Fragemnt(靜態新增Fragment,簡單的動態新增Fragment)
在這裡我們全部使用android-support-v4.jar包裡Fragment,不用系統自帶的Fragment;這兩個基本一樣,但V4包中的相對功能更強大一些。
第一步:新建一個專案工程新增一個fragment1.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" 第二步:新建一個fragment2.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#00ff00"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:layout_width fragment2.xml和fragment1.xml很像
第三步:
新建一個Fragment1類,這個類繼承Fragment,記得匯入的包是
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;package com.example.staticfragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
public class Fragment1 extends Fragment{
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment1, container, false);
//return super.onCreateView(inflater, container, savedInstanceState);
}
}
第四步驟,新建Fragment2,同樣繼承Fragment
package com.example.staticfragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
public class Fragment2 extends Fragment{
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment2, container, false);
}
}
第五步:修改main.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:baselineAligned="false"
>
<fragment android:id="@+id/frame1"
android:name="com.example.staticfragment.Fragment1"
//包名加類名
android:layout_width="0dip"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
<fragment android:id="@+id/frame2"
android:name="com.example.staticfragment.Fragment2"
android:layout_width="0dip"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
</LinearLayout>
第六步:在MainActivity中呼叫
package com.example.staticfragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentActivity;
import android.view.Menu;
public class MainActivity extends FragmentActivity{
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
}
由於上面用的的是V4包,必須將MainActivity派生自FragmentActivity,否則根本無法啟動程式!因為系統的Activity只能用來盛裝系統自帶的Fragment,而無法盛裝V4包中的Fragment,因為系統的Activity根本無法識別V4包中的Fragment,因為這根本就不是一塊的程式碼!如果不使用V4包,使用系統自帶的Fragment則不必將MainActivity派生自FragmentActivity。
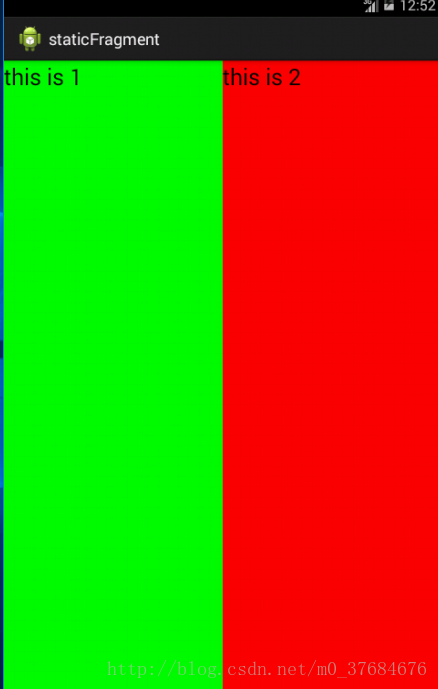
第⑦步,看下執行效果:
二、動態新增Fragment
你已經學會了如何在XML中使用Fragment,但是這僅僅是Fragment最簡單的功能而已。Fragment真正的強大之處在於可以動態地新增到Activity當中,因此這也是你必須要掌握的東西。當你學會了在程式執行時向Activity新增Fragment,程式的介面就可以定製的更加多樣化。下面我們立刻來看看,如何動態新增Fragment。
還是在上一節程式碼的基礎上修改,開啟activity_main.xml,將其中程式碼全部刪除,改成下面的樣子:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:baselineAligned="false">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="顯示Fragment1"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="顯示Fragment2"/>
<FrameLayout android:id="@+id/frame"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"/>
</LinearLayout>其它程式碼都沒有動,主要的是在MainActivity裡,點選這兩個按鈕時做的處理:
package com.example.staticfragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentActivity;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentManager;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentTransaction;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends FragmentActivity{
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button button1=(Button) findViewById(R.id.button1);
button1.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
/*1.獲取到FragmentManager,在V4包中通過getSupportFragmentManager,在系統中原生的Fragment是通過getFragmentManager獲得的。
2.開啟一個事務,通過呼叫beginTransaction方法開啟。
3.向容器內加入Fragment,一般使用add或者replace方法實現,需要傳入容器的id和Fragment的例項。
4.提交事務,呼叫commit方法提交。 */
FragmentManager manager=getSupportFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction transaction=manager.beginTransaction();
Fragment1 fragment1=new Fragment1();
transaction.add(R.id.frame, fragment1);
transaction.commit();
}
});
Button button2=(Button) findViewById(R.id.button2);
button2.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
FragmentManager manager=getSupportFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction transaction=manager.beginTransaction();
Fragment2 fragement2=new Fragment2();
transaction.add(R.id.frame, fragement2);
transaction.commit();
}
});
}
}