Koa 框架常用知識點整理

簡介
Koa 就是一種簡單好用的 Web 框架。它的特點是優雅、簡潔、表達力強、自由度高。本身代碼只有1000多行,所有功能都通過插件實現。
學前準備
檢查Nodejs版本
打開cmd命令行窗口node -v
註意:Koa 必須使用 7.6 以上的版本。如果你的版本低於這個要求,就要先升級 Node。
配套案例
一、基本用法
1.1 三行代碼架設HTTP服務
npm install koa
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
app.listen(3000);1.2 Context 對象
Koa 提供一個 Context 對象,表示一次對話的上下文(包括 HTTP 請求和 HTTP 回復)。通過加工這個對象,就可以控制返回給用戶的內容。
Context 對象所包含的:

const Koa = require('koa') const app = new Koa() app.use((ctx, next) => { //ctx是整個應用的上下文,包含常用的request、response //ctx.response代表 HTTP Response。同樣地,ctx.request代表 HTTP Request。 //ctx.response.body可以簡寫成ctx.body ctx.response.body = 'hello world' }) app.listen(3000)
1.3 HTTP Response 的類型
Koa 默認的返回類型是text/plain (純文本的形式),如果想返回其他類型的內容,可以先用ctx.request.accepts判斷一下,客戶端希望接受什麽數據(根據 HTTP Request 的Accept字段),然後使用ctx.response.type指定返回類型。
const Koa = require('koa') const app = new Koa() //聲明一個main中間件,如果你急於了解中間件可以跳轉到(三) const main = (ctx,next) =>{ if (ctx.request.accepts('json')) { ctx.response.type = 'json'; ctx.response.body = { data: 'Hello World' }; } else if (ctx.request.accepts('html')) { ctx.response.type = 'html'; ctx.response.body = '<p>Hello World</p>'; } else if (ctx.request.accepts('xml')) { ctx.response.type = 'xml'; ctx.response.body = '<data>Hello World</data>'; } else{ ctx.response.type = 'text'; ctx.response.body = 'Hello World'; }; }; //直接運行頁面中會顯示json格式,因為我們沒有設置請求頭,所以每一種格式都是ok的。 app.use(main)//app.use()用來加載中間件。 app.listen(3000)
1.4 網頁模板
實際開發中,返回給用戶的網頁往往都寫成模板文件。我們可以讓 Koa 先讀取模板文件,然後將這個模板返回給用戶。
關於fs.createReadStream
const fs = require('fs');
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
const main = ctx => {
ctx.response.type = 'html';
ctx.response.body = fs.createReadStream('./data/index.html');
};
app.use(main);
app.listen(3000);二、路由
2.1 原生路由
const Koa = require('koa')
const app = new Koa()
app.use((ctx, next) => {
if (ctx.request.url == '/') {//通過ctx.request.url獲取用戶請求路徑
ctx.body = '<h1>首頁</h1>'
} else if (ctx.request.url == '/my') {
ctx.body = '<h1>聯系我們</h1>'
} else {
ctx.body = '<h1>404 not found</h1>'
}
})
app.listen(3000)2.2 koa-router 模塊路由
npm中的koa-route
npm install koa-router
const Koa = require('koa')
const Router = require('koa-router')
const app = new Koa()
const router = new Router()
app.use(router.routes()).use(router.allowedMethods());
//routes()返回路由器中間件,它調度與請求匹配的路由。
//allowedMethods()處理的業務是當所有路由中間件執行完成之後,若ctx.status為空或者404的時候,豐富response對象的header頭.
