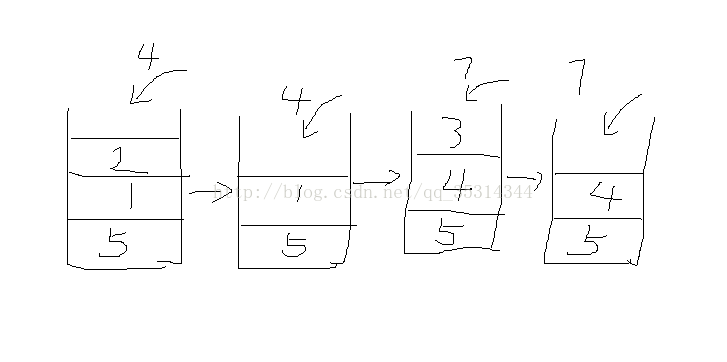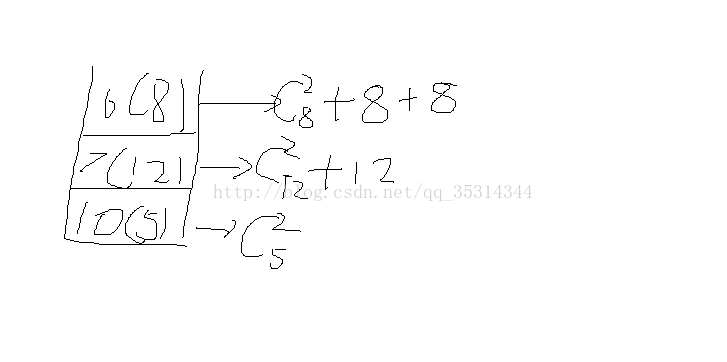左神面試演算法整理---單調棧
小B負責首都的防衛工作。
首都處於一個四面環山的盆地中,周圍的n個小山構成一個環,作為預警措施,小B計劃在每個小山上設定一個觀察哨,日夜不停的瞭望周圍發生的情況。
一旦發生外敵入侵事件,山頂上的崗哨將點燃烽煙。
若兩個崗哨所在的山峰之間的那些山峰,高度都不大於這兩座山峰,且這兩個山峰之間有相連通路,則崗哨可以觀察到另一個山峰上的烽煙是否點燃。
由於小山處於環上,任意兩個小山之間存在兩個不同的連線通路。滿足上述不遮擋的條件下,一座山峰上崗哨點燃的烽煙至少可以通過一條通路被另一端觀察到。
對於任意相鄰的崗哨,一端的崗哨一定可以發現一端點燃的烽煙。
小B設計的這種保衛方案的一個重要特性是能夠觀測到對方烽煙的崗哨對的數量,她希望你能夠幫她解決這個問題。
輸入
輸入中有多組測試資料。每組測試資料的第一行為一個整數n(3<=n<=10^6),為首都周圍的小山數量,第二行為n個整數,依次表示小山的高度h,(1<=h<=10^9)。
輸出
對每組測試資料,在單獨的一行中輸出能相互觀察到的崗哨的對數。
樣例輸入
5
1 2 4 5 3
樣例輸出
7
演算法思想:
此題可以理解為在兩個山峰之間的山峰都比兩端低時,兩端山峰就是一對,現在就是求有多少對?此題可以轉為環形連結串列中,一個數求他左右兩邊離他最近且大於他的數。
(1,2)(1,3)(2,3)(2,4)(4,5)(3,4)(3,5)
可以看出最高和次高可以組成一對,其他資料都能有兩個相鄰最大值,所以此問題通解(n-2)*2+1。
找出一個數左右最近的大於他的數,可以用單調棧實現。我們設定單調棧中,從棧頂到棧底依次變大。
假設有數 5 2 1 4 3 7
先放5,2小於5,放2,1小於2,放1,4大於1,則1彈出,1的彈出是由於4,所以4是1右邊臨近的大於他的數,2在1下面,所以2是1左面臨近大於他的數。相同原理2彈出,4進,3進,7進時同理彈出3,4,5
左 右
1 2 4
2 5 4
3 4 7
4 5 7
5 null 7
7 null null
總對數=4*2+1。此演算法複雜度可以達到O(n),遍歷演算法O(n^2)
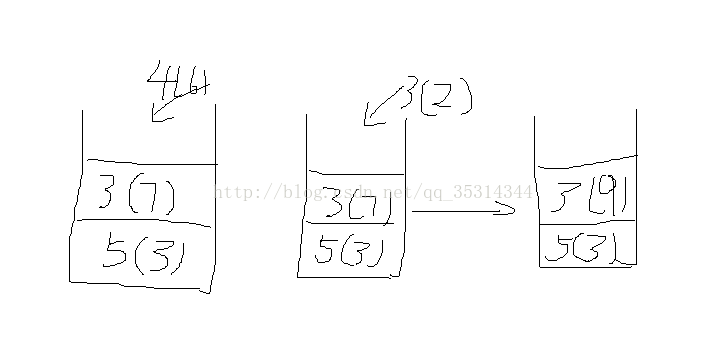
以上演算法只適用於,山峰高度都各不相等的情況下,若有相等則:一次遍歷將相鄰相等山峰合併,二次遍歷找最大值開始壓棧
將3個5壓入,7個3壓入,當6個4壓入時,7個3要出棧。7個3中,自己有對,與3相鄰的4,可以看到每個3,所以有7對,5與4同理有7對,
共7*6/2+7+7。
當壓入資料與棧頂資料相同,則只需合併個數即可。
沒有資料入棧時,只需依次出棧,
糾正上圖一個錯誤,對於7產生的個數,少加了一個12.因為只剩下7和10的時候,從10看向7和從7看向10是不一樣的所以要加兩次12
6是最後一個進棧的數,他要和棧底的數產生對數。
JAVA版
package problems_2017_07_26;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Problem_04_MountainsAndFlames {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
while (in.hasNextInt()) {
int size = in.nextInt();
int[] arr = new int[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
arr[i] = in.nextInt();
}
System.out.println(communications(arr));
}
}
public static int nextIndex(int size, int i) {
return i < (size - 1) ? (i + 1) : 0;
//相鄰相同山峰之間的對數,若只有一個,則沒有成對,若有兩個以上計算內部成對數
public static long getInternalSum(int n) {
return n == 1L ? 0L : (long) n * (long) (n - 1) / 2L;
}
public static class Pair {
public int value;
public int times;
public Pair(int value) {
this.value = value;
this.times = 1;
}
}
public static long communications(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return 0;
}
int size = arr.length;
int maxIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
maxIndex = arr[maxIndex] < arr[i] ? i : maxIndex;//找到最高山峰的位置
}
int value = arr[maxIndex];//最高山峰的高度
int index = nextIndex(size, maxIndex);//最高山峰的下一個位置
