Linux區域網檔案分享系統Samba
原作者:http://blog.csdn.net/jhq0113/article/details/44159251
上學的時候在學校機房見過FTP做的檔案分享系統,伺服器是Windows的,當時感覺功能真的很強大,不管是哪臺機器都可以共享一個資料夾,後來自己在家裡通過查閱各種資料,用自己的win7做FTP伺服器,做了一個檔案伺服器,但是真的很雞肋,操作體驗真的不盡人意。
下面介紹的是Linux伺服器平臺安裝的檔案分享系統軟體Samba,通過Samba部署的檔案分享系統可以相容Mac、Linux和Windows三大主流作業系統,而且操作體驗也非常好,自己在家裡做了一個小型分享系統,家用伺服器的配置:CPU:凌動 D2500,2G記憶體,32G SSD的一個小型伺服器,4m頻寬,速度秒殺FTP,檔案上傳和下載都在11M/s左右。
下面簡單介紹一下CentOS下yum安裝過程,如果是在公司內部用,一般會編譯安裝samba,然後會做一些細節的許可權驗證,我做家用,能用就可以了,如果你想做更細節的許可權分配,去度娘,參考資料好幾mol。
安裝:
[[email protected] ~]# yum install samba samba-client samba-swat
設定smb和nmb在3、5啟動級別隨系統啟動:
[[email protected] ~]# chkconfig --level 35 smb on
[[email protected] ~]# chkconfig --level 35 nmb on
配置Samba:
[[email protected] ~]# vim /etc/samba/smb.conf
進行如下修改:
- #======================= Global Settings =====================================
- [global]
- config file = /usr/local/samba/lib/smb.conf.%m
- # ----------------------- Network Related Options -------------------------
- #
- # workgroup = NT-Domain-Name or Workgroup-Name, eg: MIDEARTH
- #
- # server string is the equivalent of the NT Description field
- #
- # netbios name can be used to specify a server name not tied to the hostname
- #
- # Interfaces lets you configure Samba to use multiple interfaces
- # If you have multiple network interfaces then you can list the ones
- # you want to listen on (never omit localhost)
- #
- # Hosts Allow/Hosts Deny lets you restrict who can connect, and you can
- # specifiy it as a per share option as well
- #
- workgroup = MYGROUP
- server string = Samba Server Version %v
- ; netbios name = MYSERVER
- interfaces = lo eth0 192.168.1.11/24 192.168.1.1/255
- hosts allow = 127. 192.168.1. 192.168.0.
- # --------------------------- Logging Options -----------------------------
- #
- # Log File let you specify where to put logs and how to split them up.
- #
- # Max Log Size let you specify the max size log files should reach
- # logs split per machine
- log file = /var/log/samba/log.%m
- # max 50KB per log file, then rotate
- max log size = 50
- # ----------------------- Standalone Server Options ------------------------
- #
- # Scurity can be set to user, share(deprecated) or server(deprecated)
- #
- # Backend to store user information in. New installations should
- # use either tdbsam or ldapsam. smbpasswd is available for backwards
- # compatibility. tdbsam requires no further configuration.
- security=share
- #security = user
- #passdb backend = tdbsam
- # ----------------------- Domain Members Options ------------------------
- #
- # Security must be set to domain or ads
- #
- # Use the realm option only with security = ads
- # Specifies the Active Directory realm the host is part of
- #
- # Backend to store user information in. New installations should
- # use either tdbsam or ldapsam. smbpasswd is available for backwards
- # compatibility. tdbsam requires no further configuration.
- #
- # Use password server option only with security = server or if you can't
- # use the DNS to locate Domain Controllers
- # The argument list may include:
- # password server = My_PDC_Name [My_BDC_Name] [My_Next_BDC_Name]
- # or to auto-locate the domain controller/s
- # password server = *
- ; security = domain
- ; passdb backend = tdbsam
- ; realm = MY_REALM
- ; password server = <NT-Server-Name>
- # ----------------------- Domain Controller Options ------------------------
- #
- # Security must be set to user for domain controllers
- # use either tdbsam or ldapsam. smbpasswd is available for backwards
- # compatibility. tdbsam requires no further configuration.
- #
- # Domain Master specifies Samba to be the Domain Master Browser. This
- # allows Samba to collate browse lists between subnets. Don't use this
- # if you already have a Windows NT domain controller doing this job
- #
- # Domain Logons let Samba be a domain logon server for Windows workstations.
