Tensorflow例項:實現簡單的卷積神經網路
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-15
CNN最大的特點在於卷積的權值共享結構,可以大幅減少神經網路的引數量,防止過擬合的同時又降低了神經網路模型的複雜度。在CNN中,第一個卷積層會直接接受影象畫素級的輸入,每一個卷積操作只處理一小塊影象,進行卷積變化後再傳到後面的網路,每一層卷積都會提取資料中最有效的特徵。這種方法可以提取到影象中最基礎的特徵,比如不同方向的邊或者拐角,而後再進行組合和抽象形成更高階的特徵。
一般的卷積神經網路由多個卷積層構成,每個卷積層中通常會進行如下幾個操作:
- 影象通過多個不同的卷積核的濾波,並加偏置(bias),特取出區域性特徵,每個卷積核會映射出一個新的2D影象。
- 將前面卷積核的濾波輸出結果,進行非線性的啟用函式處理。目前最常見的是使用ReLU函式,而以前Sigmoid函式用得比較多。
- 對啟用函式的結果再進行池化操作(即降取樣,比如將2*2的圖片將為1*1的圖片),目前一般是使用最大池化,保留最顯著的特徵,並提升模型的畸變容忍能力。
總結一下,CNN的要點是區域性連線(local Connection)、權值共享(Weight Sharing)和池化層(Pooling)中的降取樣(Down-Sampling)。
本文將使用Tensorflow實現一個簡單的卷積神經網路,使用的資料集是MNIST,網路結構:兩個卷積層加一個全連線層。
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
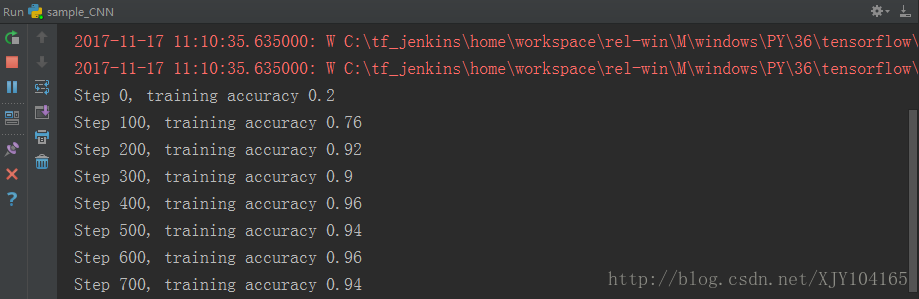
import tensorflow as 執行結果: