Android Picasso圖片載入庫原始碼剖析
Picasso是一個優秀的輕量級網路圖片載入快取庫。花了兩天時間研讀了下的閱讀了下他的原始碼。做一下的剖析:
Picasso的優點:
- 足夠輕量級:maven打包出來的jar只有130kb左右
- 二級快取策略,分別快取記憶體和磁碟空間
- 自動監控記憶體大小資料
- 很好的執行緒控制,根據網路狀態控制執行緒數量、具有優先順序排程策略。
- 圖片適應、壓縮處理策略
- 預載入功能
- 程式碼質量高、易拓展。
1 Picasso整體畫像
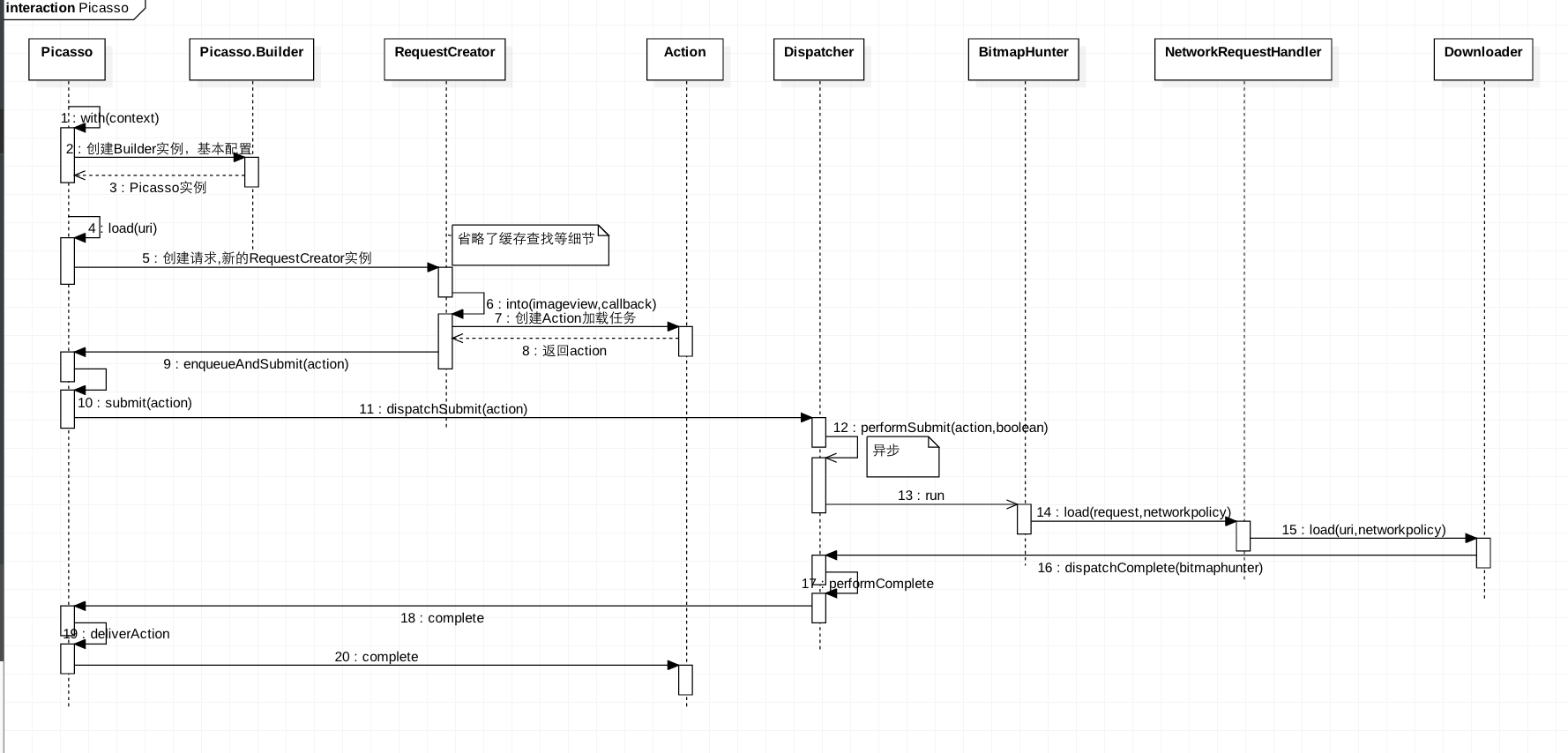
1 流程圖
2 Picasso 基本使用和概括流程
Picasso.with(context).load("http://i.imgur.com/DvpvklR.png" 看下初始化的方法。with()獲的Picasso的全域性單例。
public static Picasso with(Context context) {
if (singleton == null) {
synchronized (Picasso.class) {
if (singleton == null) {
singleton = new Builder(context).build();
}
}
}
return singleton;
} 使用Builder模式獲得例項,看起來比較清晰明瞭。
public Picasso build() {
Context context = this.context;
if (downloader == null) {
downloader = Utils.createDefaultDownloader(context);
}
if (cache == null) {
cache = new LruCache(context);
}
if (service == null) {
service = new 建造者獲得例項的時候會初始好Download(網路下載模組)、LruCache(快取核心)、RequestTransformer(Request運輸類)、Stats(檢測類)、Dispatch(事務分發中心)。
呼叫load(uri)開始執行圖片載入
load(Uri)
load(String)
load(File)
其中#load(Uri)
public RequestCreator load(Uri uri) {
return new RequestCreator(this, uri, 0);
}RequestCreator提供了圖片相關處理相關的所有API,RequestCreator所有的api方法結果return this。可以理解他同樣為一個builder模式的建造者。著重看下裝載圖片的into()方法實現。
public void into(Target target) {
long started = System.nanoTime();
//檢查是否執行在主執行緒
checkMain();
if (target == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Target must not be null.");
}
if (deferred) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Fit cannot be used with a Target.");
}
if (!data.hasImage()) {
picasso.cancelRequest(target);
target.onPrepareLoad(setPlaceholder ? getPlaceholderDrawable() : null);
return;
}
Request request = createRequest(started);
String requestKey = createKey(request);
//優先從記憶體快取讀取
if (shouldReadFromMemoryCache(memoryPolicy)) {
Bitmap bitmap = picasso.quickMemoryCacheCheck(requestKey);
if (bitmap != null) {
//取消網路的載入
picasso.cancelRequest(target);
target.onBitmapLoaded(bitmap, MEMORY);
return;
}
}
target.onPrepareLoad(setPlaceholder ? getPlaceholderDrawable() : null);
Action action =
new TargetAction(picasso, target, request, memoryPolicy, networkPolicy, errorDrawable,
requestKey, tag, errorResId);
//提交動作執行下載
picasso.enqueueAndSubmit(action);
}到這裡可以大體看到的圖片載入的流程程式碼,Picasso模組初始化之後,初始了各個核心模組,並建立RequestCreator提供出圖片相關的所有操作API,在執行啟動into下載圖片的時機優先使用快取中的資料。那麼他們各個模組是怎麼協調工作的呢?下面分塊來揭祕。
2 執行緒控制
BitmapHunter implements Runnable
這是一個單獨的圖片處理的執行緒單元。 run()方法中呼叫hunt方法獲取bitmap執行的核心程式碼
Bitmap hunt() throws IOException {
Bitmap bitmap = null;
//優先讀取記憶體
if (shouldReadFromMemoryCache(memoryPolicy)) {
bitmap = cache.get(key);
if (bitmap != null) {
stats.dispatchCacheHit();
loadedFrom = MEMORY;
if (picasso.loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_HUNTER, VERB_DECODED, data.logId(), "from cache");
}
return bitmap;
}
}
//根據網路狀況執行圖片的載入
data.networkPolicy = retryCount == 0 ? NetworkPolicy.OFFLINE.index : networkPolicy;
RequestHandler.Result result = requestHandler.load(data, networkPolicy);
if (result != null) {
loadedFrom = result.getLoadedFrom();
exifOrientation = result.getExifOrientation();
bitmap = result.getBitmap();
// If there was no Bitmap then we need to decode it from the stream.
