android graphic(2)—EGL和OpenGL ES
前面提到android EGL庫的主要作用就是將OpenGL ES和本地視窗系統結合起來。OpenGL ES就像是一個印表機,各個廠商印表機的內部實現不同(不同的OpenGL ES的實現,軟體、硬體等,實現的庫由EGL載入),但是隻要列印的文件內容相同,按下列印鍵,其輸出的結果都是相同的。當然印表機可以在不同種類的紙張上列印,A4,A5或者牛皮紙、塑料紙等等,印表機對這些都需要支援。OpenGL ES和印表機一樣,需要相容windows、塞班、android等多個不同的系統,所以它的實現是平臺無關的,而windows、android等系統需要給OpenGL ES提供紙,這個紙就是本地視窗,而不同系統的實現肯定是不同的。印表機列印的最終內容需要呈現在紙上,對軟體來說本地窗口裡面肯定有buffer的存在來儲存OpenGL ES畫的圖。
2016/03/25 注:android 4.4中已經不使用FramebufferNativeWindow了,而是使用FramebufferSurface和hwcomposer去做composer。
Android的本地視窗
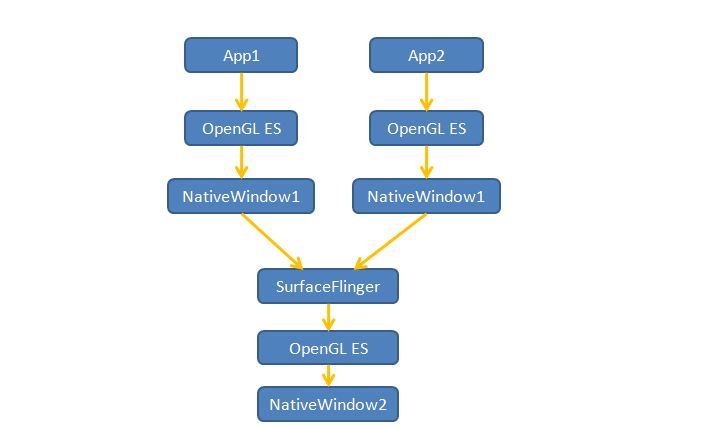
上面提到,如果需要使用OpenGL ES就需要本地視窗的加入,而在前面文章中提到有兩處使用OpenGL ES的地方:一是上層的3D繪圖,二是SurfaceFlinger對layer的合成(先不考慮Canvas和overlay)。那麼我們可以想象下面這幅圖畫:
我們需要兩種本地視窗,一種是面對app的,一種是面對SurfaceFlinger。那麼本地視窗在android中到底是什麼?我們從EGL函式的呼叫開始,在eglCreateWindowSurface函式中,有個和平臺無關的結構體為NativeWindowType,
EGLSurface eglCreateWindowSurface( EGLDisplay dpy, EGLConfig config,
NativeWindowType window,
const EGLint *attrib_list)
{
return createWindowSurface(dpy, config, window, attrib_list);
}而
typedef EGLNativeWindowType NativeWindowType; 從下面的定義可以看到,在系統為android的巨集下,本地視窗其實為ANativeWindow。
#elif defined(__ANDROID__) || defined(ANDROID)
struct ANativeWindow;
struct egl_native_pixmap_t;
typedef struct ANativeWindow* EGLNativeWindowType;
typedef struct egl_native_pixmap_t* EGLNativePixmapType;
typedef void* EGLNativeDisplayType;
下面是ANativeWindow結構體,裡面有一組函式指標,我們能夠猜到,兩個本地視窗都是繼承了ANativeWindow,然後對函式進行賦值,“實現協議”。
struct ANativeWindow
{
struct android_native_base_t common;
/* flags describing some attributes of this surface or its updater */
const uint32_t flags;
/* min swap interval supported by this updated */
const int minSwapInterval;
/* max swap interval supported by this updated */
const int maxSwapInterval;
/* horizontal and vertical resolution in DPI */
const float xdpi;
const float ydpi;
/* Some storage reserved for the OEM's driver. */
intptr_t oem[4];
int (*setSwapInterval)(struct ANativeWindow* window,
int interval);
int (*query)(const struct ANativeWindow* window,
int what, int* value);
int (*perform)(struct ANativeWindow* window,
int operation, ... );
int (*cancelBuffer_DEPRECATED)(struct ANativeWindow* window,
struct ANativeWindowBuffer* buffer);
int (*dequeueBuffer)(struct ANativeWindow* window,
struct ANativeWindowBuffer** buffer, int* fenceFd);
int (*queueBuffer)(struct ANativeWindow* window,
struct ANativeWindowBuffer* buffer, int fenceFd);
int (*cancelBuffer)(struct ANativeWindow* window,
struct ANativeWindowBuffer* buffer, int fenceFd);