- #
- # Logon Scrpit let yuou specify a script to be run at login time on the client
- # You need to provide it in a share called NETLOGON
- #
- # Logon Path let you specify where user profiles are stored (UNC path)
- #
- # Various scripts can be used on a domain controller or stand-alone
- # machine to add or delete corresponding unix accounts
- #
- ; security = user
- ; passdb backend = tdbsam
- ; domain master = yes
- ; domain logons = yes
- # the login script name depends on the machine name
- ; logon script = %m.bat
- # the login script name depends on the unix user used
- ; logon script = %u.bat
- ; logon path = \\%L\Profiles\%u
- # disables profiles support by specifing an empty path
- ; logon path =
- ; add user script = /usr/sbin/useradd "%u" -n -g users
- ; add group script = /usr/sbin/groupadd "%g"
- ; delete user script = /usr/sbin/userdel "%u"
- ; delete user from group script = /usr/sbin/userdel "%u" "%g"
- ; delete group script = /usr/sbin/groupdel "%g"
- # ----------------------- Browser Control Options ----------------------------
- #
- # set local master to no if you don't want Samba to become a master
- # browser on your network. Otherwise the normal election rules apply
- #
- # OS Level determines the precedence of this server in master browser
- # elections. The default value should be reasonable
- #
- # Preferred Master causes Samba to force a local browser election on startup
- # and gives it a slightly higher chance of winning the election
- ; local master = no
- ; os level = 33
- ; preferred master = yes
- #----------------------------- Name Resolution -------------------------------
- # Windows Internet Name Serving Support Section:
- # Note: Samba can be either a WINS Server, or a WINS Client, but NOT both
- #
- # - WINS Support: Tells the NMBD component of Samba to enable it's WINS Server
- #
- # - WINS Server: Tells the NMBD components of Samba to be a WINS Client
- #
- # - WINS Proxy: Tells Samba to answer name resolution queries on
- # behalf of a non WINS capable client, for this to work there must be
- # at least one WINS Server on the network. The default is NO.
- #
- # DNS Proxy - tells Samba whether or not to try to resolve NetBIOS names
- # via DNS nslookups.
- ; wins support = yes
- ; wins server = w.x.y.z
- ; wins proxy = yes
- ; dns proxy = yes
- # --------------------------- Printing Options -----------------------------
- #
- # Load Printers let you load automatically the list of printers rather
- # than setting them up individually
- #
- # Cups Options let you pass the cups libs custom options, setting it to raw
- # for example will let you use drivers on your Windows clients
- #
- # Printcap Name let you specify an alternative printcap file
- #
- # You can choose a non default printing system using the Printing option
- load printers = yes
- cups options = raw
- ; printcap name = /etc/printcap
- #obtain list of printers automatically on SystemV
- ; printcap name = lpstat
- ; printing = cups
- # --------------------------- Filesystem Options ---------------------------
- #
- # The following options can be uncommented if the filesystem supports
- # Extended Attributes and they are enabled (usually by the mount option
- # user_xattr). Thess options will let the admin store the DOS attributes
- # in an EA and make samba not mess with the permission bits.