if (bitmap == null) {
InputStream is = result.getStream();
try {
bitmap = decodeStream(is, data);
} finally {
Utils.closeQuietly(is);
}
}
}
if (bitmap != null) {
if (picasso.loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_HUNTER, VERB_DECODED, data.logId());
}
stats.dispatchBitmapDecoded(bitmap);
//圖片適配的處理,由於是多執行緒所以做了同步加鎖的處理DECODE_LOCK
if (data.needsTransformation() || exifOrientation != 0) {
synchronized (DECODE_LOCK) {
if (data.needsMatrixTransform() || exifOrientation != 0) {
bitmap = transformResult(data, bitmap, exifOrientation);
if (picasso.loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_HUNTER, VERB_TRANSFORMED, data.logId());
}
}
if (data.hasCustomTransformations()) {
bitmap = applyCustomTransformations(data.transformations, bitmap);
if (picasso.loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_HUNTER, VERB_TRANSFORMED, data.logId(), "from custom transformations");
}
}
}
if (bitmap != null) {
stats.dispatchBitmapTransformed(bitmap);
}
}
}
return bitmap;
}Dispatch類是一個控制的中心,控制執行緒的載入和取消、網路監聽、訊息處理等。
Dispatcher(Context context, ExecutorService service, Handler mainThreadHandler,
Downloader downloader, Cache cache, Stats stats) {
this.dispatcherThread = new DispatcherThread();
this.dispatcherThread.start();
Utils.flushStackLocalLeaks(dispatcherThread.getLooper());
this.context = context;
this.service = service;
···
程式碼省略
}其構造中獲得service 即為PicassoExecutorService ,而PicassoExecutorService 整合自ThreadPoolExecutor,是一個執行緒池。
Picasso具有根據網路狀況控制執行緒數量的方法就是有PicassoExecutorService來控制完成的
void adjustThreadCount(NetworkInfo info) {
if (info == null || !info.isConnectedOrConnecting()) {
setThreadCount(DEFAULT_THREAD_COUNT);
return;
}
switch (info.getType()) {
case ConnectivityManager.TYPE_WIFI:
case ConnectivityManager.TYPE_WIMAX:
case ConnectivityManager.TYPE_ETHERNET:
setThreadCount(4);
break;
case ConnectivityManager.TYPE_MOBILE:
switch (info.getSubtype()) {
case TelephonyManager.NETWORK_TYPE_LTE: // 4G
case TelephonyManager.NETWORK_TYPE_HSPAP:
case TelephonyManager.NETWORK_TYPE_EHRPD:
setThreadCount(3);
break;
case TelephonyManager.NETWORK_TYPE_UMTS: // 3G
case TelephonyManager.NETWORK_TYPE_CDMA:
case TelephonyManager.NETWORK_TYPE_EVDO_0:
case TelephonyManager.NETWORK_TYPE_EVDO_A:
case TelephonyManager.NETWORK_TYPE_EVDO_B:
setThreadCount(2);
break;
case TelephonyManager.NETWORK_TYPE_GPRS: // 2G
case TelephonyManager.NETWORK_TYPE_EDGE:
setThreadCount(1);
break;
default:
setThreadCount(DEFAULT_THREAD_COUNT);
}
break;
default:
setThreadCount(DEFAULT_THREAD_COUNT);
}
}上一節我們在into方法中提交執行下載enqueueAndSubmit的過程最終交由控制中心Dispatch中performSubmit來完成
void performSubmit(Action action, boolean dismissFailed) {
if (pausedTags.contains(action.getTag())) {
···
省略程式碼
hunter = forRequest(action.getPicasso(), this, cache, stats, action);
hunter.future = service.submit(hunter);
hunterMap.put(action.getKey(), hunter);
···
程式碼省略
}
}叫BitmapHunter的執行緒放入執行緒池中控制執行
hunter.future = service.submit(hunter);
@Override
public Future<?> submit(Runnable task) {
PicassoFutureTask ftask = new PicassoFutureTask((BitmapHunter) task);
execute(ftask);
return ftask;
}3 回收任務
為了避免oom,快取中Target使用了weakReference弱引用,方便被系統回收。但是有些Target(比如說ImageView)已經被回收,但是所對應的Request請求還在繼續任務(Action),就會浪費資源。Picasso中引入了一個叫CleanupThread的內部執行緒,CleanupThread是一個daemon執行緒,它的工作是找到那些Target(比如說ImageView)已經被回收的取消相應的任務Action。
看執行緒程式碼
private static class CleanupThread extends Thread {
private final ReferenceQueue<Object> referenceQueue;
private final Handler handler;
CleanupThread(ReferenceQueue<Object> referenceQueue, Handler handler) {
this.referenceQueue = referenceQueue;
this.handler = handler;
setDaemon(true);
setName(THREAD_PREFIX + "refQueue");
}
@Override public void run() {
Process.setThreadPriority(THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND);
while (true) {
try {
// Prior to Android 5.0, even when there is no local variable, the result from
// remove() & obtainMessage() is kept as a stack local variable.