};最終找到的兩個本地視窗為FramebufferNativeWindow和Surface。
FramebufferNativeWindow
SurfaceFlinger對應的本地視窗為FramebufferNativeWindow,繼承了ANativeWindow,裡面有個sp<NativeBuffer> buffers[MAX_NUM_FRAME_BUFFERS];,這應該就是“本地的紙”,而且還有和ANativeWindow對應的函式實現。
class FramebufferNativeWindow
: public ANativeObjectBase<
ANativeWindow,
FramebufferNativeWindow,
LightRefBase<FramebufferNativeWindow> >
{
public:
FramebufferNativeWindow();
framebuffer_device_t const * getDevice() const { return fbDev; }
bool isUpdateOnDemand() const { return mUpdateOnDemand; }
status_t setUpdateRectangle(const Rect& updateRect);
status_t compositionComplete();
void dump(String8& result);
// for debugging only
int getCurrentBufferIndex() const;
private:
friend class LightRefBase<FramebufferNativeWindow>;
~FramebufferNativeWindow(); // this class cannot be overloaded
static int setSwapInterval(ANativeWindow* window, int interval);
static int dequeueBuffer(ANativeWindow* window, ANativeWindowBuffer** buffer, int* fenceFd);
static int queueBuffer(ANativeWindow* window, ANativeWindowBuffer* buffer, int fenceFd);
static int query(const ANativeWindow* window, int what, int* value);
static int perform(ANativeWindow* window, int operation, ...);
static int dequeueBuffer_DEPRECATED(ANativeWindow* window, ANativeWindowBuffer** buffer);
static int queueBuffer_DEPRECATED(ANativeWindow* window, ANativeWindowBuffer* buffer);
static int lockBuffer_DEPRECATED(ANativeWindow* window, ANativeWindowBuffer* buffer);
framebuffer_device_t* fbDev;
alloc_device_t* grDev;
sp<NativeBuffer> buffers[MAX_NUM_FRAME_BUFFERS];
sp<NativeBuffer> front;
mutable Mutex mutex;
Condition mCondition;
int32_t mNumBuffers;
int32_t mNumFreeBuffers;
int32_t mBufferHead;
int32_t mCurrentBufferIndex;
bool mUpdateOnDemand;
};Surface
眾多App對應的本地視窗為Surface,繼承了ANativeWindow,類似的也有個BufferSlot mSlots[NUM_BUFFER_SLOTS];,是App的“本地的紙”,而且還有和ANativeWindow對應的函式實現。
class Surface
: public ANativeObjectBase<ANativeWindow, Surface, RefBase>
{
public:
/*
* creates a Surface from the given IGraphicBufferProducer (which concrete
* implementation is a BufferQueue).
*
* Surface is mainly state-less while it's disconnected, it can be
* viewed as a glorified IGraphicBufferProducer holder. It's therefore
* safe to create other Surfaces from the same IGraphicBufferProducer.
*
* However, once a Surface is connected, it'll prevent other Surfaces
* referring to the same IGraphicBufferProducer to become connected and
* therefore prevent them to be used as actual producers of buffers.