- #
- # Note: these options can also be set just per share, setting them in global
- # makes them the default for all shares
- ; map archive = no
- ; map hidden = no
- ; map read only = no
- ; map system = no
- ; store dos attributes = yes
- #============================ Share Definitions ==============================
- [homes]
- comment = Home Directories
- browseable = no
- writable = yes
- ; valid users = %S
- ; valid users = MYDOMAIN\%S
- [printers]
- comment = All Printers
- path = /var/spool/samba
- browseable = no
- guest ok = no
- writable = no
- printable = yes
- # Un-comment the following and create the netlogon directory for Domain Logons
- ; [netlogon]
- ; comment = Network Logon Service
- ; path = /var/lib/samba/netlogon
- ; guest ok = yes
- ; writable = no
- ; share modes = no
- # Un-comment the following to provide a specific roving profile share
- # the default is to use the user's home directory
- ; [Profiles]
- ; path = /var/lib/samba/profiles
- ; browseable = no
- ; guest ok = yes
- # A publicly accessible directory, but read only, except for people in
- # the "staff" group
- [public]
- comment = Public Stuff
- path = /share
- public = yes
- writable = yes
- printable = no
- write list = +staff
建立共享資料夾並分配nobody許可權:
[[email protected] ~]# mkdir /share
[[email protected] ~]# chown -R nobody:nobody /share
關閉防火牆:
[[email protected] ~]# chkconfig iptables off
關閉selinux:
[[email protected] ~]# vim /etc/sysconfig/selinux
修改為:
- #SELINUX=enforcing
- SELINUX=disabled
重啟:
[[email protected] ~]# init 6
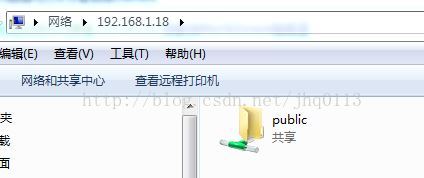
重啟完成後,就可以通過區域網內的電腦連線共享目錄了,如Windows:
連線分享目錄:Win鍵+R,然後鍵入\\IP地址\,如:\\192.168.1.18\,結果如下圖:
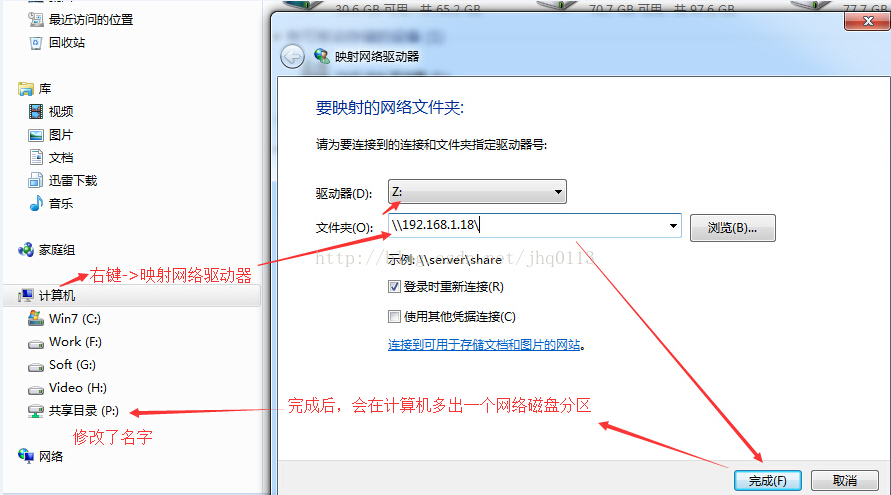
這樣你就可以操作共享目錄了。如果你想不用每次都這樣操作可以將其對映為網路地址,就可以很方便的操作了,和本地磁碟一樣方便,如下圖:
好了,Samba的配置就到這裡了,希望可以幫助到你。
相關推薦
Linux區域網檔案分享系統Samba
原作者:http://blog.csdn.net/jhq0113/article/details/44159251 上學的時候在學校機房見過FTP做的檔案分享系統,伺服器是Windows的,當時感覺功能真的很強大,不管是哪臺機器都可以共享一個資料夾,後來自己在家裡通過查
linux下檔案在系統中的傳輸
1.scp scp file [email protected]:dir ##上傳(dir為絕對路徑) scp [email protected]:file dir ##下載(file為絕對路徑) 2.rs
Linux---cifs檔案系統之samba的安裝配置及共享目錄
CIFS是一種通用網路檔案系統,主要用於網路裝置之間的檔案共享。CIFS可以在linux系統和windows系統之間共享檔案,因此這種檔案系統主要用於客戶端是windows系統。提供CIFS的服務是SAMBA,下文將介紹SAMBA服務的一些配置以及用法。
Fedora17下用samba實現windows和Linux跨平臺檔案系統訪問
第一步:在Fedora linux系統下載並安裝samba # yum -y install samba 第二步:編輯samba的配置檔案/etc/samba/smb.conf 1. 找到[homes],複製這6行 yy6p 2.修改
