設計模式面試——四種最常用的設計模式
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-17
請說出你所熟悉的幾種設計模式。並舉例說明:
下面列舉四種最常用的設計模式
一、Strategy模式
1、兩大原則
Strategy模式體現瞭如下的兩大原則:
1,針對介面程式設計,而不是針對實現程式設計。
2,多用組合,少用繼承。
2、 例子: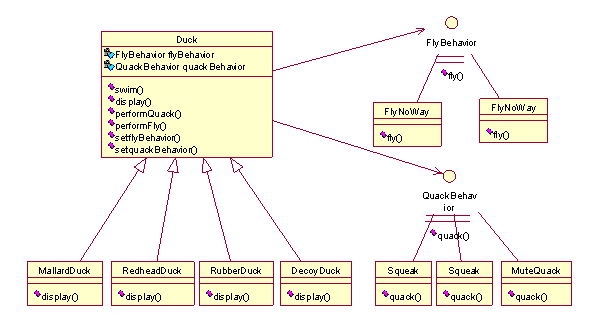
二、Iterator模式
提供一種方法順序訪問一個聚合物件中各個元素, 而又不需暴露該物件的內部表示。
這種設計模式非常普遍,
比如Java裡面的:
public interface Iterator {
boolean hasNext();
Object next();
void remove();
}
以及C++ STL裡面的 iterator使用 ++ 訪問。
三、Singleton模式
下面是個C++ singleton的類:
- 1 #ifndef SINGLETON_H
- 2 #define SINGLETON_H
- 3
- 4 #include "synobj.h"
- 5
- 6 template<class T>
- 7 class Singleton {
- 8 CLASS_UNCOPYABLE(Singleton)
- 9 public:
- 10 static T& Instance() { // Unique point of access
- 11 if (0 == _instance) {
- 12 Lock lock(_mutex);
- 13 if(0 == _instance) {
- 14 _instance = new T();
- 15 atexit(Destroy);
- 16 }
- 17 }
- 18 return *_instance;
- 19 }
- 20 protected:
- 21 Singleton(){}
- 22 ~Singleton(){}
- 23 private:
- 24 staticvoid Destroy() { // Destroy the only instance
- 25 if ( _instance != 0 ) {
- 26 delete _instance;
- 27 _instance = 0;
- 28 }
- 29 }
- 30 static Mutex _mutex;
- 31 static T * volatile _instance; // The one and only instance
- 32 };
- 33
- 34 template<class T>
- 35 Mutex Singleton<T>::_mutex;
- 36
- 37 template<class T>
- 38 T * volatile Singleton<T>::_instance = 0;
- 39
- 40 #endif/*SINGLETON_H*/
四、Factory Method模式
Factory Method模式在不同的子工廠類生成具有統一介面介面的物件,一方面,可以不用關心產品物件的具體實現,簡化和統一Client呼叫過程;另一方面,可以讓整個系統具有靈活的可擴充套件性。
- abstract class BallFactory{
- protected abstract Ball makeBall(); //Factory Method
- }
- class BasketballFact extends BallFactory{
- public Ball makeBall(){ //子類實現Factory Method決定例項化哪一個類的
- returnnew Basketball();
- }
- }
- class FootballFact extends BallFactory{
- public Ball makeBall(){ //子類實現Factory Method決定例項化哪一個類的
- returnnew Football();
- }
- }
- class Basketball extends Ball{
- publicvoid play(){
- System.out.println("play the basketball");
- }
- }
- class Football extends Ball{
- publicvoid play(){
- System.out.println("play the football");
- }
- }
- abstract class Ball{
- protected abstract void play();
- }
- publicclass test{
- publicstaticvoid main(String[] args){
- BallFactory ballFactory=new BasketballFact();
- Ball basketball=ballFactory.makeBall();
- basketball.play();
- ballFactory=new FootballFact();
- Ball football=ballFactory.makeBall();
- football.play();
- }
- }
