個節點有最小代價值).
- 獲得這個當前節點的鄰近節點,它們不是障礙物,像一堵牆或者不能穿越的峽谷一樣.
- 對於每一個鄰近節點,檢查該鄰近節點是否已在關閉列表中.如果不在,我們將為這個鄰近節點計算所有代價值(F),計算時使用下面公式:F = G + H,在前面的式子中,G是從上一個節點到這個節點的代價總和,H是從當前節點到目的節點的代價總和.
- 將代價資料儲存在鄰近節點中,並且將當前節點儲存為該鄰近節點的父節點.之後我們將使用這個父節點資料來追蹤實際路徑.
- 將鄰近節點儲存在開放列表中.根據到他目標節點的代價總和,以升序排列開放列表.
- 如果沒有鄰近節點需要處理,將當前節點放入關閉列表並將其從開放列表中移除.
- 返回第二步
這就是我們將在Unity3D中使用C#實現的演算法概覽.所以,搞起吧.
實現
我們將實現我們之前提到過的基礎類比如Node類,GridManager類和PriorityQueue類.我們將在後續的主AStar類裡面使用它們.Node
Node類將處理代表我們地圖的2D格子中其中的每個格子物件,一下是Node.cs檔案.using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
using System;
public class Node : IComparable {
public float nodeTotalCost;
public float estimatedCost;
public bool bObstacle;
public Node parent;
public Vector3 position;
public Node() {
this.estimatedCost = 0.0f;
this.nodeTotalCost = 1.0f;
this.bObstacle = false;
this.parent = null;
}
public Node(Vector3 pos) {
this.estimatedCost = 0.0f;
this.nodeTotalCost = 1.0f;
this.bObstacle = false;
this.parent = null;
this.position = pos;
}
public void MarkAsObstacle() {
this.bObstacle = true;
} public int CompareTo(object obj)
{
Node node = (Node) obj;
//Negative value means object comes before this in the sort order.
if (this.estimatedCost < node.estimatedCost)
return -1;
//Positive value means object comes after this in the sort order.
if (this.estimatedCost > node.estimatedCost)
return 1;
return 0;
}
}PriorityQueue
PriorityQueue是一個簡短的類,使得ArrayList處理節點變得容易些,PriorityQueue.cs展示如下:using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
public class PriorityQueue {
private ArrayList nodes = new ArrayList();
public int Length {
get { return this.nodes.Count; }
}
public bool Contains(object node) {
return this.nodes.Contains(node);
}
public Node First() {
if (this.nodes.Count > 0) {
return (Node)this.nodes[0];
}
return null;
}
public void Push(Node node) {
this.nodes.Add(node);
this.nodes.Sort();
}
public void Remove(Node node) {
this.nodes.Remove(node);
//Ensure the list is sorted
this.nodes.Sort();
}
}GridManager
GridManager類處理所有代表地圖的格子的屬性.我們將GridManager設定單例,因為我們只需要一個物件來表示地圖.GridManager.cs程式碼如下:using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
public class GridManager : MonoBehaviour {
private static GridManager s_Instance = null;
public static GridManager instance {
get {
if (s_Instance == null) {
s_Instance = FindObjectOfType(typeof(GridManager))
as GridManager;
if (s_Instance == null)
Debug.Log("Could not locate a GridManager " +
"object. \n You have to have exactly " +
"one GridManager in the scene.");
}
return s_Instance;
}
}public int numOfRows;
public int numOfColumns;
public float gridCellSize;
public bool showGrid = true;
public bool showObstacleBlocks = true;
private Vector3 origin = new Vector3();
private GameObject[] obstacleList;
public Node[,] nodes { get; set; }
public Vector3 Origin {
get { return origin; }
} void Awake() {
obstacleList = GameObject.FindGameObjectsWithTag("Obstacle");
CalculateObstacles();
}
// Find all the obstacles on the map
void CalculateObstacles() {
nodes = new Node[numOfColumns, numOfRows];
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numOfColumns; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < numOfRows; j++) {
Vector3 cellPos = GetGridCellCenter(index);
Node node = new Node(cellPos);
nodes[i, j] = node;
index++;
}
}
if (obstacleList != null && obstacleList.Length > 0) {
//For each obstacle found on the map, record it in our list
foreach (GameObject data in obstacleList) {
int indexCell = GetGridIndex(data.transform.position);
int col = GetColumn(indexCell);
int row = GetRow(indexCell);
nodes[row, col].MarkAsObstacle();
}
}
}GridManager有一些輔助方法來遍歷格子並得到對應格子的對局.以下是其中一些函式(附有簡短說明以闡述它們的是做什麼的).實現很簡單,所以我們不會過多探究其細節.