router.get('/',(ctx,next)=>{//.get就是發送的get請求
ctx.response.body = '<h1>首頁</h1>'
})
router.get('/my',(ctx,next)=>{
ctx.response.body = '<h1>聯系我們</h1>'
})
app.listen(3000)2.3 靜態資源
如果網站提供靜態資源(圖片、字體、樣式表、腳本......),為它們一個個寫路由就很麻煩,也沒必要koa-static模塊封裝了這部分的請求。請看下面的例子
npm中的koa-static
npm install koa-staic
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
const path = require('path');
const serve = require('koa-static');
const main = serve(path.join(__dirname));
app.use(main);
app.listen(3000);訪問 http://localhost:3000/data/index.html,在瀏覽器裏就可以看到這個文件的內容。
2.4 重定向跳轉
有些場合,服務器需要重定向訪問請求。比如,用戶登陸以後,將他重定向到登陸前的頁面。ctx.response.redirect()方法可以發出一個跳轉,將用戶導向另一個路由。
const Koa = require('koa');
const Router = require('koa-router');
const app = new Koa();
const router = new Router()
app.use(router.routes()).use(router.allowedMethods());
router.get('/cdx',(ctx,next)=>{
ctx.response.redirect('/');//發出一個跳轉,將用戶導向另一個路由。
})
router.get('/',(ctx,next)=>{
ctx.body = 'Hello World';
})
app.listen(3000);訪問 http://localhost:3000/cdx,瀏覽器會將用戶導向根路由。
三、中間件
3.1 Logger功能
Koa 的最大特色,也是最重要的一個設計,就是中間件。為了理解中間件,我們先看一下 Logger (打印日誌)功能的實現。
./logger/koa-logger.js
module.exports = (ctx, next) => {
console.log(`${Date.now()} ${ctx.request.method} ${ctx.request.url}`);//自定義
} ./logger.js
const Koa = require('koa')
const koaLogger = require('./logger/koa-logger')
const app = new Koa();
app.use(koaLogger)
app.listen(3000)打印結果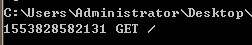
3.2中間件的概念
處在 HTTP Request 和 HTTP Response 中間,用來實現某種中間功能的函數,就叫做"中間件"。
基本上,Koa 所有的功能都是通過中間件實現的,前面例子裏面的main也是中間件。每個中間件默認接受兩個參數,第一個參數是 Context 對象,第二個參數是next函數。只要調用next函數,就可以把執行權轉交給下一個中間件。
多個中間件會形成一個棧結構,以"先進後出"的順序執行。
- 最外層的中間件首先執行。
- 調用
next函數,把執行權交給下一個中間件。 - ...
- 最內層的中間件最後執行。
- 執行結束後,把執行權交回上一層的中間件。
- ...
- 最外層的中間件收回執行權之後,執行
next函數後面的代碼。
例子:
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
app.use((ctx, next)=>{
console.log('>> one');
next();
console.log('<< one');
})
app.use((ctx, next)=>{
console.log('>> two');
next();
console.log('<< two');
})
app.use((ctx, next)=>{
console.log('>> three');
next();
console.log('<< three');
})
app.listen(3000);輸出結果:
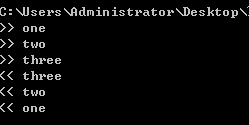
如果中間件內部沒有調用next函數,那麽執行權就不會傳遞下去。
3.4 異步中間件
迄今為止,所有例子的中間件都是同步的,不包含異步操作。如果有異步操作(比如讀取數據庫),中間件就必須寫成async 函數。
npm install fs.promised
npm中的fs.promised
const fs = require('fs.promised');
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
const main = async function (ctx, next) {
ctx.response.type = 'html';
ctx.response.body = await fs.readFile('./data/index.html', 'utf8');
};
app.use(main);
app.listen(3000);上面代碼中,fs.readFile是一個異步操作,必須寫成await fs.readFile(),然後中間件必須寫成 async 函數。