// We're forcing this reference to be cleared and replaced by looping every second
// when there is nothing to do.
// This behavior has been tested and reproduced with heap dumps.
RequestWeakReference<?> remove =
(RequestWeakReference<?>) referenceQueue.remove(THREAD_LEAK_CLEANING_MS);
Message message = handler.obtainMessage();
if (remove != null) {
message.what = REQUEST_GCED;
message.obj = remove.action;
handler.sendMessage(message);
} else {
message.recycle();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
break;
} catch (final Exception e) {
handler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
});
break;
}
}
}
void shutdown() {
interrupt();
}
}由此看出此執行緒一直在遍歷ReferenceQueue,從中找到這樣的reference,就交給handler,handler會從reference中拿到action.
取消:
private void cancelExistingRequest(Object target) {
checkMain();
Action action = targetToAction.remove(target);
if (action != null) {
action.cancel();
dispatcher.dispatchCancel(action);
}
if (target instanceof ImageView) {
ImageView targetImageView = (ImageView) target;
DeferredRequestCreator deferredRequestCreator =
targetToDeferredRequestCreator.remove(targetImageView);
if (deferredRequestCreator != null) {
deferredRequestCreator.cancel();
}
}
}4 LruCache快取
Picasso 採用LruCache快取方式,借鑑了volley。本質是使用LinkedHashMap快取。使用LinkedHashMap是因為其具有存取快,易遍歷的資料結構。
this.map = new LinkedHashMap<String, Bitmap>(0, 0.75f, true);初始化快取記憶體的大小,在LurCache初始化的時候可以傳入自定義的大小控制元件。預設的大小為記憶體的15%。
static int calculateMemoryCacheSize(Context context) {
ActivityManager am = getService(context, ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
boolean largeHeap = (context.getApplicationInfo().flags & FLAG_LARGE_HEAP) != 0;
int memoryClass = am.getMemoryClass();
if (largeHeap && SDK_INT >= HONEYCOMB) {
memoryClass = ActivityManagerHoneycomb.getLargeMemoryClass(am);
}
// Target ~15% of the available heap.
return (int) (1024L * 1024L * memoryClass / 7);
}存取很簡單就是簡單的從map中存取快取物件。
@Override public void set(String key, Bitmap bitmap) {
if (key == null || bitmap == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null || bitmap == null");
}
Bitmap previous;
//set、put可能為併發的操作,需要同步加鎖。
synchronized (this) {
putCount++;
size += Utils.getBitmapBytes(bitmap);
previous = map.put(key, bitmap);
if (previous != null) {
size -= Utils.getBitmapBytes(previous);
}
}
//是否超過最大控制元件
trimToSize(maxSize);
} 5 圖形變化
圖片變化由Transformation定義了介面。交由BitmapHunter的hunt核心程式碼中執行。
static Bitmap applyCustomTransformations(List<Transformation> transformations, Bitmap result) {
for (int i = 0, count = transformations.size(); i < count; i++) {
final Transformation transformation = transformations.get(i);
Bitmap newResult;
try {
newResult = transformation.transform(result);
} catch (final RuntimeException e) {
Picasso.HANDLER.post(new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Transformation " + transformation.key() + " crashed with exception.", e);
}
});
return null;
}
if (newResult == null) {
final StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder() //
.append("Transformation ")
.append(transformation.key())
.append(" returned null after ")
.append(i)
.append(" previous transformation(s).\n\nTransformation list:\n");
for (Transformation t : transformations) {
builder.append(t.key()).append('\n');
}
Picasso.HANDLER.post(new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
throw new NullPointerException(builder.toString());
}
});
return null;
}
if (newResult == result && result.isRecycled()) {
Picasso.HANDLER.post(new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
throw new IllegalStateException("Transformation "
+ transformation.key()
+ " returned input Bitmap but recycled it.");
}
});
return null;
}
// If the transformation returned a new bitmap ensure they recycled the original.
if (newResult != result && !result.isRecycled()) {
Picasso.HANDLER.post(new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
throw new IllegalStateException("Transformation "
+ transformation.key()
+ " mutated input Bitmap but failed to recycle the original.");
}
});
return null;
}
result = newResult;
}
return result;
}Request 維護了一個圖形變換的列表。圖片載入成功後 BitmapHunter遍歷這個集合完成圖形的變換。