Linux 記憶體檔案系統
Linux記憶體檔案系統:可滿足高IO的要求 ramdisk: 基於虛擬在記憶體中的其他檔案系統(ex2fs)。 掛載方式:mount /dev/ram /mnt/ramdisk ramfs: 實體記憶體檔案系統,只存在於實體記憶體中。其大小也不是固定的,而是隨著所需要的
mac通過samba伺服器遠端管理linux上檔案
1.下載及安裝: yum -y install samba 我的版本是CentOs7,使用的yum安裝,可以解決很多的包依賴關係,引數y,設定詢問全部yes。 2.配置samba: &n
Linux檔案在系統中的傳輸,打包及壓縮相關命令
一、Linux檔案在系統中的傳輸 scp的上傳和下載 上傳:scp file [email protected]:/dir 下載:scp [email protected]:/file dir 詳細截圖可在文章:Linux系統中ssh與sshd服務
Linux fsync和fdatasync系統呼叫實現分析(Ext4檔案系統)
參考:https://blog.csdn.net/luckyapple1028/article/details/61413724 在Linux系統中,對檔案系統上檔案的讀寫一般是通過頁快取(page cache)進行的(DirectIO除外),這樣設計的可以延時磁碟IO的操作,從而可以減少磁碟讀
Linux.ext4檔案系統 .inode和extent
最近在看相關內容,不過總是不是很系統,今日看到此部落格,感覺恍然大悟,作者寫的非常棒:轉載: https://blog.csdn.net/stringNewName/article/details/73740155 為表示對作者的尊敬,一字不動的敲擊! 最近在看ext4
linux——檔案在系統的傳輸
檔案在系統的傳輸 1.scp scp就是secure copy,一個在linux下用來進行遠端拷貝檔案的命令。 有時我們需要獲得遠端伺服器上的某個檔案,該伺服器既沒有配置ftp伺服器,也沒有做共享,無法通過常規途徑獲得檔案時,只需要通過簡單的scp命令便可達到目的。 2.rs
linux 檢視檔案系統型別
linux 檢視檔案系統型別 Linux 檢視檔案系統的方式有多種,列舉如下: mount :~$ mount /dev/sda1 on / type ext4 (rw,errors=remount-ro,user_xattr) proc on /proc type pr
linux的檔案系統以及使用者組等概念
一、Linux檔案結構及基本資料夾 目錄 描述 / 根目錄 /bin 做為基礎系統所需要的最基礎的命令就是放在這裡。比如 ls、cp、mkdir等命令;功能和
Linux EXT檔案系統恢復誤刪檔案的方法
我們在管理資料庫和系統的時候,經常需要做rm 刪除檔案的操作。由於Linux是沒有回收站的,rm刪除了檔案或者目錄以後,資料是無法從Windows所謂的回收站中找到並恢復的。這樣的話,資料被誤刪除了以後,想要恢復我們一般需要從備份中,或者找資料恢復公司來恢復資料。但是,在某些比較特殊的情況下,使用了
linux系統samba共享
/etc/samba/smb.conf 配置檔案 [global] security=share [share] path=/opt/share public=yes browseable=yes ;samba讀許可權 writeable=yes ;samba寫許可權
[Linux] ARM檔案系統移植記錄
#arm-cotex-A9 M6708 檔案系統移植記錄 本文的主要內容是:記錄在移植檔案系統時所遇到的問題。 ##工具 * ubuntu 16.04.2 server i386(開啟ssh、samba功能) * buildroot-2017.02.3 (藉助buildroot工
linux 網路檔案系統NFS伺服器配置
NFS(網路檔案系統)服務可以將遠端Linux系統上的檔案共享資源掛載到本地主機的目錄上,從而使得本地主機(Linux客戶端)基於TCP/IP協議,像使用本地主機上的資源那樣讀寫遠端Linux系統上的共享檔案。 1.配置NFS伺服器,先安裝兩個必要的軟體包,通常是預設安裝的 yum in
Linux根檔案系統介紹
分享一下我老師大神的人工智慧教程!零基礎,通俗易懂!http://blog.csdn.net/jiangjunshow 也歡迎大家轉載本篇文章。分享知識,造福人民,實現我們中華民族偉大復興!
Linux系統下python學習筆記——Linux中檔案和目錄常用命令詳解
一、檢視目錄內容 ls命令說明: 英文單詞list的簡寫,功能為列出目錄的內容,是使用者最常用的命令字義 Linux下檔案和目錄的特點: Linux檔案或目錄名稱最長可以有256個字元 以 . 開頭的檔案為隱藏檔案,需要用-a引數才能顯示(all
Linux及檔案系統基本介紹
Linux及檔案系統基本介紹 1 網際網路行業現狀 在伺服器端市場: 超級計算機
如何將HDFS檔案系統掛載到Linux本地檔案系統
本文轉自https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1078538,如果侵權請聯絡我刪除。 1.文件編寫目的 Hadoop支援通過NFSv3掛載HDFS檔案系統到本地目錄,允許使用者像訪問本地檔案系統一樣訪問HDFS,對於普通使用者來說大大的簡