app.use(async(ctx, next)=>{
ctx.body = '1'
//延時2秒執行下一個中間件,這樣是沒用的,因為是異步函數
setTimeout(()=>{
next()
},2000)
ctx.body += '2'
})
app.use(async(ctx, next)=>{
ctx.body += '3'
next()
ctx.body += '4'
})
server.js正確做法
function delay(){
return new Promise((reslove,reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
reslove()
},1000)
})
}
app.use(async(ctx, next)=>{
ctx.body = '1'
await next()
ctx.body += '2'
})
app.use(async(ctx, next)=>{
ctx.body += '3'
await delay()
await next()
ctx.body += '4'
})
3.5 中間件的合成
koa-compose 模塊可以將多個中間件合成一個。
npm中的koa-compose
npm install koa-compose
const Koa = require('koa');
const compose = require('koa-compose');
const app = new Koa();
const logger = (ctx, next) => {
console.log(`${Date.now()} ${ctx.request.method} ${ctx.request.url}`);
next();
}
const main = ctx => {
ctx.response.body = 'Hello World';
};
const middlewares = compose([logger, main]);//合成中間件
app.use(middlewares);//加載中間件
app.listen(3000);輸出結果:先打印日誌,再在頁面中顯示Hello World
四、處理錯誤
4.1 500錯誤
如果代碼運行過程中發生錯誤,我們需要把錯誤信息返回給用戶。HTTP 協定約定這時要返回500狀態碼。Koa 提供了ctx.throw()方法,用來拋出錯誤,ctx.throw(500)就是拋出500錯誤。
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
const main = ctx => {
ctx.throw(500);//這個時候你訪問首頁會報一個500的錯誤(內部服務器錯誤)服務器會報錯
};
app.use(main);
app.listen(3000);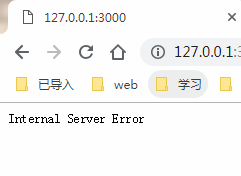
4.2 404錯誤
如果將ctx.response.status設置成404,就相當於ctx.throw(404),返回404錯誤。
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
const main = ctx => {
ctx.response.status = 404;//response返回的狀態碼就是404
ctx.response.body = 'Page Not Found';//讓頁面中顯示該內容,服務器不不報錯
};
app.use(main);
app.listen(3000);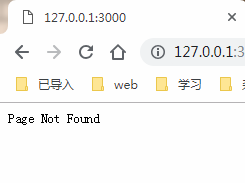
4.3 處理錯誤的中間件
為了方便處理錯誤,最好使用try...catch將其捕獲。但是,為每個中間件都寫try...catch太麻煩,我們可以讓最外層的中間件,負責所有中間件的錯誤處理。
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
const handler = async (ctx, next) => {
try {
await next();//執行下個中間件
} catch (err) {
//如果main中間件是有問題的會走這裏
ctx.response.status = err.statusCode || err.status || 500;
ctx.response.body = {
message: err.message//把錯誤信息返回到頁面
};
}
};
const main = ctx => {
ctx.throw(500);//如果這裏是沒有問題的就正常執行,如果有問題會走catach
};
app.use(handler);
app.use(main);
app.listen(3000);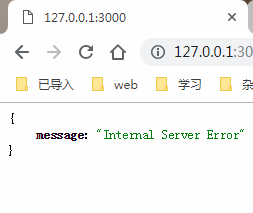
4.4 errors事件監聽
運行過程中一旦出錯,Koa 會觸發一個error事件。監聽這個事件,也可以處理錯誤。
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
const main = ctx => {
ctx.throw(500);
};
app.on('error', (err, ctx) => {
//如果有報錯的話會走這裏
console.error('server error', err);//err是錯誤源頭
});
app.use(main);
app.listen(3000);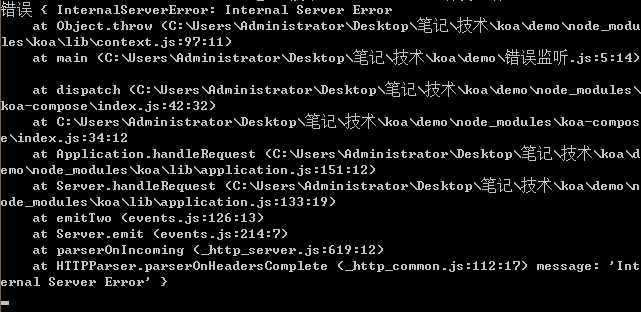
4.5 釋放error事件
需要註意的是,如果錯誤被try...catch捕獲,就不會觸發error事件。這時,必須調用ctx.app.emit(),手動釋放error事件,才能讓監聽函數生效。
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