*
* the controlledByApp flag indicates that this Surface (producer) is
* controlled by the application. This flag is used at connect time.
*/
Surface(const sp<IGraphicBufferProducer>& bufferProducer, bool controlledByApp = false);
/* getIGraphicBufferProducer() returns the IGraphicBufferProducer this
* Surface was created with. Usually it's an error to use the
* IGraphicBufferProducer while the Surface is connected.
*/
sp<IGraphicBufferProducer> getIGraphicBufferProducer() const;
/* convenience function to check that the given surface is non NULL as
* well as its IGraphicBufferProducer */
static bool isValid(const sp<Surface>& surface) {
return surface != NULL && surface->getIGraphicBufferProducer() != NULL;
}
protected:
virtual ~Surface();
private:
// can't be copied
Surface& operator = (const Surface& rhs);
Surface(const Surface& rhs);
// ANativeWindow hooks
static int hook_cancelBuffer(ANativeWindow* window,
ANativeWindowBuffer* buffer, int fenceFd);
static int hook_dequeueBuffer(ANativeWindow* window,
ANativeWindowBuffer** buffer, int* fenceFd);
static int hook_perform(ANativeWindow* window, int operation, ...);
static int hook_query(const ANativeWindow* window, int what, int* value);
static int hook_queueBuffer(ANativeWindow* window,
ANativeWindowBuffer* buffer, int fenceFd);
static int hook_setSwapInterval(ANativeWindow* window, int interval);
static int hook_cancelBuffer_DEPRECATED(ANativeWindow* window,
ANativeWindowBuffer* buffer);
static int hook_dequeueBuffer_DEPRECATED(ANativeWindow* window,
ANativeWindowBuffer** buffer);
static int hook_lockBuffer_DEPRECATED(ANativeWindow* window,
ANativeWindowBuffer* buffer);
static int hook_queueBuffer_DEPRECATED(ANativeWindow* window,
ANativeWindowBuffer* buffer);
int dispatchConnect(va_list args);
int dispatchDisconnect(va_list args);
int dispatchSetBufferCount(va_list args);
int dispatchSetBuffersGeometry(va_list args);
int dispatchSetBuffersDimensions(va_list args);
int dispatchSetBuffersUserDimensions(va_list args);
int dispatchSetBuffersFormat(va_list args);
int dispatchSetScalingMode(va_list args);
int dispatchSetBuffersTransform(va_list args);
int dispatchSetBuffersTimestamp(va_list args);
int dispatchSetCrop(va_list args);
int dispatchSetPostTransformCrop(va_list args);
int dispatchSetUsage(va_list args);
int dispatchLock(va_list args);
int dispatchUnlockAndPost(va_list args);
protected:
virtual int dequeueBuffer(ANativeWindowBuffer** buffer, int* fenceFd);
virtual int cancelBuffer(ANativeWindowBuffer* buffer, int fenceFd);
virtual int queueBuffer(ANativeWindowBuffer* buffer, int fenceFd);
virtual int perform(int operation, va_list args);
virtual int query(int what, int* value) const;
virtual int setSwapInterval(int interval);
virtual int lockBuffer_DEPRECATED(ANativeWindowBuffer* buffer);
virtual int connect(int api);
virtual int disconnect(int api);
virtual int setBufferCount(int bufferCount);
virtual int setBuffersDimensions(int w, int h);
virtual int setBuffersUserDimensions(int w, int h);
virtual int setBuffersFormat(int format);
virtual int setScalingMode(int mode);
virtual int setBuffersTransform(int transform);
virtual int setBuffersTimestamp(int64_t timestamp);
virtual int setCrop(Rect const* rect);
virtual int setUsage(uint32_t reqUsage);
public:
virtual int lock(ANativeWindow_Buffer* outBuffer, ARect* inOutDirtyBounds);
virtual int unlockAndPost();
protected:
enum { NUM_BUFFER_SLOTS = BufferQueue::NUM_BUFFER_SLOTS };
enum { DEFAULT_FORMAT = PIXEL_FORMAT_RGBA_8888 };
private:
void freeAllBuffers();
int getSlotFromBufferLocked(android_native_buffer_t* buffer) const;
struct BufferSlot {
sp<GraphicBuffer> buffer;
Region dirtyRegion;
};
// mSurfaceTexture is the interface to the surface texture server. All
// operations on the surface texture client ultimately translate into
// interactions with the server using this interface.
// TODO: rename to mBufferProducer
sp<IGraphicBufferProducer> mGraphicBufferProducer;
// mSlots stores the buffers that have been allocated for each buffer slot.
// It is initialized to null pointers, and gets filled in with the result of
// IGraphicBufferProducer::requestBuffer when the client dequeues a buffer from a
// slot that has not yet been used. The buffer allocated to a slot will also
// be replaced if the requested buffer usage or geometry differs from that
// of the buffer allocated to a slot.
BufferSlot mSlots[NUM_BUFFER_SLOTS];
// mReqWidth is the buffer width that will be requested at the next dequeue
// operation. It is initialized to 1.
uint32_t mReqWidth;
// mReqHeight is the buffer height that will be requested at the next
// dequeue operation. It is initialized to 1.
uint32_t mReqHeight;
// mReqFormat is the buffer pixel format that will be requested at the next
// deuque operation. It is initialized to PIXEL_FORMAT_RGBA_8888.
uint32_t mReqFormat;
// mReqUsage is the set of buffer usage flags that will be requested
// at the next deuque operation. It is initialized to 0.
uint32_t mReqUsage;
// mTimestamp is the timestamp that will be used for the next buffer queue
// operation. It defaults to NATIVE_WINDOW_TIMESTAMP_AUTO, which means that
// a timestamp is auto-generated when queueBuffer is called.
int64_t mTimestamp;
// mCrop is the crop rectangle that will be used for the next buffer
// that gets queued. It is set by calling setCrop.
Rect mCrop;
// mScalingMode is the scaling mode that will be used for the next
// buffers that get queued. It is set by calling setScalingMode.
int mScalingMode;
// mTransform is the transform identifier that will be used for the next
// buffer that gets queued. It is set by calling setTransform.
uint32_t mTransform;
// mDefaultWidth is default width of the buffers, regardless of the
// native_window_set_buffers_dimensions call.
uint32_t mDefaultWidth;
// mDefaultHeight is default height of the buffers, regardless of the
// native_window_set_buffers_dimensions call.
uint32_t mDefaultHeight;
// mUserWidth, if non-zero, is an application-specified override
// of mDefaultWidth. This is lower priority than the width set by
// native_window_set_buffers_dimensions.
uint32_t mUserWidth;
// mUserHeight, if non-zero, is an application-specified override
// of mDefaultHeight. This is lower priority than the height set
// by native_window_set_buffers_dimensions.
uint32_t mUserHeight;
// mTransformHint is the transform probably applied to buffers of this
// window. this is only a hint, actual transform may differ.
uint32_t mTransformHint;
// mProducerControlledByApp whether this buffer producer is controlled
// by the application
bool mProducerControlledByApp;
// mSwapIntervalZero set if we should drop buffers at queue() time to
// achieve an asynchronous swap interval
bool mSwapIntervalZero;
// mConsumerRunningBehind whether the consumer is running more than
// one buffer behind the producer.
mutable bool mConsumerRunningBehind;
// mMutex is the mutex used to prevent concurrent access to the member
// variables of Surface objects. It must be locked whenever the
// member variables are accessed.
mutable Mutex mMutex;
// must be used from the lock/unlock thread
sp<GraphicBuffer> mLockedBuffer;
sp<GraphicBuffer> mPostedBuffer;
bool mConnectedToCpu;
// must be accessed from lock/unlock thread only
Region mDirtyRegion;
};