GetGridCellCenter方法從格子索引中返回世界座標系中的格子位置,程式碼如下:
public Vector3 GetGridCellCenter(int index) {
Vector3 cellPosition = GetGridCellPosition(index);
cellPosition.x += (gridCellSize / 2.0f);
cellPosition.z += (gridCellSize / 2.0f);
return cellPosition;
}
public Vector3 GetGridCellPosition(int index) {
int row = GetRow(index);
int col = GetColumn(index);
float xPosInGrid = col * gridCellSize;
float zPosInGrid = row * gridCellSize;
return Origin + new Vector3(xPosInGrid, 0.0f, zPosInGrid);
} public int GetGridIndex(Vector3 pos) {
if (!IsInBounds(pos)) {
return -1;
}
pos -= Origin;
int col = (int)(pos.x / gridCellSize);
int row = (int)(pos.z / gridCellSize);
return (row * numOfColumns + col);
}
public bool IsInBounds(Vector3 pos) {
float width = numOfColumns * gridCellSize;
float height = numOfRows* gridCellSize;
return (pos.x >= Origin.x && pos.x <= Origin.x + width &&
pos.x <= Origin.z + height && pos.z >= Origin.z);
} public int GetRow(int index) {
int row = index / numOfColumns;
return row;
}
public int GetColumn(int index) {
int col = index % numOfColumns;
return col;
}public void GetNeighbours(Node node, ArrayList neighbors) {
Vector3 neighborPos = node.position;
int neighborIndex = GetGridIndex(neighborPos);
int row = GetRow(neighborIndex);
int column = GetColumn(neighborIndex);
//Bottom
int leftNodeRow = row - 1;
int leftNodeColumn = column;
AssignNeighbour(leftNodeRow, leftNodeColumn, neighbors);
//Top
leftNodeRow = row + 1;
leftNodeColumn = column;
AssignNeighbour(leftNodeRow, leftNodeColumn, neighbors);
//Right
leftNodeRow = row;
leftNodeColumn = column + 1;
AssignNeighbour(leftNodeRow, leftNodeColumn, neighbors);
//Left
leftNodeRow = row;
leftNodeColumn = column - 1;
AssignNeighbour(leftNodeRow, leftNodeColumn, neighbors);
}
void AssignNeighbour(int row, int column, ArrayList neighbors) {
if (row != -1 && column != -1 &&
row < numOfRows && column < numOfColumns) {
Node nodeToAdd = nodes[row, column];
if (!nodeToAdd.bObstacle) {
neighbors.Add(nodeToAdd);
}
}
}void OnDrawGizmos() {
if (showGrid) {
DebugDrawGrid(transform.position, numOfRows, numOfColumns,
gridCellSize, Color.blue);
}
Gizmos.DrawSphere(transform.position, 0.5f);
if (showObstacleBlocks) {
Vector3 cellSize = new Vector3(gridCellSize, 1.0f,
gridCellSize);
if (obstacleList != null && obstacleList.Length > 0) {
foreach (GameObject data in obstacleList) {
Gizmos.DrawCube(GetGridCellCenter(
GetGridIndex(data.transform.position)), cellSize);
}
}
}
}
public void DebugDrawGrid(Vector3 origin, int numRows, int
numCols,float cellSize, Color color) {
float width = (numCols * cellSize);
float height = (numRows * cellSize);
// Draw the horizontal grid lines
for (int i = 0; i < numRows + 1; i++) {
Vector3 startPos = origin + i * cellSize * new Vector3(0.0f,
0.0f, 1.0f);
Vector3 endPos = startPos + width * new Vector3(1.0f, 0.0f,
0.0f);
Debug.DrawLine(startPos, endPos, color);
}
// Draw the vertial grid lines
for (int i = 0; i < numCols + 1; i++) {
Vector3 startPos = origin + i * cellSize * new Vector3(1.0f,
0.0f, 0.0f);
Vector3 endPos = startPos + height * new Vector3(0.0f, 0.0f,
1.0f);
Debug.DrawLine(startPos, endPos, color);
}
}
}注意:你可以從Unity3D參考文件瞭解到更多有關gizmos的資料
AStar
類AStar是將要使用我們目前所實現的類的主類.如果你想複習這的話,你可以返回演算法部分.如下面AStar.cs程式碼所示,我們先宣告我們的openList和closedList,它們都是PriorityQueue型別.
