自定義TabHost,TabWidget樣式 .
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-16
大家好,今天我為大家分享TabHost中怎樣修改TabWidget樣式。在很多介面美觀的應用中很多都用到了TabHost,但他們要比系統預設的要漂亮得多。先看幾張圖:
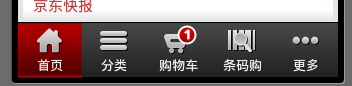
京東商城底部選單欄
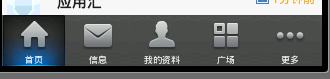
新浪微博底部選單欄
好了,看到這些漂亮的選單欄是不是很驚訝,你可能會說用Button就可以實現啊 ,可是用Button的話控制顯示的內容很麻煩,不如用TabHost控制效率更高。很想知道用TabHost是怎麼實現的吧,下面就來研究如何實現這種漂亮的TabHost。先看一下效果圖:

介面比較簡單,要想做得漂亮換幾張圖片就可以了。
第一步:先在佈局(這裡用了main.xml建立時自動生成的)裡面放上TabHost ,只要將TabHost控制元件託至螢幕中就可:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <TabHost android:id="@+id/tabhost" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:id="@+id/linearLayout1" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:orientation="vertical"> <TabWidget android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@android:id/tabs"></TabWidget> <FrameLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:id="@android:id/tabcontent"> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:id="@+id/tab1"></LinearLayout> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:id="@+id/tab2"></LinearLayout> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:id="@+id/tab3"></LinearLayout> </FrameLayout> </LinearLayout> </TabHost>
這裡我們已經把LinearLayout和TextView去掉了,並將“xmlns:android="……" ”新增大TabHost裡了,這裡要注意我們將TabHost的id定義為自己定義的id比不用android規定的id="@android:id/tabhost"。
第二步:建立顯示此TabWidget的佈局tabmini.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="40dp" android:paddingLeft="5dip" android:paddingRight="5dip" android:background="@drawable/head_bg"> <TextView android:id="@+id/tab_label" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerInParent="true" android:gravity="center" android:textColor="#000000" android:textStyle="bold" android:background="@drawable/tabmini"/> </RelativeLayout>
第三步:建立一個selector在drawable裡面 命名tabmini.xml,用來點選TabHost的一個tab時TextView的變化:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<selector
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item android:state_selected="true"
android:drawable="@drawable/add_managebg_down"/>
<item android:state_selected="false"
android:drawable="@drawable/add_managebg"/>
</selector>
第四步:在Activity裡實現TabHost:
package cn.li.tabstyle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.TabHost;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class TabHostStyleActivity extends Activity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
View niTab = (View) LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.tabmini, null);
TextView text0 = (TextView) niTab.findViewById(R.id.tab_label);
text0.setText("ni");
View woTab = (View) LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.tabmini, null);
TextView text1 = (TextView) woTab.findViewById(R.id.tab_label);
text1.setText("wo");
View taTab = (View) LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.tabmini, null);
TextView text2 = (TextView) taTab.findViewById(R.id.tab_label);
text2.setText("ta");
View weTab = (View) LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.tabmini, null);
TextView text3 = (TextView) weTab.findViewById(R.id.tab_label);
text3.setText("we");
TabHost tabHost = (TabHost)findViewById(R.id.tabhost);
tabHost.setup(); //Call setup() before adding tabs if loading TabHost using findViewById().
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("nitab").setIndicator(niTab).setContent(R.id.tab1));
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("wotab").setIndicator(woTab).setContent(R.id.tab2));
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tatab").setIndicator(taTab).setContent(R.id.tab3));
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("wetab").setIndicator(weTab).setContent(R.id.tab4));
}
}
這裡我們用findViewById建立了TabHost,這樣的話我們就需要在新增tab時呼叫TabHost的setup()方法;這裡我們新增內容時新增的是佈局,我們完全可以換成自己建立的Activity。
好了,讓我們來看看執行效果吧:

好了,我們自定義的TabHost算是結束了。不過看到Activity裡的程式碼很多都是重複的我們可以這樣把他們簡化:
package cn.li.tabstyle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.TabHost;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class TabHostStyleActivity extends Activity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
String[] title = new String[]{"ni","wo","ta","we"};
View userTab,articeTab,feedTab,weTab;
View[] tabs = new View[]{userTab,articeTab,feedTab,weTab};
int[] tabIds = new int[]{R.id.tab1,R.id.tab2,R.id.tab3,R.id.tab4};
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
TabHost tabHost = (TabHost)findViewById(R.id.tabhost);
tabHost.setup(); //Call setup() before adding tabs if loading TabHost using findViewById().
for(int i=0;i<tabs.length;i++){
tabs[i] = (View) LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.tabmini, null);
TextView text = (TextView) tabs[i].findViewById(R.id.tab_label);
text.setText(title[i]);
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec(title[i]).setIndicator(tabs[i]).setContent(tabIds[i]));
}
}
}