const handler = async (ctx, next) => {
try {
await next();
} catch (err) {
ctx.response.status = err.statusCode || err.status || 500;
ctx.response.type = 'html';
ctx.response.body = '<p>有問題,請與管理員聯系</p>';
ctx.app.emit('error', err, ctx);//釋放error事件
}
};
const main = ctx => {
ctx.throw(500);
};
app.on('error', function (err) {
//釋放error事件後這裏的監聽函數才可生效
console.log('錯誤', err.message);
console.log(err);
});
app.use(handler);
app.use(main);
app.listen(3000);上面代碼main函數拋出錯誤,被handler函數捕獲。catch代碼塊裏面使用ctx.app.emit()手動釋放error事件,才能讓監聽函數監聽到。
五、Web App的功能
5.1 cookie
ctx.cookies用來讀寫 Cookie。
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
const main = function(ctx) {
//讀取cookie//沒有返回0
const n = Number(ctx.cookies.get('view') || 0) + 1;
ctx.cookies.set('view', n);//設置cookie
ctx.response.body = n + ' views';//顯示cookie
}
app.use(main);
app.listen(3000);5.2 表單
Web 應用離不開處理表單。本質上,表單就是 POST 方法發送到服務器的鍵值對。koa-body模塊可以用來從 POST 請求的數據體裏面提取鍵值對。
npm中的koa-body
npm install koa-body
const Koa = require('koa');
const koaBody = require('koa-body');
const app = new Koa();
const main = async function (ctx) {
const body = ctx.request.body;
if (!body.name){
ctx.throw(400, '.name required')
};
ctx.body = { name: body.name };
};
app.use(koaBody());
app.use(main);
app.listen(3000);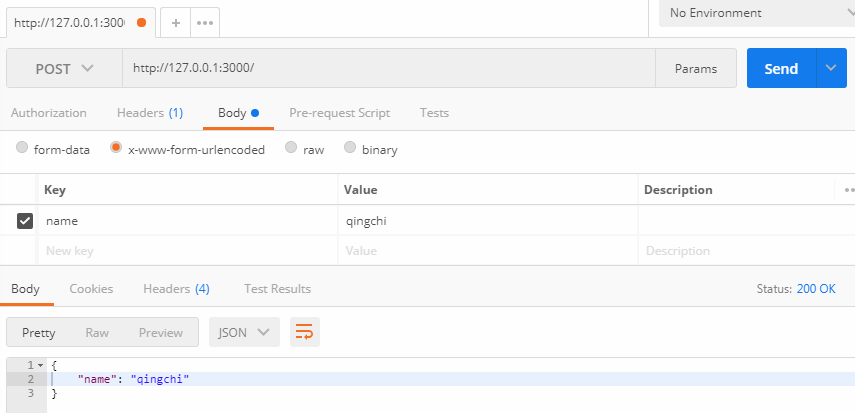
上面代碼使用 POST 方法向服務器發送一個鍵值對,會被正確解析。如果發送的數據不正確,就會收到錯誤提示。
5.3 文件上傳
koa-body模塊還可以用來處理文件上傳。
./demo/文件上傳.js
const Koa = require('koa');
const koaBody = require('koa-body');
const Router = require('koa-router');
const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
const router = new Router()
const app = new Koa();
app.use(koaBody({
multipart: true,//解析多部分主體,默認false
formidable: {
maxFileSize: 200 * 1024 * 1024 // 設置上傳文件大小最大限制,默認2M
}
}));
app.use(router.routes()).use(router.allowedMethods());
router.post('/uploadfile', (ctx, next) => {
// 上傳單個文件
const file = ctx.request.files.file; // 獲取上傳文件
// 創建可讀流
const reader = fs.createReadStream(file.path);
let filePath = path.join(__dirname, 'data/') + `/${file.name}`;
// 創建可寫流
const upStream = fs.createWriteStream(filePath);
// 可讀流通過管道寫入可寫流
reader.pipe(upStream);
return ctx.body = "上傳成功!";
});
app.listen(3000)./demo/web/index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="http://127.0.0.1:3000/uploadfile" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" name="file" id="file" value="" multiple="multiple" />
<input type="submit" value="提交"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>nodejs中的fs文件系統模塊,可以幫你讀文件寫文件,但是不會幫你創建文件夾。
本文思路來源http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2017/08/koa.html
?
Koa 框架常用知識點整理