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
public class AStar {
public static PriorityQueue closedList, openList; private static float HeuristicEstimateCost(Node curNode,
Node goalNode) {
Vector3 vecCost = curNode.position - goalNode.position;
return vecCost.magnitude;
} public static ArrayList FindPath(Node start, Node goal) {
openList = new PriorityQueue();
openList.Push(start);
start.nodeTotalCost = 0.0f;
start.estimatedCost = HeuristicEstimateCost(start, goal);
closedList = new PriorityQueue();
Node node = null; while (openList.Length != 0) {
node = openList.First();
//Check if the current node is the goal node
if (node.position == goal.position) {
return CalculatePath(node);
}
//Create an ArrayList to store the neighboring nodes
ArrayList neighbours = new ArrayList();
GridManager.instance.GetNeighbours(node, neighbours);
for (int i = 0; i < neighbours.Count; i++) {
Node neighbourNode = (Node)neighbours[i];
if (!closedList.Contains(neighbourNode)) {
float cost = HeuristicEstimateCost(node,
neighbourNode);
float totalCost = node.nodeTotalCost + cost;
float neighbourNodeEstCost = HeuristicEstimateCost(
neighbourNode, goal);
neighbourNode.nodeTotalCost = totalCost;
neighbourNode.parent = node;
neighbourNode.estimatedCost = totalCost +
neighbourNodeEstCost;
if (!openList.Contains(neighbourNode)) {
openList.Push(neighbourNode);
}
}
}
//Push the current node to the closed list
closedList.Push(node);
//and remove it from openList
openList.Remove(node);
}
if (node.position != goal.position) {
Debug.LogError("Goal Not Found");
return null;
}
return CalculatePath(node);
}- 獲得openList的第一個節點.記住每當新節點加入時openList都需要再次排序.所以第一個節點總是有到目的節點最低估計代價值.
- 檢查當前節點是否是目的節點,如果是推出while迴圈建立path陣列.
- 建立陣列列表儲存當前正被處理的節點的臨近節點.使用GetNeighbours方法來從格子中檢索鄰接節點.
- 對於每一個在鄰接節點陣列中的節點,我們檢查它是否已在closedList中.如果不在,計算代價值並使用新的代價值更新節點的屬性值,更新節點的父節點並將其放入openList中.
- 將當前節點壓入closedList中並將其從openList中移除.返回第一步.
private static ArrayList CalculatePath(Node node) {
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
while (node != null) {
list.Add(node);
node = node.parent;
}
list.Reverse();
return list;
}
}這就是我們的AStar類.我們將在下面的程式碼裡寫一個測試指令碼來檢驗所有的這些東西.之後建立一個場景並在其中使用它們.
TestCode Class
程式碼如TestCode.cs所示,該類使用AStar類找到從開始節點到目的節點的路徑.