long res = 0L;
Stack<Pair> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(new Pair(value));
while (index != maxIndex) {
value = arr[index];
while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek().value < value) {
int times = stack.pop().times;
//res += getInternalSum(times) + times;
//res += stack.isEmpty() ? 0 : times;
res += getInternalSum(times) + times*2;//因為棧底是最大元素,所以在此階段不可能跳出
}
if (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek().value == value) {
stack.peek().times++;
} else {
stack.push(new Pair(value));
}
index = nextIndex(size, index);
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int times = stack.pop().times;
res += getInternalSum(times);
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
res += times;
if (stack.size() > 1) {//當棧底還剩大於1個的時候,彈出的那個數還可以與棧底的數稱為對數
res += times;
} else {
res += stack.peek().times > 1 ? times : 0;
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
C++版
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
struct Pair
{
long value;
long sum;
Pair(long value):value(value),sum(1){}
};
int findindex(int i,int size)
{
return i<size-1?i+1:0;
}
int internalsum(Pair a)
{
int n=a.sum;
return n*(n-1)/2;
}
int fun(vector<int> vec)
{
int n=vec.size();
Pair temp(vec[0]);
vector<Pair> a;
int max=0;
int maxi=0;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
if(vec[i]==vec[i-1])
temp.sum++;
else
{
a.push_back(temp);
if(max<temp.value)
{
max=temp.value;
maxi=a.size()-1;
}
temp.value=vec[i];
temp.sum=1;
}
}
a.push_back(temp);
if(max<temp.value)
{
max=temp.value;
maxi=a.size()-1;
}
stack<Pair> sta;
Pair val=a[maxi];
sta.push(val);
int index=findindex(maxi,a.size());
int count=0;
while(index!=maxi)
{
while(!sta.empty()&&a[index].value>sta.top().value)
{
count+=internalsum(sta.top())+2*sta.top().sum;
sta.pop();
}
if(!sta.empty()&&a[index].value==sta.top().value)
sta.top().sum+=a[index].sum;
else
sta.push(a[index]);
index=findindex(index,a.size());
}
while(!sta.empty())
{
count+=internalsum(sta.top());
int p=sta.top().sum;
sta.pop();
if(!sta.empty())
{
count+=p;
if(sta.size()>1)
count+=p;
else
count+=sta.top().sum>1?p:0;
}
}
return count;
}
int main()
{
int n;
while(cin>>n)
{
vector<int> vec;
int in;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>in;
vec.push_back(in);
}
int result=fun(vec);
cout<<result<<endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}