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
public class TestCode : MonoBehaviour {
private Transform startPos, endPos;
public Node startNode { get; set; }
public Node goalNode { get; set; }
public ArrayList pathArray;
GameObject objStartCube, objEndCube;
private float elapsedTime = 0.0f;
//Interval time between pathfinding
public float intervalTime = 1.0f; void Start () {
objStartCube = GameObject.FindGameObjectWithTag("Start");
objEndCube = GameObject.FindGameObjectWithTag("End");
pathArray = new ArrayList();
FindPath();
}
void Update () {
elapsedTime += Time.deltaTime;
if (elapsedTime >= intervalTime) {
elapsedTime = 0.0f;
FindPath();
}
} void FindPath() {
startPos = objStartCube.transform;
endPos = objEndCube.transform;
startNode = new Node(GridManager.instance.GetGridCellCenter(
GridManager.instance.GetGridIndex(startPos.position)));
goalNode = new Node(GridManager.instance.GetGridCellCenter(
GridManager.instance.GetGridIndex(endPos.position)));
pathArray = AStar.FindPath(startNode, goalNode);
} void OnDrawGizmos() {
if (pathArray == null)
return;
if (pathArray.Count > 0) {
int index = 1;
foreach (Node node in pathArray) {
if (index < pathArray.Count) {
Node nextNode = (Node)pathArray[index];
Debug.DrawLine(node.position, nextNode.position,
Color.green);
index++;
}
}
}
}
}Scene setup
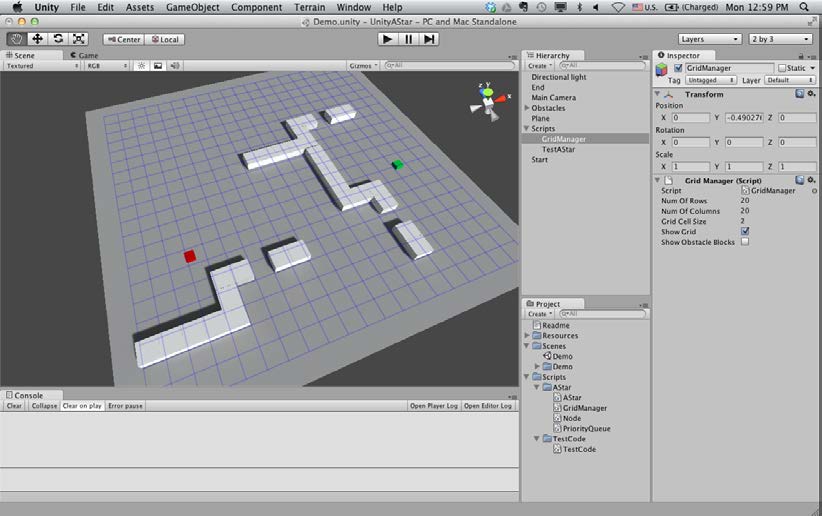
我們將要建立一個類似於下面截圖所展示的場景:
Sample test scene
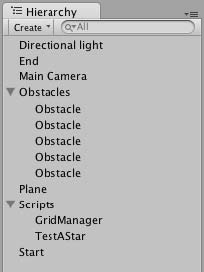
我們將有一個平行光,開始以及結束遊戲物件,一些障礙物,一個被用作地面的平面實體和兩個空的遊戲物件,空物件身上放置GridManager和TestAstar指令碼.這是我們的場景層級圖.
Scene hierarchy
建立一些立方體實體並給他們加上標籤Obstacle,當執行我們的尋路演算法時我們需要尋找帶有該標籤的物件.
Obstacle nodes
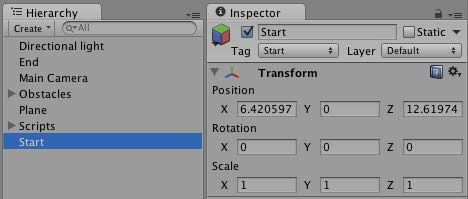
建立一個立方體實體並加上標籤Start
Start node
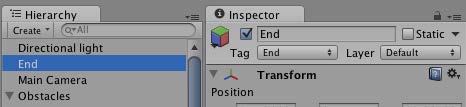
建立另一個立方體實體並加上標籤End
End node
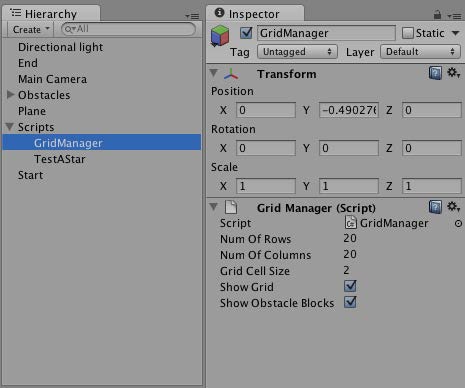
現在建立一個空的遊戲物件並將GridManager指令碼賦給它.將其名字也設定回GridManager因為在我們的指令碼中使用該名稱尋找GridManager物件.這裡我們可以設定格子的行數和列數和每個格子的大小.
GridManager script
Testing
我們點選Play按鈕實打實的看下我們的A*演算法.預設情況下,一旦你播放當前場景Unity3D將會切換到Game檢視.由於我們的尋路形象化(visualization)程式碼是為我編輯器檢視中的除錯繪製而寫,你需要切換回Scene檢視或者勾選Gizmos來檢視找到的路徑.
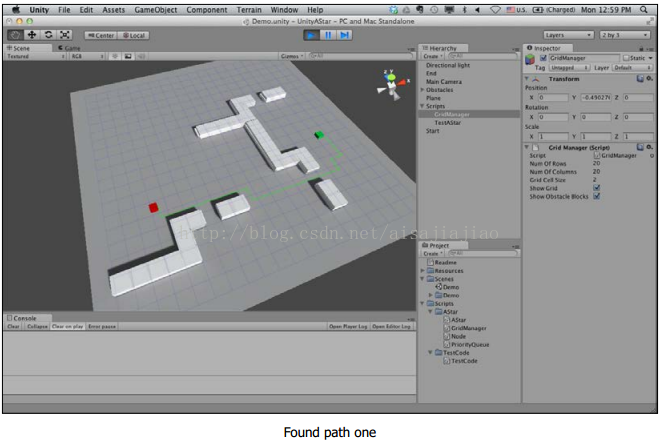
現在在場景中嘗試使用編輯器的移動工具移動開始和結束節點.(不是在Game檢視中,而是在Scene檢視中)
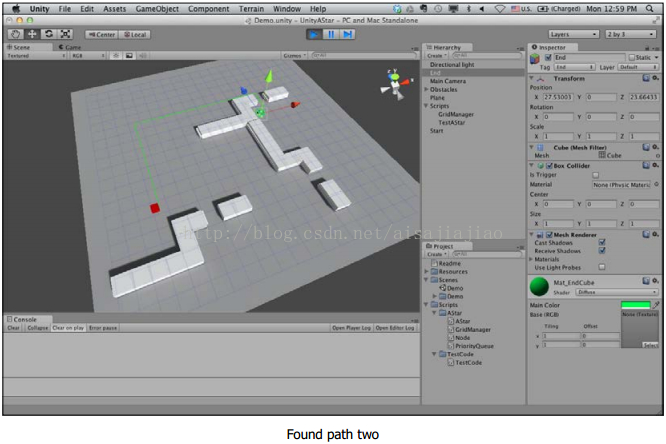
如果從開始節點到目的節點有合法路徑,你應該看到路徑會對應更新並且是動態實時的更新.如果沒有路徑,你會在控制視窗中得到一條錯誤資訊.
總結
在本章中,我們學習瞭如何在Unity3D環境中實現A*尋路演算法.我們實現了自己的A*尋路類以及我們自己的格子類,佇列類和節點類.我們學習了IComparable介面並重寫了CompareTo方法.我們使用除錯繪製功能(debug draw functionalities)來呈現我們的網格和路徑資訊.有了Unity3D的navmesh和navagent功能你可能不必自己實現尋路演算法.不管怎麼樣,他幫助你理解實現背後的基礎演算法.
在下一章中,我們將檢視如何擴充套件藏在A*背後的思想看看導航網格(navigation meshes).使用導航網格,在崎嶇的地形上尋路將變得容易得多.